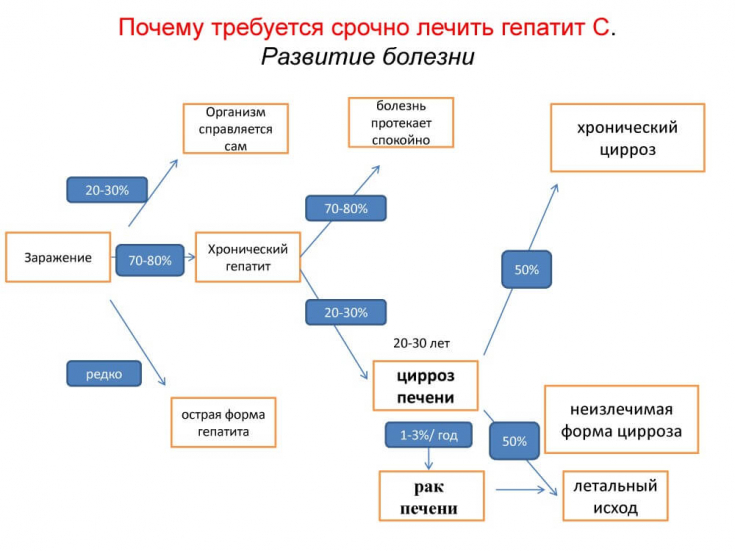
Chronic viral hepatitis C (CHC) − an infectious disease caused by the RNA-containing hepatitis C virus (HCV). According to the World Health Organization (WHO), today 71 million people in the world live with chronic viral hepatitis C. About 1,750,000 new infections caused by HCV are registered annually. After exposure to HCV, 55-85% of people develop a chronic form of viral hepatitis C.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com what is dangerous about viral hepatitis C and what are the approaches treatment of this disease allows you to completely exclude its further development.
- Dangerous consequences of hepatitis C infection
- Modern approaches to the treatment of chronic hepatitis C
- Main drugs and treatment regimens for viral hepatitis С
Dangerous consequences of hepatitis C infection
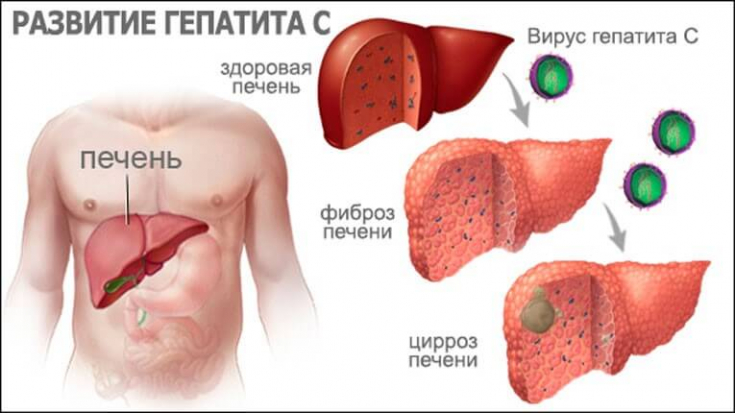
If left untreated, chronic inflammation of the liver leads to progression of fibrosis, development of liver cirrhosis (LC) and hepatocellular carcinoma.
A much worse prognosis is observed with a combination of hepatitis B and C, which is often observed in patients with a chronic course of the disease.
Follow us on Instagram!
Today, there are highly effective schemes for antiviral treatment of patients who suffer from chronic viral hepatitis C.
Because viral hepatitis C does not integrate into the human genome, modern antiviral therapeutic regimens allow achieving complete eradication of the virusa.
Modern approaches to the treatment of chronic hepatitis C
Treatment of patients with CHC has the following objectives:
- Sustained virological response (SVR) − absence of hepatitis C virus RNA as determined by polymerase chain reaction 12 weeks after completion of antiviral therapy.
- Prevention of complications of progression of liver cirrhosis, development of hepatocellular carcinoma and decompensated disease requiring liver transplantation.
The effectiveness of modern antiviral drugs used to treat patients with chronic viral hepatitis C exceeds 95%.
According to the recommendations of Infectious Diseases Society of America − IDSA and American Associations for the Study of Liver Diseases (American Associations for the Study of Liver Diseases &minus ; AASLD), all patients require antiviral treatment (except in cases where life expectancy cannot be extended by antiviral treatment, liver transplantation, or other etiotropic therapy).
In turn,WHO recommends treatment for all persons with viral hepatitis C at age > 12 years, except for pregnant.
Since all patients with hepatitis C cannot be immediately provided withantiviral drugs due to their high cost, priority in treatment, according to the preliminary recommendations of IDSA / AASLD, have patients with:
- severe liver fibrosis;
- compensated liver cirrhosis;
- severe extrahepatic complications;
- liver transplant recipients.
contactsm.
Acute bronchitis: the effectiveness of drug therapy from the standpoint of evidence-based medicine
Direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs)
direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) affect specific replication targets for viral hepatitis C, inhibiting this stage of the virus life cycle: NS
This results in a sustained virological response (SVR) in 90-95% of cases, in contrast to dual therapy with pegylated interferon/ribavirin which results in SVR in 50-70% of cases.
Rationale for prescribing probiotics for gastroenteritis
DAAsdepending on their mechanism of action and target of HCV replication: NS
- 3/4 - protease inhibitors:
- boceprevir, telaprevir, simeprevir, pratiprevir, grazoprevir, glecaprevir; NS 5
- B - polymerase inhibitors: nucleotide inhibitors (sofosbuvir), non-nucleoside inhibitors (dasabuvir); NS 5
- A - replication complex inhibitors: ledipasvir, daclatasvir, ombitasvir, elbasvir, velpatasvir, pibrentasvir.
 antiviral regimens
antiviral regimens
. At the same time, antiviral treatment regimens for patients with CHC are very expensive.
Recommendations for diagnosis and treatment are regularly updated, and therefore, specialists are advised to follow up-to-date information on management of management of hepatitis C on the official websites of
AASLD and ISDA. Myths about rosacea treatment







Add a comment