Among the many urological pathologies, one of the most dangerous conditions are diseases of the main organ of the urinary system - the kidneys. The kidney is an organ that purifies the human blood and thus regulates the body's chemical homeostasis. This is a paired organ, which is located behind the peritoneum in the lumbar region, where it is fixed with the help of its ligamentous apparatus. When exposed to certain factors, such as trauma or infection, the fixing apparatus of the kidney can be damaged, resulting in the development of nephroptosis - prolapse of the kidney. Such a pathological condition threatens the body with the development of serious complications, since favorable conditions are created for their occurrence.
How to diagnose nephroptosis in the early stages and avoid complications
In the early stages, nephroptosis tends to be almost asymptomatic, and the earliest manifestations of the pathology can be so minimal that patients often do not pay attention to them. At the same time, the pathological process continues to worsen, creating more and more suitable conditions for the development of complications. One of the earliest signs of nephroptosis is the occurrence of dull pain in the lumbar region. Pain syndrome occurs during physical exertion, but disappears at rest or when the patient is in a horizontal position. Therefore, patients often perceive pain as one of the manifestations of spinal pathology. Timely diagnosis of nephroptosis helps to avoid the development of complications and manage the treatment of pathology only by conservative methods.
Nephroptosis:
- basic instrumental methods for diagnosing nephroptosis;
- conservative treatment of nephroptosis: bandage and physical education;
- What complications can be caused by a prolapsed kidney.
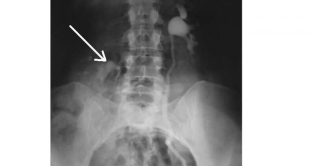
Basic instrumental methods for diagnosing nephroptosis
The most informative methods for diagnosing nephroptosis are instrumental studies, such as:
- excretory urography - performed in a horizontal and vertical position, allows you to determine the displacement of the kidney due to its relationship to the vertebrae. Normal mobility of the kidneys is the height of the body of a maximum of one and a half vertebrae;
- ultrasound examination - also allows you to determine the pronounced mobility of the kidney;
- radioisotope methods make it possible to determine the violation of kidney function due to the degree of decrease in secretion and slowing down the evacuation of urine;
- arteriography and venography of the kidneys make it possible to determine changes in the blood supply to the kidneys.
Conservative treatment of nephroptosis: bandage and physical education
Conservative treatment of nephroptosis is possible in the early stages of the disease, when the displacement of the kidney is insignificant. At the same time, conservative therapy is aimed not only at reducing the degree of nephroptosis, but also at preventing complications that may be caused by the pathological position of the kidneys. The most effective method of conservative treatment of nephroptosis is the wearing of a special elastic bandage in combination with a complex of physiotherapy exercises. Patients put on the bandage in the morning, before they get out of bed, that is, being in a horizontal position. Most physical exercises are also performed lying down, with legs raised up. The patient is prohibited from playing sports and any physical activity, except for swimming. In addition, it is important to adjust the diet of patients,
What complications can be caused by kidney prolapseIn the later stages of nephroptosis, when kidney function is significantly impaired, various complications of nephroptosis may occur, the most dangerous of which are:
- pyelonephritis is the most common complication of nephroptosis, it can occur in chronic, acute purulent and non-obstructive forms. An inflammatory process develops as a result of obstruction of venous outflow and impaired passage of urine;
- renal venous hypertension is provoked by physical exertion, occurs most often at the end of the day, manifests itself as macro- and microhematuria and disappears when the patient is in a horizontal position of the body;
- Arterial hypertension occurs as a result of narrowing of the renal artery in response to its tension and torsion.






Add a comment