Eyes – this is a mirror of the soul, into which anyone can look, and immediately add up their impression of the owner of these eyes. And the eyelids are a kind of frame for these eyes, which, of course, also attracts attention. The main function of the eyelids is to protect the eyes from various damaging agents, but the eyelid tissues themselves can also be damaged. Blepharitis – This is an inflammatory disease of the edges of the eyelids, which is one of the most common ophthalmic pathologies. Why does blepharitis occur, how does it happen, and what symptoms indicate damage to the tissues of the eyelid – read on estet-portal.com.
Why does blepharitis occur and what are the symptoms
Blepharitis – it is always a bilateral inflammatory process, which in most cases has a chronic course. Pathology develops mainly in women aged 30-50 years. The main danger of this inflammatory process is that it can lead to the development of inflammation in the conjunctiva and cornea, be combined with functional insufficiency of the lacrimal apparatus and aggravate the symptoms of inflammation in other parts of the eye, allergic reactions and dry eye syndrome. Therefore, it is very important to know the symptoms of various types of blepharitis, to diagnose and treat this disease in a timely manner.
Blepharitis:
- classification of blepharitis depending on location and symptoms;
- etiology of blepharitis: why inflammation of the eyelid margins occurs;
- clinical picture of blepharitis: characteristic symptoms.
Classification of blepharitis depending on location and symptoms
Blepharitis is classified depending on the localization of the inflammatory process, as well as in accordance with its clinical manifestations. Depending on the localization, the following forms of blepharitis are distinguished:
- anterior marginal blepharitis – characterized by the development of the pathological process of the anterior plate of the eyelids, the appearance of local signs of skin pathology, and is accompanied by infection;
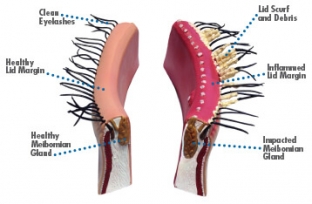
- posterior marginal blepharitis affects the posterior plate of the eyelids, resulting from dysfunction of the meibomian glands.
Depending on the clinical form, it is customary to distinguish scaly or seborrheic blepharitis, ulcerative or staphylococcal, marginal or posterior, as well as demodicosis blepharitis.
Etiology of blepharitis: why inflammation of the eyelid margins occurs
Blepharitis can be infectious and inflammatory in nature. In most cases, the etiological factor of blepharitis is staphylococcus aureus, and blepharitis of this nature in 80% of cases develops in women at the age of about 40 years.
 Other pathogens include streptococci, herpes simplex and zoster viruses, molluscum contagiosum viruses, pathogenic fungi, lice and arthropod mites. Infectious blepharitis develops as a result of the body's immunological response to pathogen antigens.
Other pathogens include streptococci, herpes simplex and zoster viruses, molluscum contagiosum viruses, pathogenic fungi, lice and arthropod mites. Infectious blepharitis develops as a result of the body's immunological response to pathogen antigens.
Non-infectious blepharitis occurs with seborrhea, eczema, rosacea, various immunodeficiency states. Forms of blepharitis such as marginal or posterior blepharitis are associated with disruption of the meibomian glands.
Clinical picture of blepharitis: characteristic symptoms
The clinical picture of blepharitis differs depending on which form of the disease is observed in the patient:
- with scaly blepharitis, small scales are observed on the skin of the edges of the eyelid and eyelashes, while the patient feels burning, itching, heaviness of the eyelids, eye fatigue;
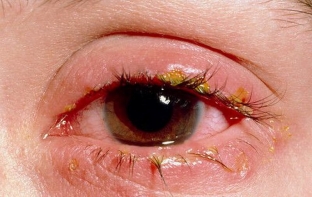
- ulcerative blepharitis is characterized by the formation of purulent crusts and ulcers on the edges of the eyelids, the patient's eyelashes stick together, he feels like a foreign body in the eye, itching and burning;
- marginal blepharitis is manifested by redness and thickening of the edges of the eyelids, the accumulation of yellowish-gray discharge in the outer corners of the eyes, the formation of telangiectasias at the clogged gland openings. Patients complain of itching and burning, watery eyes, a feeling of dryness of the eyes and the presence of a foamy discharge from them.
- with demodectic blepharitis, redness and thickening of the edges of the eyelids occur, scales, crusts and white muffs form on the eyelashes, the main complaints of patients are itching in the eyelids, which is aggravated by heat, burning, heaviness and foamy discharge.








Add a comment