Cancer – this is a word that people today associate far from with an aquatic animal or a zodiac sign. Oncological diseases are one of the main causes of high mortality among the world's population. The causes of oncological pathology in most cases are not reliably studied, which leads to the lack of a single effective method of treating such diseases. Kidney cancer is perhaps the most dangerous oncological pathology that can take the life of a patient in a very short time. About the causes and types of kidney cancer & nbsp; estet-portal.com.
Etiological factors and classification of kidney cancer
Today, kidney cancer is a problem predominantly of older and older men: men get sick almost three times more often than women. Kidney cancer develops from epithelial cells of various parts of the nephron and collecting ducts: the epithelium of the glomerular capsule and renal tubules. Kidney cancer is classified according to the TNM world clinical classification: depending on the size of the primary tumor focus, damage to regional lymph nodes and the presence of distant & nbsp; metastases. In the last decade, with the advent of new effective methods of diagnosis and treatment, the survival prognosis for patients with kidney cancer has improved significantly.
Kidney cancer:
- classification of kidney cancer: main types of tumors;
- what factors influence the occurrence of kidney cancer;
- to which organs can kidney cancer metastasize.
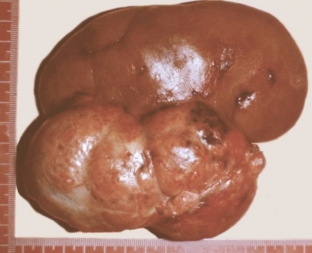
Classification of kidney cancer: main types of tumors
Almost 90% of all malignant neoplasms of the kidney are clear cell carcinoma. There are several histological forms:
- intrinsic clear cell renal cell carcinoma;
- alveolar kidney cancer;
- dark cell or granular cell carcinoma;
- solid tubular cancer;
- polymorphic cancer;
- sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma.
Combined histological forms of kidney cancer are quite often observed, and therefore it can be difficult to determine the nature of the neoplasm: is it a primary tumor or its metastasis. According to the morphological structure, glandular, papillary and solid cell forms of kidney cancer are distinguished. The tumor can be located in different parts of the kidney and range in size from a few millimeters to more than 3 centimeters in diameter.
What factors influence the occurrence of kidney cancer
The causes of kidney cancer, like most oncological pathologies, are not fully understood today. The main theory is considered to be genetic: the disease may be due to the loss of genes that have the ability to suppress & nbsp; malignancy of kidney cells. In addition, there are other factors that contribute to the malignant transformation of the kidney, such as congenital malformations of the organ, the influence of hormonal or chemical factors, traumatic kidney injury, smoking, and so on. Both the right and left kidneys are affected with equal frequency, with bilateral kidney cancer being extremely rare.
To which organs can kidney cancer metastasize
Metastasis is the main factor determining the prognosis for a patient with oncological pathology. Metastasis refers to the spread of malignant cells throughout the body. In kidney cancer, metastasis occurs in three main ways:
- hematogenous – with blood flow;
- lymphogenic – with lymph flow;
- lymphohematogenous – metastasis in both blood and lymphatic vessels.
Kidney cancer metastases can be localized in different organs: lungs, liver, spleen, brain, flat and tubular bones, vertebrae, as well as in paracaval and paraaortic lymph nodes. As a metastatic tumor grows, it can spread to nearby tissues and organs. A feature of kidney cancer metastases is the fact that their first symptoms may occur even earlier than the symptoms of the development of the primary tumor focus. The earliest possible detection and removal of both the primary focus and metastases of kidney cancer significantly prolongs the life of the patient.







Add a comment