Routine clinical urinalysis consists of chemical analysis (test strips) and cell counting (basic microscopy or advanced differential microscopy) performed either by urine sediment microscopy or using automated analyzers.
The sensitivity of the multi-reagent test is approximately 20 x leukocytes; 106 cells / l (2-3 cells per field of view), for erythrocytes - 10 x; 106 cells / l (1-2 cells per field of view).
If a urinary tract infection is suspected, a bacteriological culture with isolation of the culture is required. However, tuberculous bacilli, chlamydia and gonococci do not grow on conventional media. If a malignant neoplasm is suspected, a cytological examination of the urine sediment is necessary.
The urine sample sent for testing should be as fresh as possible. It is also important that it is in the bladder for at least 2-3 hours before donation. If the sample cannot be delivered to the laboratory within two hours, it should be centrifuged and the pellet fixed in 50% alcohol. Read about these and no less important nuances of urinalysis at the present stage of development of medicine in this article on the website estet-portal.com.
Clinical urinalysis for bacteriuria and pyuria
The diagnosis of chronic cystitis is established on the basis of the clinical picture. Urinalysis is used to establish the presence of pyuria and/or bacteriuria by counting leukocytes and nitrites.
The sensitivity of a urinalysis for detecting bacteriuria in a patient with dysuria is only about 50-60% compared to the sensitivity of bacterial culture even with a small increase in uropathogens (from 103 colony forming units [CFU] / ml).
Follow us on Telegram
Staphylococcus saprophyticus and some types of enterococci do not have nitrate reductase. The patient's type of diet, bladder irritation, short urine retention time in the bladder does not always favor nitrite production in infections caused by other bacteria.
The sensitivity of microscopy compared to bacterioscopic method is higher than that of the reagent test strip. In addition, the result is more accurate with automatic counting.
High vitamin C intake will give a false negative white blood cell count when tested with reagent strips.
Delays in sample transport as well as centrifugation will destroy leukocytes and erythrocytes, resulting in incorrect results. Diagnosis of urinary tract infection in young children includes checking for the presence of pyuria followed by bacteriological examination of urine, which is preferably obtained by puncture of the bladder.
A positive bacteriological result should be questioned if:
- the patient has no symptoms,
- sediment microscopy is normal,
- the results contain three or more types of bacteria (incorrectly collected sample, mixed flora),
- there is another etiology of pyuria, such as glomerulonephritis or interstitial cystitis.
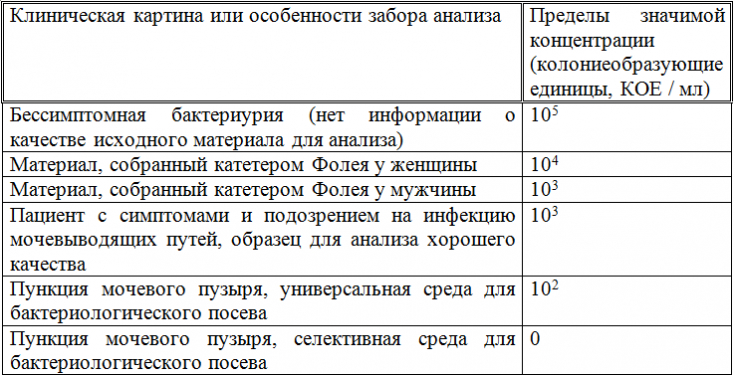
Table 1. Clinically significant ranges of uropathogen concentrations
Clinical urinalysis for hematuria and proteinuria
Hamaturia can be caused by:
- a systemic disease (for example, vasculitis),
- a pathology of the kidneys or urinary tract,
- an artifact (menstruation),
- excessive physical exertion.
Chemical testing with a reagent test strip is sufficient for screening. However, it should be remembered that heme from myoglobin in rhabdomyolysis is also detected using a test strip.
The principle of determining blood in the urine with a test strip is based on the ability of hemoglobin to catalyze the oxidation of the indicator by organic peroxide contained in the indication zone.
The upper reference limit for RBC counts in healthy individuals depends on urine output and on the urinalysis method, and is approximately 10-20 x; 106 / l.

Upper control limits for early morning urine for an adult (sedimentary microscopy, in Finnish standardization, 1 field of view = 0.12-0.17 µl depending on the diameter of the field of view of the eye in the microscope):
- women: 3-4 granulocytes, 1-2 epithelial cells, 1-2 erythrocytes per field of view;
- men: 1-2 granulocytes, 1-2 erythrocytes per field of view.
Screening using standard reagents detects albumin at a concentration of 0.2 g/l, i.e. 200 mg/l and above. More sensitive methods are required to detect microalbuminuria associated with diabetes or hypertension (at least 10 mg/l of albumin must be detected): measured in 24-hour urine or in one morning urine sample (albumin/creatinine ratio). Excretion of immunoglobulin light chains in myeloma is diagnosed by fractionation of serum and urine proteins (electrophoresis).
Clinical urinalysis for other chemical changes
The detection of elevated glucose concentrations in clinical urinalysis using test strips has become popular. Ketone bodies can be detected by Legal test strips.
The sensitivity of the indicator zone to acetoacetic acid is 0.5 mmol/l, for acetone – 10 mmol / l, to beta-hydroxybutyric acid is practically absent. Therefore, when monitoring diabetic ketosis in the hospital, it is recommended to measure plasma beta-hydroxybutyric acid with test strips. It should be taken into account that acetone appears in the urine after 12 hours of fasting.
Read our article in the Endocrinology section: The Hunger Games or how acetonemic syndrome occurs
Acetone test strip impregnated with sodium nitroprusside and alkaline buffer. At low pH, the indicator reacts with acetoacetic acid, the Legal reaction is carried out, a red complex is formed (color saturation is proportional to the concentration of ketone bodies).
Measurement of relative density (formerly specific gravity) provides information on the concentration capacity of the kidneys:
- diluted urine: relative density 1.000-1.005;
- isotonic urine: relative density;
- 1.010-1.015 concentrated urine: relative density of 1.020 or more.
The osmolality of plasma and isotonic urine is approximately 300 mOsm/kg H2O. Urinary osmolality can also be approximated based on plasma creatinine concentration or urinary conductivity.
The urine sample for bacteriological examination should be cultured as soon as possible because the time to preliminary results is only 18-24 hours (rich bacterial growth becomes noticeable in a shorter time, weak growth will grow within 48 hours).
Bacteria identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing will take an additional 24-72 hours. The bacterial culture sample will be kept in the refrigerator for 24 hours; or 48 hours if they are contained in tubes containing preservatives (for Pseudomonas aeruginosa only 24 hours).
Clinical urinalysis as an indicator of the functioning of the body
The diagnostic approach to the patient has been enriched by an extended clinical analysis of urine, which allows to detect deviations in the functioning of not only the urinary system, but also other organs. An attentive attitude to any manifestations of pathology in the patient's symptoms leads to the search for the cause of the disease, and a well-chosen arsenal of diagnostic measures allows you to confirm or refute the theory of the clinician.
It is important to prescribe the necessary examination method, comply with all requirements of the analysis methodology and, of course, interpret the results of the analysis in the range of the whole organism, and not just one organ system.
For more information about the methods of diagnosing the urinary system, read the article on our website estet-portal.com in the "Urology" section: Modern methods for diagnosing pyelonephritis: how to detect the disease
According to the Evidence-Based Medicine Guidelines







Add a comment