Inflammatory processes of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses are a fairly common occurrence among the world's population, affecting representatives of completely different ages and genders. Such diseases, with their timely detection and effective complex therapy, are quickly and successfully cured, returning the patient to his usual way of life. Otherwise, infectious processes of the nose and sinuses can lead to serious rhinogenic intracranial complications, since the structures of the nose are located in close proximity to the brain. Brief information about the main rhinogenic intracranial complications is provided by estet-portal.com.
Causes of rhinogenic intracranial complications
The penetration of an infectious agent from the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses into the skull occurs in several ways: contact, lymphogenous, hematogenous and perineural. There are several main causes of rhinogenic intracranial complications:
- anatomical features of the structure of the nose: structures of the nose and paranasal sinuses are in close proximity to the contents of the cranium;
- vascular-nerve connections: the veins of the nasal cavity have anastomoses with the cavernous sinus and venous plexuses of the dura mater;
- lymphatic connections: the lymphatic network of the nasal cavity has connections with the subarachnoid space of the brain.
Rhinogenic purulent meningitis: symptoms and treatment
Rhinogenic purulent meningitis is one of the most common rhinogenic intracranial complications. This is an inflammation of the membranes of the brain, which develops as a result of the spread of an infectious agent from the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses into the cranial cavity. Infection most often occurs by contact. Clinically, the disease is manifested by symptoms of intoxication of the body: nausea, vomiting, headache. Body temperature rises significantly, convulsive seizures, loss of consciousness, symptoms of irritation of the meninges may occur. The patient is shown an urgent surgical intervention in the form of a radical operation on the paranasal sinuses with exposure of the meninges, in parallel with this, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, dehydration therapy is performed.
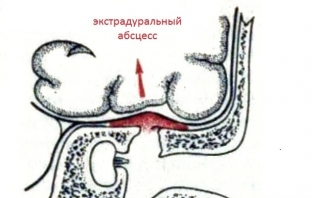
Extradural abscess: causes, symptoms and treatment
Extradural abscess – this is a collection of pus between the bone and the dura mater, resulting from the spread of infection from the paranasal sinuses. The condition is quite dangerous, clinically often manifests itself poorly, headaches, periodic attacks of nausea and vomiting, and difficulty in retracting the eyeball on the side of the lesion may occur. In most cases, an extradural abscess is discovered incidentally during surgery. Treatment consists of a radical operation on the inflamed sinuses in order to eliminate the source of infection, expose the meninges and drain the resulting abscess.
Cavernous sinus thrombosis: symptoms and treatment
Cavernous sinus thrombosis involves the formation of a thrombus and the occurrence of occlusion of the lumen of the sinus, with inflammation of its vascular wall. Clinically, this condition is manifested by cerebral and meningeal symptoms, as well as local symptoms: swelling of the eyelids and conjunctiva, conjunctival chemosis, exophthalmos, paralysis of the eye muscles and ptosis of the eyeballs. Treatment of cavernous sinus thrombosis consists in emergency sanitation of the inflammatory focus in the paranasal sinuses and massive antibiotic therapy in combination with anticoagulants according to the appropriate scheme.
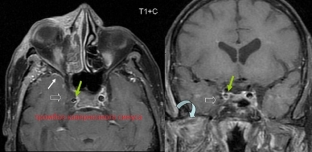
Rhinogenic brain abscess: symptoms and treatment
Rhinogenic brain abscess is a limited accumulation of pus in the brain, and occurs as a secondary infection against the background of an inflammatory process in the paranasal sinuses. Clinically, a rhinogenic brain abscess is manifested by cerebral, focal and meningeal symptoms, as well as local symptoms, such as swelling of the eyelids and conjunctiva and exophthalmos. To eliminate the rhinogenic abscess of the brain, an emergency operation is performed – surgical elimination of the purulent process in the paranasal sinuses, then the dura mater is exposed, punctured and the brain abscess is drained.









Add a comment