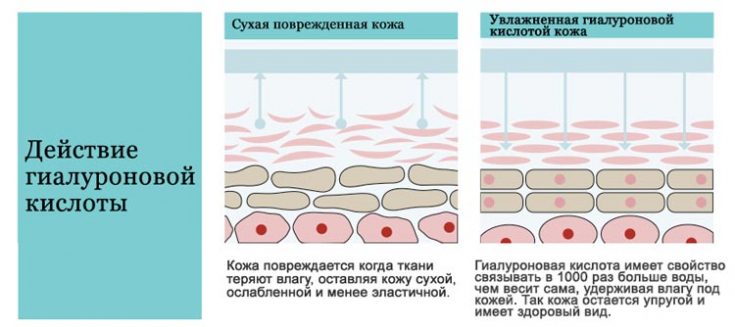
Hyaluronic acid is widely used in aesthetic medicine due to its specific properties, which allow it to bind a large number of water molecules, which improves tissue hydration and their resistance to mechanical damage.
The interest in this compound in the field of medicine is also evident from the fact of the wide availability of hyaluronic acid and high biocompatibility.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com what physical and chemical properties of hyaluronic acid determine its active use not only in aesthetic medicine, but also in other areas.
Physical and chemical properties of hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid is currently the most commonly used drug in injectable dermatology and cosmetology as a filler, the function of which is to fill and expand the extracellular space.
Follow us on Instagram!
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a biopolymer consisting of repeating units of disaccharides, which include molecules of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine linked by glycosides b- (1-4) and b- (13). It belongs to a group of substances called mucopolysaccharides belonging to the glycosaminoglycan (GAG) family.
Members of this group also include other commonly known compounds such as chondroitin sulfate, keratan sulfate I and II, heparin, heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate.
Hyaluronic acid is the only mucopolysaccharide that is not synthesized in the Golgi apparatus. There are three HA synthases that are responsible for its formation (Has1, Has2 and Has3). These enzymes are located in the cell membrane with the active end facing the inside of the cell. Synthesis occurs on the inner side of the cell membrane and holds the individual parts of the polymer that extend outside the cell. This differs from the synthesis of other polymers as it correlates with the length of the hyaluronic acid molecules and their viscosity.
Bionic hyaluronic acid: a breakthrough in filler correction
The difference between the results noted for these three synthases is the length of the hyaluronic acid chain they produce. Depending on the chain length, we can distinguish between small, medium and large polymers. The first two forms have pro-angiogenic and anti-apoptotic properties that stimulate the synthesis of heat shock proteins (HSP) and are powerful immunostimulants. Large polymers mainly act on immunosuppressive and anti-angiogenic function.
Hyaluronic acid can be catabolized either enzymatically or chemically. The following hyaluronidases are distinguished: HYAL1− is a lysosome-associated enzyme that degrades hyaluronic acid to tetrasaccharides, HYAL2 − decomposes high molecular weight hyaluronic acid to 20 kD products, 3 HYAL3 .minus; it is an enzyme whose mechanism of action is not fully understood. In turn, chemical degradation is associated with reactive oxygen species.
How to minimize bruising and swelling after filler
Using the properties of hyaluronic acid in medicine
The active use of hyaluronic acid in aesthetic medicine is associated with its viscoelastic properties and high biocompatibility. Small volumes of hyaluronic acid administered intradermally or subcutaneously can maintain approximately 6 months of full effect, leaving skin smooth and firm.
Hyaluronic acid has many applications in ophthalmology, both in conservative treatment and in the surgical aspect. It is often the main ingredient in artificial tear formulations used for dry eye syndrome. Possessing powerful moisture-retaining properties, it reduces irritation, moisturizes the eyes and compensates for the lack of sodium hyaluronate in the tear film. Hyaluronic acid also plays an important role in ophthalmic surgery.
Its effects are based on properties in creating and maintaining comfortable conditions conducive to the healing of a postoperative wound.
Cosmetology revolution: nanotechnologies in medicine
Physiological properties of hyaluronic acid in orthopedics
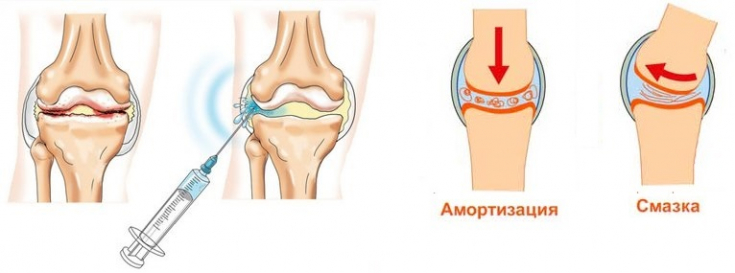
Due to the natural synthesis of hyaluronic acid in the synovial fluid, joint capsule and articular cartilage, it is widely used in orthopedics. This compound is used primarily for joint disorders such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
Intra-articular hyaluronic acid preparations are characterized by good tolerability and therapeutic properties (pain reduction), which is confirmed in randomized trials. A very important advantage of intra-articular injections is the absence of systemic adverse reactions. Studies of the therapeutic properties of intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid have shown that it promotes the synthesis of cartilage matrix, prevents its degradation, reduces inflammation, stimulates the synthesis of endogenous hyaluronic acid and improves cartilage elasticity.
Beauty Boostering: Radiant Skin in an Instant
Use of hyaluronic acid in oncology
A further direction in which the properties of hyaluronic acid can be used more widely is in the field of oncology. Many tumors show an increased content of hyaluronic acid in the tumor stroma and in the surrounding tissue matrix. A particularly significant increase in the level of hyaluronic acid can be observed in tumors of epithelial origin (according to Kultti, up to 87% of cases of pancreatic adenocarcinoma have a high expression of HA). In most cases, this process is associated with a poor prognosis.
You simply shine: effective skin lightening

The properties of hyaluronic acid have also been reported to promote tumor progression by altering stromal cells and stimulating angiogenesis. The process of angiogenesis is one of the fundamental processes required for the progression of cancer cells.
Follow our articles and be the first to know about major research in the field of medicine.
Interesting histology: exposure to hyaluronic acid fillers









Add a comment