Infectious urogenital diseases today constitute a significant part of not only medical problems, but also socio-economic ones. Infectious processes of the urogenital tract are complicated by damage to internal organs, the development of infertility, infection of the fetus and congenital malformations in children. The incidence of STIs continues to increase, which is associated with low public awareness, changes in sexual behavior standards, sexual freedom, early onset of sexual activity, extramarital and premarital relationships, and low sanitary and hygienic culture. One of the first places in the structure of STIs is occupied by urogenital trichomoniasis.
The main clinical manifestations of urogenital trichomoniasis
According to statistics, 334 million new cases of STIs are registered annually in the world, of which about 170 thousand are urogenital trichomoniasis. The causative agent of this disease is Trichomonas vaginalis. Methods for detecting Trichomonas, read further on estet-portal.com. The course of urogenital trichomoniasis has the following features: multifocal lesions, polymorphism, the possibility of asymptomatic carriage and frequent chronic course with relapses. The diagnosis is established on the basis of clinical complaints and identification of the pathogen in the test materials.
The main clinical symptoms and complaints in urogenital trichomoniasis:
- hyperemia of the vagina and vulva;
- yellow-green frothy discharge (seen in 12% of women);
- dyspareunia;
- itching;
- dysuria;
- the cervix and vagina, when viewed in the mirrors, looks like a "strawberry" - pinpoint hemorrhages occur in 2% of women.
Methods for diagnosing and detecting the pathogen in urogenital trichomoniasis
Asymptomatic urogenital trichomoniasis occurs in half of the cases, so the main reliable method of diagnosis is the isolation of the pathogen. For this purpose, clinical material is taken from the most suspicious foci in relation to possible infection - this is the cervix, vagina, urethra, cervical canal, prostate gland.
Microscopy of the native preparation is carried out in order to identify Trichomonas in it. The material is prepared by mixing a drop of the test material with a drop of warm isotonic sodium chloride solution or Ringer-Locke solution. After covering with a cover slip, look under a microscope with an objective magnification of 40 and an eyepiece of 7 or 10.
For research, take the secret of the prostate gland, ejaculate, urine centrifugate, separated from the cervical canal or urethra. When studying native material in the process of diagnosing urogenital trichomoniasis, special attention is paid to the shape, size, internal contents of cells and the nature of their movement.
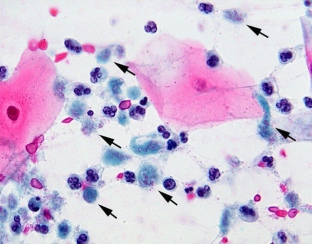
Trichomonas under microscopy looks like this: an oval or pear-shaped body 13-17 microns in size, which makes forward jerky movements. Sometimes you can see the movement of free flagella. The cytoplasm is granular, vacuolated. The nucleus is poorly differentiated or absent altogether.
The method of phase-contrast microscopy allows you to see Trichomonas in more detail and clearly.
How to diagnose urogenital trichomoniasis?
It is important to remember that in the absence of typical forms of trichomoniasis, the diagnosis of urogenital trichomoniasis is considered only an assumption.
During the last decades, atypical metabolic low-active individuals of the parasite, which are deprived of organelles of movement, have been increasingly identified. This greatly complicated the diagnosis of infection, since morphology and motility are the main criteria for identifying protozoa. With asymptomatic forms of urogenital trichomoniasis, as well as with an insufficient number of visual fields, the sensitivity of the microscopic method decreases.
It is worth noting the possibility of false positive results, which are caused by the adoption of epithelial cells for Trichomonas.
It is important to remember that the diagnosis of an STI entails not only medical problems, but also a violation of relationships and trust in the family, which can have various consequences, up to divorce and suicide.
Therefore, it is necessary to accurately verify the diagnosis and, at the slightest doubt, confirm urogenital trichomoniasis with more sensitive methods.






Add a comment