Hyperthyroidism or hyperthyroidism (thyrotoxicosis) – a pathological condition caused by an increased content of thyroid hormones in the blood, namely thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
Thyroid hormones affect the metabolism of absolutely all tissues of the human body. Excessive production of T4 and T3 disrupts the normal functioning of organs and systems.
Read about what pathological processes affect the nervous system and mental state in thyrotoxicosis on the website estet-portal.com in our article.
Pathogeny of the action of hormones T3 and T4 in hyperfunction of the thyroid gland
Thyroid hormones realize their function due to:
1. increased sensitivity of adrenergic receptors;
2. activation of protein synthesis;
3. increased uptake of Ca2+ from the blood;
4. stimulation of lipolysis, proteolysis, glycogenolysis;
5. intensification of anabolic processes due to the transport of amino acids and glucose into the cell;
6. increased heat production as a by-product of mitochondrial function.
In hydatidiform mole and choriocarcinoma, the secretion of human chorionic gonadotropin, which is similar in chemical structure to TSH and stimulates the thyroid gland to produce T3 and T4, increases.
Knowledge of the structure and mechanisms of action of thyroid hormones in hyperfunction of the thyroid gland is necessary for absolutely all clinicians to understand the pathological process in the patient's body and successful treatment.
Follow us on Telegram
Features and origin of neurological symptoms in hyperthyroidism
On neurological examination of patients with symptoms of hyperthyroidism, tremor of the eyelids attracts attention. Postural tremor occurs when the fingers move. Thyrotoxic myopathy in the form of limb paresis against the background of atrophy develops as a result of necrosis of muscle fibers, which is confirmed by biopsy results.
Symmetrical hyperreflexia indicates damage to the corticospinal tract. During the test of reflexes, fasciculations are noted as a result of pathological activity of muscle fibers. Distal symmetric polyneuropathy of the "stocking" type; causes a violation of sensitivity.
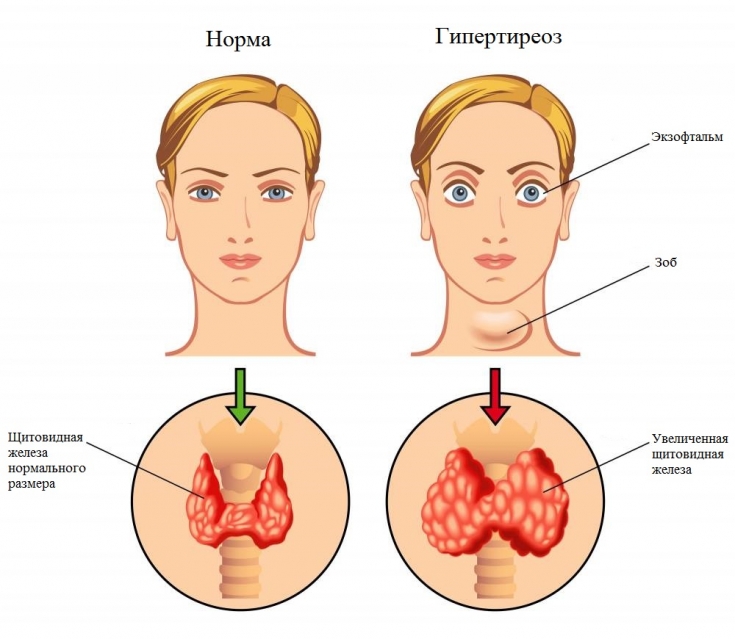
Ophthalmopathy as a "visiting card" patient with hyperthyroidism
Patients with hyperthyroidism are characterized by eyelid retraction, limited mobility of the eyeball due to edema of the retrobulbar tissue, and diplopia. Damage to the optic nerve by compression mechanisms leads to visual impairment.
There is a tumor of the ovary struma ovarii, which consists of thyroid cells and secretes thyroid hormones in excess.
K. Graves in 1776 first described thyroid ophthalmopathy. As a result of the autoimmune reaction of T-lymphocytes with the release of cytokines, fibroblast proliferation, collagen formation and the production of glycosaminoglycans are induced. The latter have the ability to bind water, resulting in the development of edema of the retrobulbar tissue. Subsequently, the edema is replaced by fibrous tissue, which is an irreversible process.
Other signs include:
1. Dalrymple's symptom - a strip of sclera between the upper eyelid and the iris (look straight);
2. Graefe's symptom - lowering of the upper eyelid lags behind the downward movement of the eyeball;
3. Stellvag's symptom - blinking, tremor of the eyelids when closing.
Mental state of patients with hyperthyroidism
The mental state of patients with hyperthyroidism is characterized by irritability, anxiety, emotional lability, sleep disturbance. Less common are apathy, depression and delirium with hyperkinesis. Electrolyte imbalances lead to severe confusion, psychomotor agitation, which can turn into stupor and coma.
Patients without adequate medical therapy may develop partial and generalized epileptic seizures. When conducting electroencephalography, generalized slow waves, an increase in the frequency of alpha waves, focal spikes are observed.
You may be interested in our article: Convulsive syndrome. What to do for seizures
Prognosis and drug therapy of hyperthyroidism
The drugs of choice for hyperfunction of the thyroid gland are thyreostatic drugs: thiamisole 20-45 mg / day, & nbsp; propylthiouracil 300-400 mg/day. The duration of treatment is 12-18 months. Oculomotor disorders and decreased vision can be reduced by taking 60-80 mg of prednisolone per day to suppress autoimmune aggression in the retrobulbar zone. Muscle weakness can be leveled by taking propranolol in a daily dose of 40-80 mg.
TSH level is not used to adjust the dose of cytotoxic drugs. 4 weeks after the appointment of the drug, the level of T4 is controlled. After reaching a normal level of T4, they switch to a maintenance dose of a cytostatic 7.5 mg.
Thus, an increased content of thyroid hormones leads to functional and structural changes in the body of a patient with thyrotoxicosis. Knowledge The main neurological and mental signs of hyperthyroidism are necessary for every doctor to refer him to an endocrinologist in time for the selection of medical correction of the pathological condition.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles on the site in the "Endocrinology" section. You may also be interested in: Anatomical structure and functions of the thymus gland









Add a comment