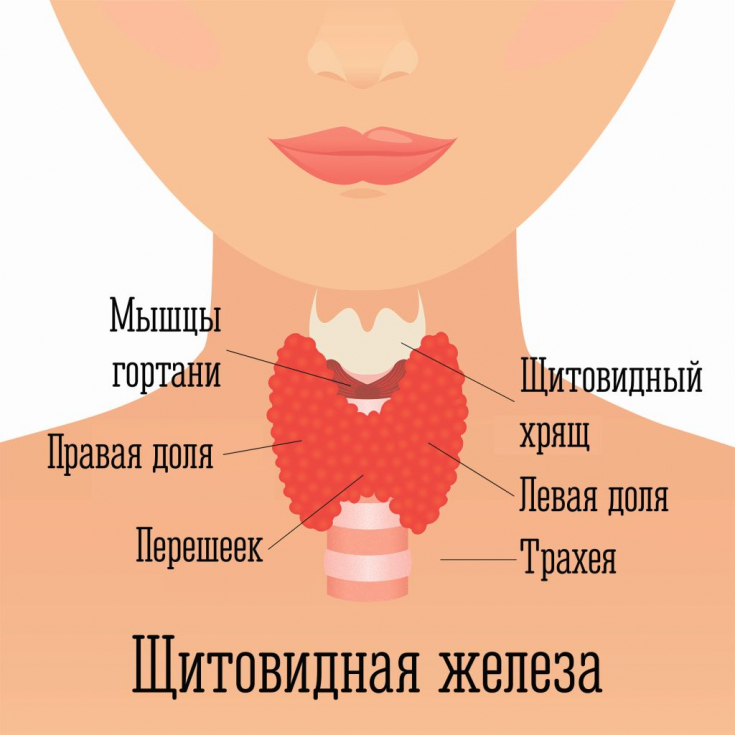
Relevance of the problem of differential diagnosis of neoplasms thyroid gland is a constant increase in the frequency of thyroid cancer and the number of surgical interventions, the lack of reliable criteria for malignancy in the early stages (lack of regional and distant metastasis, invasion of surrounding structures, ENT symptoms) and the difficulty of choosing an adequate method of surgical treatment of patients, which is possible only if the pathomorphological structure of the neoplasm is studied.
Therefore, it is so important to pay attention to the timely diagnosis of thyroid neoplasms in order to prevent possible complications. Find out in the article on estet-portal.com about modern approaches to the treatment and diagnosis of single-nodular forms of thyroid goiter.
Surgical methods of treatment of thyroid pathology
Surgical treatment of patients with Solitary thyroid nodules, with benign pathology, in general, consists in performing a hemithyroidectomy (or removal of the isthmus with medial resection of the lobes with appropriate localization of the node), in the diagnosis of thyroid cancer, thyroidectomy is recommended with central neck dissection (with the exception of hemithyroidectomy in case of a solitary tumor of differentiated thyroid cancer up to 1 cm without signs of invasion, in young patients without complicated hereditary and radiological anamnesis).
Follow us on Instagram!
In the surgical treatment of patients with a single-nodular thyroid goiter, there is always a risk of performing an intervention that is inadequate in scope, in particular, hemithyroidectomy, provided that thyroid cancer is diagnosed only at the final histopathological examination or thyroidectomy with a solitary benign nodule without concomitant thyroid pathology.
Attention to the face: signs of possible thyrotoxicosis in the patient
In the first category of patients, repeated surgical interventions are performed, and patients in the second category should unjustifiably receive substitution therapy.
Methods of differential diagnosis of thyroid diseases
Ultrasound diagnosis and fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) are the main methods of differential diagnosis of thyroid neoplasms, which determine the indications for surgical treatment and indicate the choice of method.
The main ultrasonographic criteria that indicate a high risk of malignancy of the node are: fuzzy (incorrect) contours, hypoechoicity, the presence of microcalcifications, increased intranodular blood flow.
When analyzing the results of a fine needle aspiration biopsy, one can rely with relatively high reliability on the conclusions of only two groups: a positive result (thyroid cancer is confirmed in 67-97%) and a negative result (benign pathology, the risk of a pseudo-negative result is 5%). Quite often (15-30%) when performing ATAB, non-informative results are obtained.
How does the skin react to a lack of thyroid hormones
The results of fine needle aspiration biopsy with an uncertain malignant potential (7-11%) remain debatable, such a node is commonly called follicular neoplasia (FN) and this condition is considered an indication for surgical treatment of patients. Routine histopathological examination diagnoses the presence of thyroid cancer in such patients in 15-25%.
Recently, it has been proposed to introduce additional categories of aspiration biopsy results, which are characterized by different rates of cancer diagnosis: suspicious for malignancy (risk of thyroid cancer 50-75%), indeterminate follicular mass (risk of cancer is 5-10%).
Hypothyroidism treatment: what you need to know about the features of the disease
Intraoperative diagnosis of thyroid neoplasms
The role of intraoperative morphological diagnostics in the scientific community is interpreted ambiguously, its overall diagnostic accuracy varies between 50-90% depending on the pathology. Intraoperative cytology (IOCI) is considered the most accurate compared to fine needle biopsy because it is a "targeted" smear rather than aspiration, but it is also impossible to differentiate follicular neoplasia.
The main criteria for the malignancy of FN is the invasion of the neoplasm capsule and tumor germination into the vessels of the thyroid gland, the diagnosis of which is possible only with the use of intraoperative histological examination (IOGI).
However, IOGI also has its drawbacks, the main of which are: possible tissue deformation during freezing, difficulties in diagnosing minimally invasive carcinomas, the inability to perform a large number of sections for a complete analysis, and time limitations.
The frequency of adequate surgical intervention for patients with single-nodular goiter, taking into account the results of only preoperative research methods, is 89.78%, and when using intraoperative morphological diagnostics − 97.99%.
Tormented by insomnia? It's time to see an endocrinologist

The use of intraoperative morphological studies justified increases the frequency of organ-preserving surgical interventions for thyroid neoplasms and reduces the risk of the need for repeated surgical access.
Why autoimmune thyroiditis develops







Add a comment