Skin color depends on a number of factors, including capillary stacks, blood flow, and properties of the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin. However, the most important influencing factor is skin pigmentation. Pigmentation – a complex biochemical process involving special cells located in the basal layer of the epidermis called melanocytes. The skin pigment melanin is synthesized in melanocytes and enclosed in melanosomes, which are subsequently transmitted through the dendrites of melanocytes to the surface layers of the epidermis. Melanogenesis – the result of the biochemical synthesis of melanin from the amino acids L-phenylalanine and L-tyrosine. A number of enzymes are involved in this process, the most important of which is tyrosinase, which converts L-tyrosine to L-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA). The level of skin pigmentation mainly depends on the activity and number of melanocytes in the skin. In some cases, abnormal pigmentation (hyperpigmentation) of the skin may occur, which leads to the appearance of dark pigment spots on the skin.
 Maurizio Ceccarelli talks about using a combination of hyaluronic and succinic acids to eliminate hyperpigmentation and other skin changes as a result of exposure to UV rays and photodamage.
Maurizio Ceccarelli talks about using a combination of hyaluronic and succinic acids to eliminate hyperpigmentation and other skin changes as a result of exposure to UV rays and photodamage.
Melanogenesis and photodamage: why does skin hyperpigmentation occur?
Melanogenesis – it is a protective reaction of the skin to exposure to ultraviolet radiation, which leads to photodamage of the skin. Photodamaged skin is characterized by an increase in the thickness of the stratum corneum and the production of melanin, the synthesis of which is activated as a result of biological damage.
Photodamage stimulates the production of melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MMH), which activates the synthesis of melanin-containing melanosomes and their movement into the cells of epidermis.
Tyrosinase – a copper-containing enzyme that catalyzes the production of melanin from tyrosine through oxidation.
Melanogenesis – it is a protective reaction of the skin to exposure to ultraviolet radiation, which leads to photodamage of the skin.
Tyrosinase – a single-chain glycoprotein that is synthesized in ribosomes and travels through the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus, where it is glycolyzed and placed in vesicles called premelanosomes. The process of glycolization is important for the spatial arrangement of the formed protein, as well as for the creation of its active site. In the presence of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, tyrosinase function is completely suppressed.
In addition to activating melanogenesis, ultraviolet radiation causes photodamage to the skin, resulting in photoaging. The most harmful in this regard are ultraviolet rays of the A spectrum (320 & ndash; 400 nm), which penetrate deep into the skin to the superficial hypodermis and negatively affect proteins, collagen and elastin.
 UV B rays (280-320 nm) penetrate the superficial layers of the skin, mainly the epidermis, but both spectra can cause burning and have a mutagenic effect, suppress the immune system and lead to pigmentation. In this aspect, photodamage, photoaging and pigmentation are closely related. This fact must be taken into account when carrying out aesthetic procedures to eliminate pigmentation – not only to eliminate superficial signs of aging, but also to influence the mechanisms of skin aging.
UV B rays (280-320 nm) penetrate the superficial layers of the skin, mainly the epidermis, but both spectra can cause burning and have a mutagenic effect, suppress the immune system and lead to pigmentation. In this aspect, photodamage, photoaging and pigmentation are closely related. This fact must be taken into account when carrying out aesthetic procedures to eliminate pigmentation – not only to eliminate superficial signs of aging, but also to influence the mechanisms of skin aging.
If the level of photodamage is fairly high, melanin granules will be distributed in the dermal layer of the skin and this hyperpigmentation will be quite persistent because, unlike the epidermis, the dermis does not renew itself regularly. In this case, imperfections persist for a long period. And while such skin hyperpigmentation can be eliminated by removing the melanin-containing dermis layer, a traumatic procedure (chemical or laser peeling, dermabrasion and phototherapy) can start a new post-inflammatory melanogenesis.
Read also: Modern hyperpigmentation therapy: methods and means
The only option to eliminate hyperpigmentation of the skin is phagocytosis of melanotic granules by macrophages. Macrophages can be activated to stimulate the process of phagocytosis and removal of melanosomes by stimulating CD44 tyrosine kinase receptors. They are activated by binding to the injected hyaluronic acid fragments (20 & ndash; 38 monomers (from 8000 to 20000 daltons)).
Moreover, acetylglucosamine, as the end product of hyaluronic acid metabolism, acts as an inhibitor of tyrosinase glycolysis, blocking its function, as well as the biosynthesis of new melanin.
We'll look at:
- the role of succinic and hyaluronic acids in the elimination of skin hyperpigmentation;
- redermalization as a method of combating skin hyperpigmentation.
The role of succinic and hyaluronic acids in the elimination of skin hyperpigmentation
Research results show that succinic acid is able to reduce the severity of pigmentation by blocking the enzymatic activity of tyrosinase and completely losing the function of the enzyme.
Moreover, succinic acid is a weak acid and has an oxidizing and antioxidant effect. Sodium succinate, injected into the dermis, decomposes and releases succinic acid, which has an antioxidant effect, inhibiting the effects of free radicals and oxidizing tyrosinase.
The intensity of the color of melanin is reduced by converting melanin from an oxidized state (black) to a reduced state (brown) due to the reducing action of succinic acid.
Hyaluronic acid – one of the most popular ways to correct age-related signs of aging. In practice, the combination of hyaluronic acid with other active ingredients has many advantages compared to HA monotherapy.
An age-related protocol that has been shown to be effective in reducing skin hyperpigmentation:
Three concentrations of HA solution (11 mg/ml, 18 mg/ml, 22 mg/ml) and succinic acid (16 mg/ml) are administered every two weeks (papular technique), 3 & ndash; 5 sessions are required.
The procedure is carried out according to the type of skin aging and the site of injection. Small wrinkles and other signs of photoaging, as a rule, are eliminated with minimal and average concentrations of HA (11-18 mg / ml) using the papular technique – intradermal papules at a distance of 0.5-1 cm.
Deeper expression lines require papular or linear technique, and medium to high concentrations of HA (18mg/ml and 22mg/ml) for linear technique).
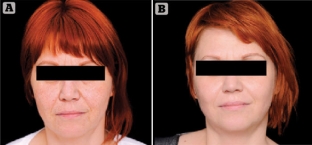
Figure 1. The result of the elimination of hyperpigmentation of the skin. Woman 40 years old, deformation type of aging. (A) before and (B) 30 days after a single redermalization treatment using a combination of 1.1% HA and 1.6% succinic acid
It is recommended to start treatments with a less concentrated solution to initiate metabolic processes in the dermis, you can switch to higher concentrations from the second or third treatment. >
Redermalization as a method of combating skin hyperpigmentationThe effect of the redermalization procedure with the use of hyaluronic and succinic acid is quite pronounced:
- skin lifting;
- deep moisturizing;
- skin smoothing;
- skin color improvement;
- elimination of
- skin hyperpigmentation.
The result after the procedures usually lasts from 6 to 9 months, but the residual effect associated with the stimulating effect of succinic acid can last much longer. However, for best long-term results, it is recommended to repeat redermalization sessions once or twice every 9 months.
For patients with skin hyperpigmentation and other signs of photoaging, redermalization can be an excellent alternative to laser rejuvenation or chemical peels.









Add a comment