The treatment of urolithiasis today depends on many different factors: the characteristics, quantity and localization of the formed stones, the clinical picture of the disease, comorbidities, and so on. The most commonly used methods are conservative treatment of urolithiasis and shock wave lithotripsy, which involves non-invasive crushing of stones.
Nevertheless, quite often there are situations in which such methods are not enough, and it is simply impossible to do without surgery for urolithiasis. Estet-portal.com tells when and what types of operations are used for urolithiasis.
In what cases is surgery performed for urolithiasis
Surgical treatment of kidney and ureteral stones is widely used today, the reason for this is the often complicated course of the disease and the large size of stones, while non-surgical methods of treatment are not effective enough. The purpose of surgery is not only to remove the stone from the urinary tract, but also to create conditions for the resumption of urine outflow.
In most cases, organ-preserving surgeries are performed, such as stone removal and kidney resection. In some cases, it is impossible to do without nephrectomy – complete removal of the damaged kidney, which is performed only if the second kidney is functioning normally.
Urolithiasis surgery:
- indications for surgery for urolithiasis;
- types of surgical interventions for urolithiasis;
- ureterolithotomy – surgical removal of stones from the ureters.
Indications for surgery for urolithiasis
Any surgical intervention, including in case of urolithiasis, should be performed only if there are strict indications for it. Most often, surgical removal of kidney stones is performed in such cases:
- frequent bouts of renal colic or complaints of constant, excruciating pain;
- impaired urine outflow followed by hydronephrotic transformation of the kidneys;
- obstructive anuria;
- frequent acute pyelonephritis or progressive chronic pyelonephritis with a high risk of developing renal failure;
- total hematuria;
- calculous pyonephrosis, apostematous pyelonephritis, or renal carbuncle;
- kidney stone obstructing urine flow;
- Ureteric stone that cannot pass on its own.
Types of surgical interventions for urolithiasis
The choice of surgery for urolithiasis depends on the characteristics of the calculus in each individual case. Stones can be removed in several basic ways:
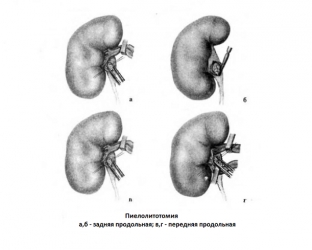
- pyelolithotomy – removal of stones through incisions in the wall of the renal pelvis, the choice of technique (subcortical, anterior, posterior, upper or lower pyelolithotomy) depends on the localization of the calculus;
- calicolithotomy – used to remove a stone from the calyx through an incision in its wall;
- nephrolithotomy – removal of a stone through the parenchyma of the kidney is performed when the stones are located deep in the pelvis, and it is impossible to remove them by means of pyelolithotomy;
- kidney resection – removal of part of the kidney is performed for large stones that cause hydrocalicosis with depletion of the renal parenchyma.
Follow us on Instagram!
Ureterolithotomy – surgical removal of stones from the ureters
Ureterolithotomy – This is an operation to cut the ureter and remove the calculus from its lumen. The choice of operative access to the ureter depends on the localization of the calculus. All approaches for ureterolithotomy are divided into three groups: retroperitoneal, transperitoneal and combined. Surgical intervention is carried out in stages: the retroperitoneal space is dissected and the ureter is exposed at the location of the stone, two sutures are placed above it, the wall of the ureter is cut between them and the stone is removed, the edges of the incision are sutured with the installation of a drainage tube and subsequent closure of the wound.







Add a comment