The appearance on the body of rough areas resembling "goosebumps" is familiar to a huge number of people. The official name of this variety of dermatitis — follicular hyperkeratosis. What is the cause of this skin disease? Is it contagious? How dangerous is it for the general state of human health and is it treatable? What actions should you take when you find yourself having this problem? Together with estet-portal.com we will try to give comprehensive answers to questions related to the causes, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of follicular hyperkeratosis.
Follicular hyperkeratosis — what is this
Follicular hyperkeratosis — dermatological pathology caused by a violation of the process of exfoliation of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Accumulations of particles of dead skin clog the ducts of the hair follicles. The secret of the sebaceous glands sticks together the scales of the epidermis, the skin under them becomes inflamed, reddens, becomes rough and rough, with characteristic pimples resembling "goose skin".
The foci of the disease are usually localized in areas where the skin is especially prone to dryness: on the forearms, near the elbows, on the hips and buttocks. In some cases, the disease may involve patches of skin on the face.
Although not a cause for concern, goosebumps tend to "catch" if not treated appropriately. new parts of the body.
The disease is not contagious, it can neither be infected nor infect others. In addition, it does not harm the general state of health, but it can cause significant psychological discomfort.
Hypovitaminosis provoking the development of follicular hyperkeratosis
Modern dermatology cannot yet give a clear and unambiguous answer about the causes of the development of follicular hyperkeratosis. Among the most important external factors provoking this disease, there are various forms of hypovitaminosis:
1. A lack of vitamin C leads to a decrease in collagen production, which, in turn, causes dryness and flabbiness of the skin, as well as a decrease in the elasticity of small blood vessels. Violation of blood microcirculation serves as an impetus to disruption of metabolic processes and excessive & nbsp; proliferation of keratinized epidermis.
2. Insufficient intake of vitamin A in the body causes a violation of the processes of renewal of skin cells, its premature aging, a decrease in normal tone and loss of moisture. In addition, with a lack of vitamin A, the nutrition of the hair follicles worsens, the ducts of the hair follicles become blocked, which leads to the development of inflammation.
3. Reduced production of vitamin D, which, in addition to many other important functions, also prevents the pathological growth of epidermal cells, and is one of the factors leading to the development of follicular hyperkeratosis.
The impact of chronic stress and poor nutrition
Dermatologists are unanimously convinced that malnutrition — one of the possible causes of the development of the disease. Problems in the work of the gastrointestinal tract, dysbacteriosis, disruption of normal metabolism are directly related to the lack of B vitamins, which negatively affects the condition of the skin.
Among other factors provoking the development of this disease:
· hereditary predisposition;
· taking hormonal drugs (for example, oral contraceptives) that cause excessive growth of epidermal cells;
· stress and overwork, leading to overexpenditure of B vitamins;
· wrong hoopoe behind the skin using aggressive cosmetics — soaps, washing gels, antibacterial tonics that cause overdrying of the skin.
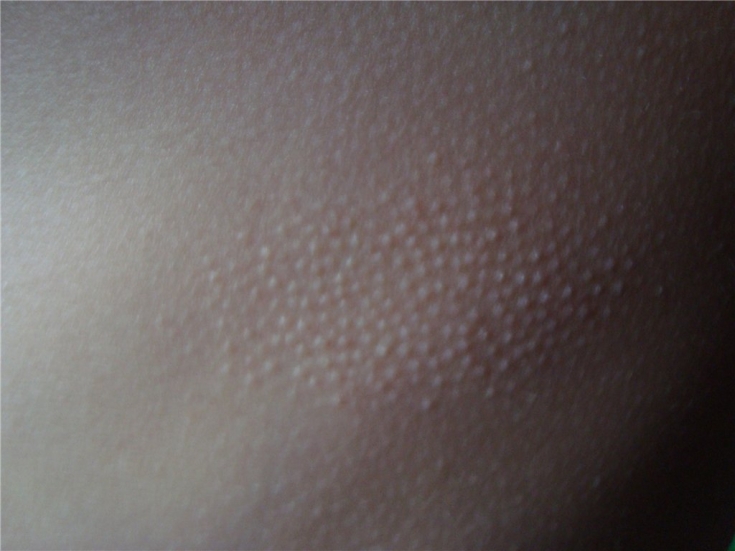
Peculiarities of diagnosis and treatment of follicular hyperkeratosis
Although patches of rough skin are usually not a cause for concern and may be completely invisible under clothes, if you find a similar pathology in yourself, you should not postpone a visit to a specialist.
Many skin diseases can have similar manifestations, and therefore it is better to be safe than to miss the beginning of the development of a more dangerous pathology. In addition, even such a completely "harmless" cosmetic defect may indicate more serious health problems.
Usually, a visual examination of the focus of the disease, a general blood test and a test for vitamin deficiency are enough for a specialist to diagnose. To completely exclude (or confirm) the presence of pathologies of internal organs, it is worth additionally consulting with a general practitioner, gastroenterologist and endocrinologist.
Methods of treatment and skin care
First of all, it should be noted that at present there is no way to completely cure this type of dermatitis. The treatment strategy is formed depending on the cause that provokes the development of the disease.
Dermatologist usually prescribes:
· Topical treatment aimed at eliminating inflammation and dryness of the skin. Products containing lactic acid, emollients are effective;
· Topical treatment with anti-inflammatory steroids;
· courses of vitamins that are necessary to overcome the consequences of hypovitaminosis.
Caring for skin affected by follicular hyperkeratosis also has its own characteristics. Beauticians warn against the use of rough scrubs, hard washcloths. Mechanical injury to the skin will not eliminate, but only aggravate the problem, since it can lead to infection with pathogenic microbes and the formation of abscesses. That is why it is also not recommended to wear clothes that rub and additionally injure the affected area of the body. In addition, prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light and low temperatures should be avoided.
Salon and home treatments for follicular hyperkeratosis
So, we have established that the affected areas should not be subjected to hard mechanical stress. And this means that chemical peels (using salicylic, glycolic and lactic acid) are more suitable for us. After such a peeling, the beautician usually applies moisturizing and softening cosmetics to avoid overdrying the skin.
In addition, with follicular hyperkeratosis, laser resurfacing of the face will be effective. For skin care at home, baths with the addition of a decoction of thyme, celandine, horse chestnut, chamomile or nettle are recommended. After taking a bath, apply a nourishing cream or body milk to help relieve inflammation. In addition, masks (compresses) with aloe, propolis, grated potatoes will be useful.
Treatment and prevention of the disease will be more effective if you normalize your sleep and rest regimen, adjust your diet, and lead a healthy lifestyle. In addition, special attention should be paid to the choice of face and body skin care products, giving preference to gels, foams and tonics that will soften and moisturize the skin.
You may be interested in: Acne. Mechanisms of development and predisposing factors
More interesting information about skin and any other diseases can be found on the website estet-portal.com.








Add a comment