Together with the alienation of modern people from natural nutrition and regular fasting, the number of gastroenterological diseases has increased. Irrational nutrition, a large amount of fatty foods, overeating, eating chemical foods, eating late in the evening and eating once or twice a day leads to the fact that the organs of the digestive system begin to malfunction. One of the manifestations of such failures is cholangitis. How to detect cholangitis in time, read on estet-portal.com.
What types of cholangitis are there? Classification of cholangitis
Cholangitis can be acute or chronic. Acute cholangitis may be purulent, catarrhal, diphtheric, or necrotic. The formation of fibrinous films on the epithelium of the walls of the bile ducts indicates the severity of the process.
Cholangitis is quite common and may initially be chronic or may be the result of a transition from an acute to a chronic condition. There are many forms of chronic cholangitis, one of which is sclerosing. This form of cholangitis is characterized by the fact that the growth of connective tissue during the development of the process causes strictures of the bile ducts, which further deforms them.
Depending on the site of inflammation, there are:
- choledochitis (inflammation of the common bile duct),
- papillitis (process in the papilla of vater),
- angiocholitis (extrahepatic and intrahepatic ducts affected).
The main causes of acute cholangitis
The causes of inflammation of all these structures can be bacterial, parasitic and purulent.
A significant part of cholangitis develops due to the entry of bacterial flora into the bile ducts. This occurs in an ascending way from the duodenum, a hematogenous route through the portal vein and lymphogenous – with enteritis, cholecystitis and pancreatitis. Parasitic cholangitis is always accompanied by concomitant opisthorchiasis, lumbliosis, ascariasis or fascioliasis.
Aseptic cholangitis develops against the background of irritation of the walls of the bile ducts by activated pancreatic juice. In such cases, a bacterial infection joins a second time. Inflammation is of an autoimmune nature, which is observed with sclerosing cholangitis. Then the patient, along with cholangitis, is diagnosed with one of the following pathologies: & nbsp; Crohn's disease, vasculitis, thyroiditis, ulcerative colitis.
A predisposing factor to the development of cholangitis is cholestasis, which is present in biliary dyskinesia, anomalies in the development of the bile ducts, cancer of the biliary tract, choledochal cyst, stenosis of the Vater papilla. The onset of cholangitis can be triggered by iatrogenic medical endoscopic procedures.
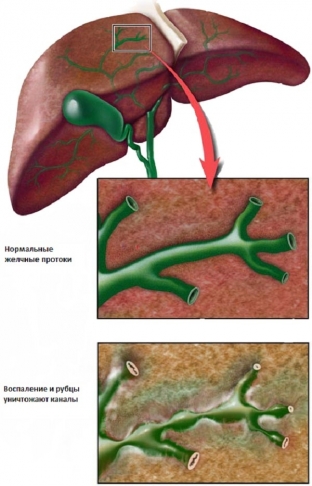
What clinical manifestations will indicate the development of acute cholangitis?
Clinical manifestations of acute cholangitis develop abruptly with manifestations of the Charcot triad - jaundice, pain in the projection of the right hypochondrium and high fever. The patient is shivering, there is severe sweating. Pain in the right hypochondrium is intense and resembles biliary colic. The pain radiates to the right shoulder blade, shoulder and neck.
Diarrhea may occur. Symptoms of intoxication increase rapidly and are characterized by weakness, loss of appetite, and headache. Jaundice appears last and is accompanied by itching of the skin, which intensifies at night. In patients with acute cholangitis, scratching is found on the skin. The severe course of the process with a weakened immune system is characterized by impaired consciousness and shock phenomena. Then the symptom complex is called the Reynolds pentad.
Clinical manifestations and complications of chronic cholangitis
Chronic cholangitis has an erased clinical symptomatology, but a progressive character. The patient periodically feels pain in the right hypochondrium and bursting in the epigastrium. Yellowing of the skin in the chronic course of the process indicates a long-standing process.
Cholangitis can be complicated by cholecystopancreatitis, hepatitis, liver abscess, biliary cirrhosis, liver failure, sepsis, infectious-toxic shock. Therefore, the symptoms of chronic cholangitis, which are often overlooked by patients, should not be overlooked. Treatment of chronic cholangitis will prevent the development of acute cholangitis and dangerous complications.







Add a comment