Injuries to the male genital organs are very dangerous for male reproductive health, as they threaten the development of long-term severe consequences, one of which is the development of hydrocele. This disease is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the scrotal cavity, the amount of which can reach several liters. A greatly enlarged scrotum not only impairs a man's overall quality of life, causing discomfort and disrupting his sex life. The fluid accumulated in the scrotal cavity can become infected and threaten the development of severe inflammatory processes, which can ultimately lead to the development of infertility. That is why, dropsy of the testicle requires the earliest possible diagnosis and timely treatment.
Causes of hydrocele: classification by etiology
Dropsy of the testicles or hydrocele is characterized by the accumulation of serous fluid between the internal and parietal plates of the vaginal membrane of the testis. Hydrocele can be congenital and acquired, which means that pathology can occur at absolutely any age. Congenital dropsy of the testicular membranes is of two types: isolated dropsy, and dropsy, which, due to the narrow passage of the unclosed vaginal process of the peritoneum, is connected to the abdominal cavity. Since the vaginal process is a kind of narrow tunnel, the contents of the abdominal cavity cannot enter the scrotum, but the fluid produced by the vaginal membrane can freely enter the abdominal cavity. Acquired hydrocele is also of two types: primary, the cause of which cannot be determined, and secondary, the occurrence of which is provoked, first of all, by injuries of the scrotum and infectious processes of the male genital organs. In addition, dropsy of the testicles is classified into single and multi-chamber, acute and chronic.
Clinical picture of hydrocele: main symptoms
The size of the scrotum with dropsy of the testicle can be different: from a tennis ball to a few kilograms of watermelon. A characteristic feature of a hydrocele is an increase in the scrotum due to a change in the size of that half of it, which is subject to a pathological process.
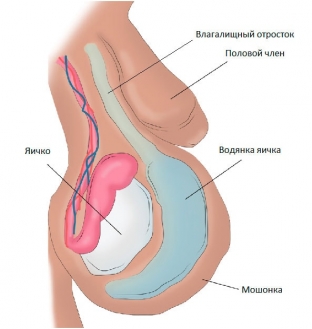 At the same time, the general quality of life of the patient is disturbed: motor activity worsens, up to the complete inability to move with the impressive size of the scrotum. Sexual intercourse becomes impossible, in some cases there are painful sensations in the scrotum, both during physical exertion and at rest. The serous fluid that accumulates in the membranes of the testis may be clear or yellowish green and contains a large amount of protein. In case of infection, this fluid becomes purulent - a pyocele develops. Even with a minor injury to the enlarged scrotum, a hamatocele occurs - blood appears in the serous fluid.
At the same time, the general quality of life of the patient is disturbed: motor activity worsens, up to the complete inability to move with the impressive size of the scrotum. Sexual intercourse becomes impossible, in some cases there are painful sensations in the scrotum, both during physical exertion and at rest. The serous fluid that accumulates in the membranes of the testis may be clear or yellowish green and contains a large amount of protein. In case of infection, this fluid becomes purulent - a pyocele develops. Even with a minor injury to the enlarged scrotum, a hamatocele occurs - blood appears in the serous fluid.
Instrumental methods for diagnosing hydrocele
Diagnosis of dropsy of the testicular membranes is based primarily on the data of an objective examination. When examining the patient, an enlarged scrotum is determined, the folds of which are smoothed out. A symptom of fluctuation will be positive: with a slight push with the fingers on one side of the scrotum, the fingers located on the other side will feel the shock wave due to the fluctuation of the fluid. Of the instrumental methods, the most informative today is ultrasound, which provides the maximum amount of information about the state of the testicle, its appendages and membranes. Less commonly used is tomography, which, with a hydrocele, visualizes an increase in the area of temperature zones on the side of the lesion, as well as diaphanoscopy: transillumination of the scrotum with a beam of light in order to determine the fluid in it.
Which technique should be chosen for the treatment of hydrocele
Treatment of dropsy of the testicles depends on its immediate cause. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the etiological factor, if it is, for example, an infectious process. Patients are prescribed anti-inflammatory therapy, cold compresses in the first few days. Nevertheless, today the surgical method of treating hydrocele is preferred, since this condition threatens the development of spermatogenesis disorders and the occurrence of infertility. There are two most common types of surgery. According to the Winckelmann method, the vaginal membrane of the testis is dissected and sutured behind it. This technique is effective for small dropsy of the testis. In other cases, preference is given to surgical intervention according to the Bergman method: the parietal plate of the vaginal membrane of the testicle, which secretes serous fluid, the remaining edges of the vaginal membrane are completely removed and sheathed with a continuous suture. After a successful operation, the prognosis for the life and reproductive function of the patient is favorable: a complete recovery occurs.








Add a comment