From the moment of birth, your muscles grow and get stronger until about 30 years old, after which the process begins to flow in the opposite direction – You begin to lose muscle mass, which is accompanied by a weakening of muscle function. This age-related change is called sarcopenia. The loss of muscle mass in physically inactive people after 30 years averages 3-5% in 10 years, active people manage to maintain more muscle mass, however, completely & nbsp; it is not yet possible to reverse this process. Why exactly does sarcopenia develop and can this process be slowed down?
Causes of sarcopenia: why do we lose muscle mass as we age?
While there is no generally accepted test or level of muscle loss to diagnose sarcopenia, it should be understood that any loss of muscle mass is significant as it results in reduced mobility and muscle strength.
As a rule, the older the person, the faster the development of sarcopenia, reaching its peak around the age of 65-80 years. This increases the likelihood of falls and the risk of fractures in the elderly.
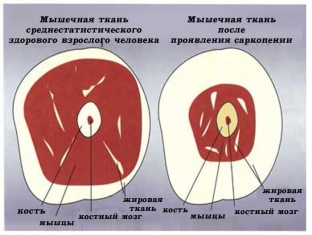
Among the main signs of sarcopenia are musculoskeletal weakness and loss of stamina, which reduce the level of a person's physical activity. And in conditions of lack of physical activity, muscle mass continues to decrease.
Read also: Life is just getting started: how to stay fit after 40
Specialists believe that the following factors are significant in age-related muscle loss:
- age-related decrease in the number of nerve cells responsible for the transmission of signals initiating movement from the brain to the muscles;
- decreased levels of certain hormones, including growth hormone, testosterone, and insulin-like growth factor;
- decrease in the body's ability to synthesize proteins;
- malnutrition that prevents the maintenance of muscle mass.
Are there ways to prevent and treat sarcopenia?
Exercise is the main component of the treatment of sarcopenia. Strength training helps to strengthen muscles and increase endurance. That is why to prevent and treat sarcopenia recommend doing exercises with weights or an expander.
Strengthening exercises have been shown to have a positive effect on:
- neuromuscular system;
- hormone concentrations;
- protein synthesis.
In order to maximize the benefits and minimize the risk of injury, it is important to choose the right amount, intensity and frequency of strength training. That is why it is best to make such a plan with an experienced doctor or trainer.
Read also: 5 simple exercises to strengthen bones: technique
An equally important factor in maintaining healthy muscle mass is a balanced diet, selected by a competent nutritionist, including a sufficient amount of protein and vitamins (certain vitamin complexes may be prescribed if necessary).
While drug therapy is not the preferred treatment for sarcopenia, research is ongoing:
- urocortin II – a peptide that stimulates the production of ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) in the pituitary gland and is able to prevent muscle atrophy;
- hormone replacement therapy (HRT), which increases lean body mass, results in short-term belly fat loss, and prevents bone loss;
- testosterone supplements;
- growth hormone supplements;
- drugs for the treatment of metabolic syndrome.
However, there is no approved drug for use in the treatment of sarcopenia. Experts believe that it is a well-chosen exercise and nutrition program that will help maintain muscle mass, strength and endurance at any age.






Add a comment