All systems of the female body are very susceptible to the influence of hormones, and the slightest changes in the hormonal background of a woman immediately affect the work of almost all systems and organs of the female body. It's no secret that it is precisely because of the susceptibility to hormonal influence that women are much more emotional than men. It is as a result of hormonal imbalances, as well as under the influence of some other factors in the female body, such a gynecological pathology as endometriosis can develop. One of the forms of this disease - endometriosis of the pelvic peritoneum is described in detail by estet-portal.com.
Pelvic peritoneal endometriosis symptoms and methods of pathology diagnostics
Endometriosis of the pelvic peritoneum occurs as a result of a pathological benign growth of the uterine tissue with its subsequent spread to the organs and structures of the small pelvis. Such a pathology significantly affects the functioning of the organs of the female reproductive system, and affects the general condition of the body. The clinical picture of endometrioid lesions differs depending on the form of endometriosis, and often the disease can go unnoticed for a long time. Nevertheless, timely diagnosis of endometriosis of the pelvic peritoneum will help protect a woman from the occurrence of complications of this condition.
Pelvic peritoneal endometriosis:
- main forms of endometriosis of the pelvic peritoneum;
- what symptoms would indicate an endometrioid lesion of the peritoneum;
- basic methods for diagnosing endometriosis of the pelvic peritoneum.
The main forms of endometriosis of the pelvic peritoneum
The pathogenetic mechanism of the development of endometriosis of the pelvic peritoneum is based on the interaction of peritoneal mesotheliocytes and elements of the endometrium of the uterus. The process is triggered as a result of retrograde reflux of menstrual blood from the uterine cavity into the pelvic cavity, under the influence of endocrine disorders in the woman's body, as well as with a general weakening of the body's defense mechanisms. Depending on the prevalence of the pathological process, two main forms of endometriosis of the pelvic peritoneum are distinguished:
- in the first form, the pathological process is limited only to the pelvic peritoneum;
- in the second form, in addition to the defeat of the peritoneum, the ovaries, fallopian tubes and the uterus itself may be involved in the pathological process.
What symptoms indicate endometriosis peritoneal disease
The clinical picture of endometriosis of the pelvic peritoneum is not specific. In many cases, especially with a small form of endometrioid lesions, the pathological process can be asymptomatic for a long time. Only in the case of the spread of the pathological process from the pelvic peritoneum to the muscular layer of the rectum and pararectal tissue can the first symptoms of the disease occur. In the clinical picture, painful cider comes to the fore: the patient is disturbed by intense pain in the pelvic region, which intensifies on the eve of menstruation and after it. In addition, pain may appear during intercourse. In almost 90% of cases, even with small forms of endometriosis of the pelvic peritoneum, infertility occurs in patients.
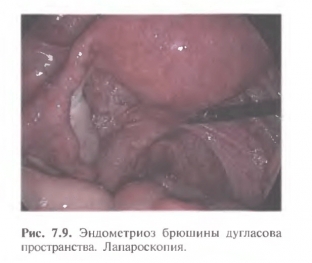
Basic methods for diagnosing endometriosis of the pelvic peritoneum
The diagnostic process of pelvic peritoneal endometriosis begins with a thorough collection of anamnestic data. The patient's characteristic complaints of persistent pain in the pelvis, pain during intercourse and the inability to conceive a child may lead the doctor to the idea of endometriosis. To clarify the localization of the pathological process in this form of pathology, laparoscopy most effectively helps, which is the main method for diagnosing endometriosis of the pelvic peritoneum. There are such main manifestations of foci of endometriosis on the peritoneum:
- atypical vesicles;
- hemorrhagic vesicles;
- pigmented spots and bumps of yellow-brown color;
- typical superficial and deep lesions are blue, purple or black.








Add a comment