Increased body temperature, even coughing and severe pain in the chest, sometimes difficulty in breathing can signal the development of pleurisy. This disease is not independent and occurs as a complication after pneumonia or bronchitis. Pleurisy often proceeds almost imperceptibly against the background of another ailment, therefore it may not be detected, and the person does not even suspect that he is being treated for two diseases at once. But not all types of pleurisy are as harmless as they might seem. Therefore, with a complication of the flu or a cold, it is worth considering the possible development of pleurisy. So that in the future there are no problems with the breathing process even after recovery, you should clearly know how to treat pleurisy and what preventive measures to take.
What is pleurisy, description and possible complications
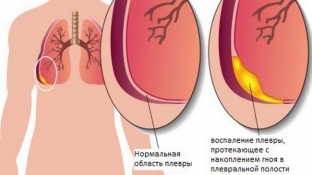
Human lungs are covered with a thin protective film – pleura. The outer layer of the pleura covers the inside of the chest, and the inner layer of the pleura – envelops the lungs and diaphragm. Between these pleural sheets is the pleural cavity with a small amount of fluid necessary for the sliding of the pleura during the respiratory process.
Pleurisy disease is an inflammatory process that damages the pleura: when fibrin (high molecular weight protein) is deposited on the sheets with dry pleurisy or fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity with exudative pleurisy. Therefore, it is important to remember how to treat pleurisy, and what methods of prevention can be used.
Pleurisy can be infectious or aseptic. Infectious pleurisy is characterized by the presence of infection on the pleural sheets, most often due to pneumonia or a purulent process in the lungs. Aseptic pleurisy occurs without infection, occurs as a result of injury or during surgical intervention with hemorrhage in the cavity.
Symptoms and causes of pleurisy
Symptoms of dry or fibrinous pleurisy:
- proceeds extremely sharply, immediately begins to hurt in the area of the ribs, in the place where the pleura is damaged;
- body temperature rises;
- feeling of general weakness.
Symptoms of exudative pleurisy:
- heaviness in the chest;
- shortness of breath;
- dry cough;
- headache;
- weakness and fever.
When the fluid accumulates and reaches an acceptable threshold, the patient begins to suffocate, shortness of breath and dry cough do not stop even during rest. Symptoms of intoxication of the body may worsen the condition.
With an infectious course of pleurisy, the infection in the body enters the pleural cavity and affects the pleura. The cause may be the ingestion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The route of infection: along with blood, when injured or from a focus of infection from the lungs.
Read also: The first symptoms of cancer that everyone should know about!
The cause of non-infectious pleurisy may be the presence of metastases from other affected organs, the course of an autoimmune disease, such as lupus erythematosus. It can also be caused by a chest injury. In acute pancreatitis, pancreatic enzymes can enter the pleural cavity through the diaphragm and cause damage to the pleura.
Main causes of pleurisy:
- presence of infection in the pleural cavity;
- development of pulmonary pathology (pneumonia, tuberculosis, pulmonary infarction);
- rib fracture and pleura injury;
- oncological diseases.
More about pneumonia: Signs of pneumonia to be aware of
How to treat pleurisy effectively
How to treat pleurisy so that the infection does not spread throughout the body, if it is an infectious type of pleurisy? For this, the patient must be sent to the hospital so that he is under the supervision of doctors. It is imperative for the effective treatment of pleurisy to adhere to bed rest and a balanced diet. Liquid and salt intake should be limited.
In infectious pleurisy, antibiotic therapy is indicated along with anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers. If too much fluid has accumulated in the pleural cavity, it is possible that surgical removal of the exudate will be required to prevent suppuration. When fluid is removed, adhesions may form between the sheets of the pleura. To prevent the occurrence of adhesions, it is necessary to engage in therapeutic breathing exercises. It is also better to do a chest massage and do not forget about physiotherapy.








Add a comment