Epstein-Barr virus, EBV for short, is considered the most common virus among humans. This herpesvirus infection can affect young children, ranging from a year old, schoolchildren, adolescents and adults.
If a baby encounters it after a year, the symptoms of the disease are mild, very similar to a mild flu. If the infection occurred after 2-3 years against the background of reduced immunity, the child develops a rich clinical picture.
Epstein-Barr virus in adolescents occurs in the form of infectious mononucleosis. More than 90% of people on the planet are infected with this group of herpesviruses and are carriers of the disease.
The danger of infection with this virus in children is manifested by disorders of the brain, lymphatic system, liver and spleen. Consider the main causes, symptoms and consequences of the development of the Epstein-Barr virus.
Introducing Epstein-Barr Virus
The virus was first identified by Michael Anthony Epstein in 1964 in collaboration with graduate student Yvonne M. Barr. The discovery of the virus occurred after examining samples of Burkitt's lymphoma tumors.
Samples were provided by surgeon Denis Parson. He studied the development of lymphoma in children younger than 7 years old living in Africa.
Adenoids in children: causes and treatment.
Epstein-Barr virus in children is transmitted by airborne droplets, through saliva, personal hygiene products, utensils, blood transfusions or transplants. After infection and recovery, a person usually develops strong immunity to this group of viruses.
Although neither a child nor an adult will be able to completely get rid of the presence of a virus in the body. Epstein-Barr virus in children and adults will be dormant after successful treatment.
Epstein-Barr virus symptoms
The salivary glands, lymph nodes, and tonsils are the first organs to become infected with the virus.
In the first years of a child's life after infection with the virus, the clinical picture does not manifest itself in any way or mild symptoms are noticeable, which often resemble a cold. Therefore, pediatricians are more likely to treat a cold than a virus.
What is the relationship between immunity and the occurrence of the disease
If the infection enters the body of a child after 2 years, there may be an increase in lymph nodes, salivary glands, adenoids. In addition, the temperature rises to 37-38 degrees, the child feels weak, unwilling to sleep or eat, frequent abdominal pains appear, the nasopharynx swells, nasal discharge may appear.
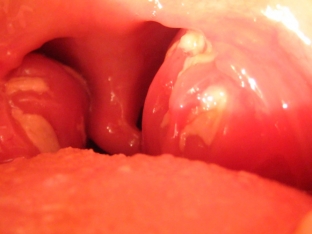
Possible consequences and diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus
If the infection in the child's body was acute and fast, most likely, there will be violations of the kidneys, liver, spleen, immune system.
Oncological processes can also develop in the lymph nodes, or other organs: cancer of the stomach, nasopharynx, colon or small intestine, oral mucosa.
In addition, the development of EBV in children can be the cause of not only enlarged lymph nodes, the development of lymphadenopathy or lymphadenitis, but also permanent tonsillitis.
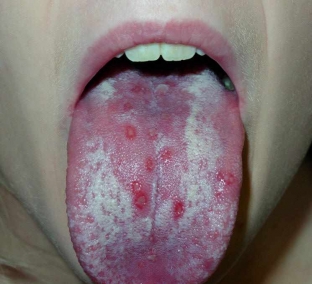
If the Epstein-Barr virus in children occurs in the form of infectious mononucleosis, the characteristic symptoms may be: vomiting, soreness in the abdomen, rare stools, pneumonia, swollen lymph nodes, weakness and headache.
A child who has recovered from mononucleosis may experience enlarged lymph nodes and problems with the liver, kidneys and spleen for a year and a half, tonsillitis and pharyngitis may occur.
It is especially dangerous to send a child for vaccination if he is infected with the – the unpredictability of the reaction puts the life of the baby at risk.
Attention! If the child has the above symptoms and manifestations, please kindly check the child for the presence of the Epstein-Barr virus!
How to diagnose a virus
To detect infection with a child's virus, it is necessary to donate blood and saliva for laboratory testing: complete blood count, biochemical blood test, immunogram, serological methods.
Epstein-Barr virus treatment
Today, there are no effective methods of curing sick children infected with the Epstein-Barr virus. Doctors can only eliminate the clinical manifestations and transfer the active infection to a latent phase, which is not terrible for the health of the child.
Find out:Mitchegan Virus: what's in store for us this winter.
Infectious mononucleosis and virus-affected organs in the child's body are treated in a hospital. In addition, if there is still a chance that the virus may further affect the brain and vital organs, doctors prescribe antibiotics, antihistamines, and means to relieve acute manifestations: relieve swelling in the nose, normal lymph outflow.
Learn more: Epstein Barr virus: symptoms, treatment, consequences.
If there are slight enlargements of the lymph nodes and a slight swelling in the nasopharynx, the pediatrician can treat. In all other cases, observation and treatment is carried out by an infectious disease specialist.








Add a comment