Glucocorticoids are called steroid hormones of the adrenal cortex, as well as their synthetic analogues. These substances were discovered more than seventy years ago by the American physician Philip Gench. In 1950 he was awarded the Nobel Prize for "...discoveries concerning the hormones of the adrenal cortex, their structure and biological effects." From that time until today, glucocorticoids have remained the most effective anti-inflammatory drugs in medicine.
For more information about the indications for the use of glucocorticoids, their modern classification, age restrictions for prescribing, as well as practical issues of combining glucocorticoids with other groups of pharmacological drugs, read on estet-portal.com in this article.
What are the indications for prescribing glucocorticoid drugs
Today it is difficult to imagine the treatment of many dermatological, rheumatological, allergic and hematological diseases without the use of glucocorticoids.
Due to their powerful anti-inflammatory action, glucocorticoids are used in the treatment of many chronic and urgent pathological conditions.
Analogues of adrenal hormones are used to treat the following pathologies:
1. allergic: bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis;
2. dermatological: eczema, psoriasis, erythroderma, exfoliative dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis;
3. rheumatological: rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, systemic scleroderma, periarthritis nodosa, ankylosing spondylitis;
4. endocrinological: Addison's disease, adrenogenital syndrome;
5. gastroenterological: Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis;
6. extreme conditions: acute adrenal insufficiency, shock, status asthmaticus, hepatic coma, hypoglycemic state.
Thus, glucocorticoids have an extremely wide range of clinical indications. But what should be taken into account by the doctor who prescribes their use to the patient? Read more about this later in the article.
Follow us on Telegram
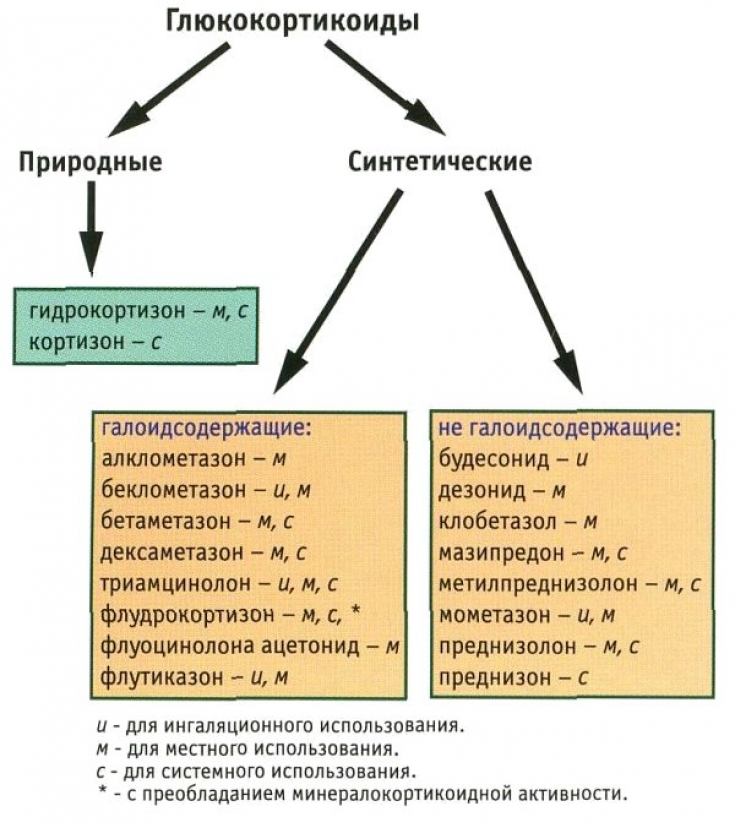
Glucocorticoids: modern approaches to drug classification
Today, there are several approaches to the classification of glucocorticoid drugs. According to the method of application, they are divided into the following groups:
1. glucocorticoids for oral and parenteral use: dexamethasone, prednisolone, methylprednisolone, triamcinolone;
2. inhaled glucocorticoids: budesonide, beclomethasone, flunisolide, fluticasone, betamethasone;
3. glucocorticoids for external use: budesonide, triamcinolone acetonide, hydrocortisone, betamethasone, fluocinolone acetonide, fluorometholone, clobetasol, mometasone.
There is also a classification of glucocorticoids according to the degree of power of their anti-inflammatory effect.
According to it, there are such groups of drugs:
1. First group (weak anti-inflammatory effect): prednisone, hydrocortisone;
2. Second group (moderate anti-inflammatory effect): triamcinolone, aclomethasone;
3. Third group (strong anti-inflammatory effect): betamethasone, fluocinolone, mometasone, methylprednisolone, fluticasone;
4. Fourth group: (strongest anti-inflammatory effect): clobetasone.
The doctor also needs to take into account age restrictions in the use of glucocorticoids: hydrocortisone butyrate and fluticasone can be prescribed from three months of age; methylprednisolone – from four months; clobetasone, triamcinolone and prednisolone – from one year; mometasone – from two years old. There are no clinical data on the safety of betamethasone in children.
Things to remember for a doctor who prescribes glucocorticoids to a patient
Attention should be paid to some practical aspects of the use of glucocorticoids. A doctor who prescribes glucocorticoid agents to a patient must be sure to remember the following points:
1. It is impossible to combine the use of hydrocortisone and vitamin D;
2. It is impossible to combine the use of triamcinolone with rifampicin and barbiturates;
3. Concomitant use of prednisolone, triamcinolone with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs increases the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding;
4. The simultaneous use of any representatives of glucocorticoid drugs with anticoagulants increases the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding;
5. & nbsp; Sudden withdrawal of glucocorticoids causes "withdrawal" syndrome.
Thus, today there is a wide arsenal of glucocorticoid drugs with varying degrees of effectiveness.
The doctor should be guided by the modern classification of glucocortioids and the possibility of their use, taking into account the power of the anti-inflammatory action, as well as the advisability of combining with other groups of pharmacological substances.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Dermatology" section. You may also be interested in what your doctor needs to know about modern antihistamines.









Add a comment