Any allergic reaction of the body to harmless food or food ingredients can be considered a food allergy. Intolerance to benign food products is not associated with metabolic disorders, it is due to immunological reactions and the breakdown of biologically active substances by a non-immune mechanism (type of anaphylactoid reactions). Food allergy – a very common disease with nonspecific semiotics and difficult diagnosis. It occurs in both adults and children, but is usually diagnosed at an early age.
Features of the development of food allergies and its manifestations
According to the method of development, primary and secondary forms of food allergy are divided. The primary form is genetically determined, hereditary and / or couple allergic. The latter occurs most often in young children with an anomaly inherent in the constitution of the child (according to the exudative-catarrhal type).
Secondary forms of food allergy can be summarized as a group of diseases associated with the state of the gastrointestinal tract. The most significant of them are:
- pathology of the development of the gastrointestinal tract,
- intestinal infections,
- dysbacteriosis.
Diseases of the liver and pancreas are also of great importance. Less commonly, allergies are caused by helminthiases, hypovitaminosis, as well as hereditary diseases such as cystic fibrosis and celiac disease.
Mechanism of development of food allergy and trigger factors
In essence, food allergy is an immunopathological process in the human body. This is a complex of reactions associated with the production of immunoglobulin E (Ig E) and the activation of mast cells.
According to the main mechanism of development, food allergies are divided with prevalence:
- immediate reactions,
- delayed hypersensitivity,
- immunocomplex vascular reactions,
- combined immunobiological reactions.
The most common food allergies are cow's milk, eggs, fish, peanuts, seafood, and wheat.
Cow's milk is the most allergenic. It contains more than 25 antigens, which are the triggers (provocateurs) of allergies. Most of them reduce their pathogenic properties during heat treatment of milk. Seafood antigens, on the other hand, are very stable, and any heat treatment will not reduce the reaction caused in any way.
If we are talking about products of plant origin, then the most allergenic of them are citrus fruits, apricots, apples, red berries. Sensitization to wheat, rye and legume proteins is very common.
Clinical presentation of food allergy
The clinical picture of this disease is quite variable and depends on the etiology, age evolution of the disease, localization of the pathological process and the strength of the body's immune response.
The clinical manifestations of PA include the following clinical syndromes:
- oropharyngeal symptoms (Lessof's syndrome) - rapid onset of rashes and local angioedema of the lips, cheilitis, gingivitis, glossitis, stomatitis;
- gastrointestinal symptoms (18-40%): abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, abdominal tenderness, palpation tenderness; Gastrointestinal syndromes in food allergies are especially pronounced in young children;
- skin symptoms (50%): urticaria, eczema, Quincke's edema;
- respiratory symptoms (3-7%) - from manifestations of rhinitis to the clinic of bronchial asthma (dry cough, wheezing, suffocation). Food allergy can cause recurrence of laryngeal stenosis, asthma exacerbations;
- neurological symptoms: headache, sleep disturbance, irritability;
- anaphylactic shock reaction (0.5-1.5%) most often develops with the consumption of fish, seafood, nuts);
- nephrotic syndrome (1-4%).
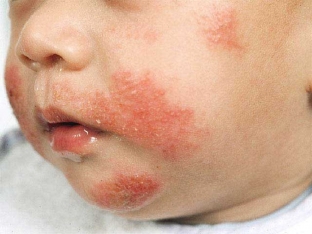
Food Allergy aggravates the course of pathological processes in the digestive tract and other organs.
Diagnosis of food allergy and methods of its treatment
Diagnosis of food allergy includes collecting complaints, anamnesis, keeping a food diary.
Laboratory conduct a study of general analysis and blood biochemistry, coprological study (with the determination of individual enzymes);
Ultrasound of the internal organs, fibrogastroduodenoscopy, skin allergy testing (determination of the cause of food allergy), determination of the level of total IgE, analysis for the presence of specific IgE for certain food allergens (accurate method).
Immunological research methods are carried out in vivo and in vitro. Among the methods that are carried out in vivo, skin and provocative allergic diagnostic tests are distinguished, in vitro - laboratory diagnostic methods.
The main therapeutic measure for food allergies is an elimination diet. Pharmacotherapy of the disease involves the use of:
- antihistamines per os in the acute period, therapy with them continues with a prophylactic purpose for several months;
in the case of a generalized form, antihistamines are used parenterally (intramuscularly or intravenously);
- glucocorticoids parenterally (if antihistamines are ineffective);
- cell membrane stabilizers;
- enterosorbents.
Treatment of food allergies includes dietary modification and pharmacotherapy aimed at eliminating the manifestations of the disease and preventing its occurrence in the future.









Add a comment