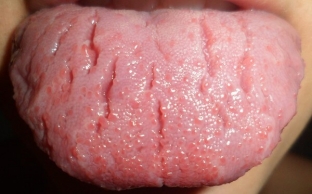
Language changes – these are violations of the color of the tongue, the integrity of its surface, its size or shape. The type of tongue can be of great diagnostic value and indicate an existing disease. Approximately 2% of the normal population is found with architectural changes in language, which are characterized by multiple deep grooves. According to dermatologists, this disease is listed as “scrotal tongue”. Often it is found in Mongolism and, as a partial symptom, in the Melkerson-Rosenthal syndrome. What is a geographic language? Under what conditions is the soreness of the tongue, read further on estet-portal.com
What does the geographical language indicate?
Geographical tongue is a benign chronic disease. The histological picture is adjacent areas with hypertrophic and atrophic filiform papillae, and the boundaries are very clear, polycyclic and bizarre (similar to a geographic map). Atrophic areas appear reddened, they cause a subjective burning sensation when consumption of spices, hot drinks.
The localization of these language changes is constantly changing. As for the duration of the course of the disease, these spots begin to appear mostly in childhood and persist throughout life, notes estet-portal.com. However, they are likely to disappear in adulthood. The histological picture of the areas of the coated tongue shows sloughed epithelial cells, protruding mucin, bacteria, etc.
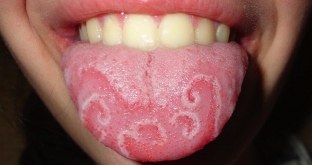
It is important to know the fact that half of children with geographic tongue have signs of rickets.
As for the hyperemic areas, the stratum corneum is completely absent there, in addition, thin layers of precipitated protein and lymphocytes are found. The pattern of the papillae is atrophic. In the dermis, only in some places there are limited areas of infiltration. The etiology of such changes in the language may be the presence of exudative diathesis.
Provoking factors that cause language changes (geographic language) in children:
- presence of goiter;
- anemia;
- gastrointestinal disorders
- helminthiases.
Changes in the tongue, accompanied by painful sensations in it
Glossodynia (glossalgia) is a neurostomatological disease and is manifested by paresthesias in the form of burning, tingling in the tongue. Often, these sensations are accompanied by a feeling of swelling, awkwardness, heaviness in the tongue. Dry mouth appears, saliva is viscous and sticky. Patients may experience paresthesias in the lips, palate, cheeks, throat, and esophagus, and very rarely in the neck and eyelids.
Glossodynia may accompany the following diseases:
- pernicious anemia;
- chronic gastritis;
- Plummer-Vinson syndrome;
- Sjögren's syndrome;
- various vitamin deficiencies (sprue, pellagra);
- diabetes;
- tetany (night pain in the tongue);
- atherosclerosis;
- carcinophobia.
Painful sensations manifest themselves differently in the same patient. They can occur for no apparent reason or worsen after eating spicy food, after a long conversation, as a result of mental or physical overwork.
Paresthesias are undulating in nature, over time they can intensify, become more frequent and exist for months or even years, after which they may further disappear on their own without any treatment.
Glossalgia in young women occurs without any pathology.
Macroglossia is a change in the language, which is characterized by its increase in size. Macroglossia can occur suddenly, as a result of damage to the mucosa, as well as with glossitis, Ludwig's angina, syphilis, angioedema angioedema. At the same time, the volume of the tongue increases so much that a tracheostomy is required to eliminate asphyxia.
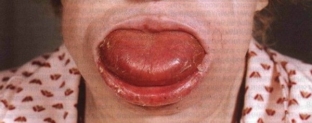
In tumor-like growths, changes in the tongue in the form of its increase are asymmetrical. If any change in the language is detected, it is urgent to consult a doctor, because this can be a signal of serious diseases that require urgent treatment.







Add a comment