Neglect of personal hygiene as well as a poor nutritional culture can have bad consequences for patients. In this article on estet-portal.com, we will look at diseases that are caused by protozoa belonging to the sporozoans, commonly known under the name "cryptosporidium".
For more information on what cryptosporidiosis is, the mechanisms of its transmission, as well as what methods of diagnosis, treatment and prevention of the disease exist, read on estet-portal.com in this article.
Cryptosporidiosis as a consequence of eating contaminated food
Cryptosporidiosis is caused by the protozoa C. hominis and C. pavrum. Recently, the disease is especially relevant, which is associated with frequent epidemics, as well as the prevalence of complications in patients with HIV infection.
Transmission of pathogens occurs by the fecal-oral mechanism by ingestion of cysts through contaminated food or drink.
One of the main carriers of the parasite C. pavrum is livestock: calves, piglets, lambs. There is also a high risk of infection in people who are in constant contact with fresh water, including recreational waters such as swimming pools.
Main routes of human infection with cryptosporidiosis – water and food.
Two other protozoans, Cyclospora cayetanensis and Cycloisospora belli (formerly Isospora belli), can cause cryptosporidium-like infections.
Are dirty hands to blame: a modern view of viral hepatitis A
Cryptosporidiosis: features of the clinical picture of the disease
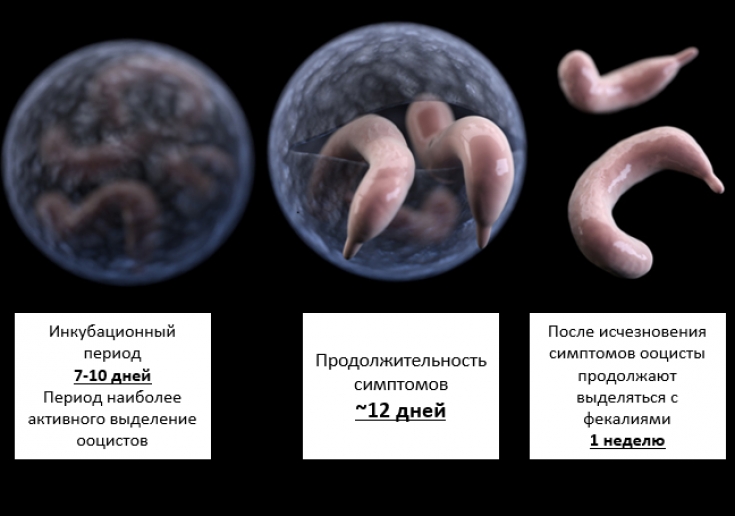
The incubation period of the disease is 7 to 10 days. Sometimes the infection can manifest two weeks or even a month after infection.
Symptoms begin with the development of watery diarrhea and epigastric discomfort. Diarrhea can last up to several weeks, and the patient may become dehydrated. Often the disease is accompanied by nausea, sometimes vomiting.
One-third of patients experience a short (up to 24 hours) period of fever.
Symptoms last an average of 12 days, although this period can range from 2 days to 1 month.
In immunosuppressed patients, the clinical picture of cryptosporidiosis is always more severe.
Follow us on Telegram
Diagnosis of cryptosporidiosis: microscopy and nucleic acid test
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by detection of nucleic acid in the material (PCR), or the parasite is identified microscopically.
The most sensitive method for diagnosing cryptosporidiosis is the detection of parasitic nucleic acids in faeces. If a nucleic acid test is not possible, microscopy is an alternative.
Double detection of the pathogen by microscopic examination of feces, performed on two different days, is sufficient to make a diagnosis of cryptosporidiosis.
Oocysts continue to be shed in the faeces for about 1 week after symptoms disappear.
Identification of pathogen antigens is an alternative secondary diagnostic test because it is less sensitive than PCR.
Read also: Amebiasis: modern principles of diagnosis and treatment of the disease
Optimal treatment and prevention options for cryptosporidiosis
In healthy individuals, cryptosporidiosis may resolve spontaneously and treatment is usually symptomatic only. Some infected individuals remain asymptomatic carriers.
For immunocompetent patients with severe symptoms, Nitazoxanide is the drug of choice, which is used as follows:
- for adults – 500 mg twice a day for 3 days;
- for children aged 1-3 years – 100 mg twice a day for 3 days;
- for children aged 4-11 – 200 mg twice a day for 3 days.
However, the appropriateness of using this drug remains controversial, since the effectiveness has been proven in only half of the cases of cryptosporidiosis.
In immunosuppressed patients (eg, those with HIV or those taking immunosuppressive therapy), diarrhea can be extremely profuse. In this case, the disease persists for several months and tends to generalize. Sometimes fatal consequences are possible.
There is no consensus on the effectiveness of drug treatment in immunocompromised patients. Among the drugs used in the treatment of HIV-infected patients, protease inhibitors have some effectiveness.
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole is used in the treatment of infections caused by Cyclospora cayetanensis and Cycloisospora belli.
Prevention of cryptosporidiosis is based on good personal hygiene, as well as timely detection and treatment of infected patients.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the Infectology section.
You may also be interested in: Polymorphic photodermatosis: problems caused by solar radiation
Adapted from EBM Guidelines "Cryptosporidiosis"







Add a comment