Gonorrheal lesions of the oral cavity are distinguished by specialists as a special group, since these manifestations of gonorrhea are very similar in their symptoms to tonsillitis, pharyngitis, stomatitis, gingivitis, laryngitis, and therefore patients often do not receive adequate treatment for a long time. Moreover, in women, the defeat of the tonsils & nbsp; may be the only manifestation of gonorrhea, and the disease will proceed almost without symptoms. It is very important in case of long-term unsuccessful treatment of sore throat in a patient to refer him to additional examinations – it is very possible that he has gonorrhea.
Manifestations of gonorrhea in oral lesions
Oral gonorrhea most commonly occurs after oral sex with an infected partner, but other forms of sexual contact may cause gonorrhea in the mouth and throat. Some researchers believe that transmission of gonococcal infection is possible even through kissing.
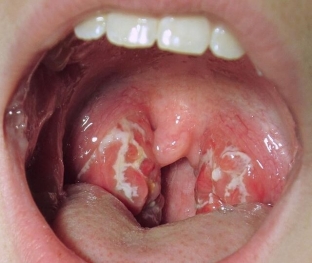
The causative agent of gonorrhea causes an inflammatory process on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and pharynx, which looks like a purulent plaque on the gums, tonsils, which occurs with sore throat.
The plaque can go beyond the tonsils and cover the palatine arches, tongue. Patients usually complain of pain when swallowing and general malaise, hoarseness, bad breath.
Sometimes the manifestation of gonorrhea resembles a sore throat – with chills, fever, purulent plaque on the tonsils, difficulty in swallowing. At the same time, the purulent plaque is very plentiful, fetid, and always affects both tonsils. According to experts, such symptoms may be due to a co-infection, when other bacteria that can cause inflammation (for example, streptococcus) join the causative agents of gonorrhea. In addition, in many patients with manifestations of gonorrhea in the oral cavity and pharynx, a meningococcal infection is also isolated in a laboratory study, which leads to the likelihood of severe complications if treatment is inadequate.
Character of the course of the disease and treatment of manifestations of gonorrhea
In 80% of cases of pharyngeal gonorrhea, the disease is almost asymptomatic or non-specific. A patient may come to the doctor's office with complaints of significantly hypertrophied tonsils and plaque on them, swollen lymph nodes and discomfort when swallowing.
Gonococci are absolutely resistant to anti-angina drugs, including antibiotics, and therefore after treatment – if the diagnosis was made incorrectly – the manifestations of gonorrhea will disappear, but the disease itself will not disappear anywhere, but will gradually become chronic. Moreover, there is a risk of developing resistance of gonococcus to antibiotics, which worsens the prognosis and requires the use of combinations of potent drugs.
Laboratory examination for pharyngeal gonorrhea is subject to all patients with suspected gonococcal infection, as well as those who are observed by a doctor for chronic tonsillitis or pharyngitis.
It is very important to take a thorough history and identify probable oral contact with sexual partners if pharyngeal gonorrhea is suspected. This will help to make a correct diagnosis and start adequate therapy.
Therapy for the manifestations of gonorrhea in the oral cavity and larynx is carried out in a complex manner, based on antibacterial drugs of the penicillin and cephalosporin series, selected taking into account the individual response of the patient. A combination of antibiotics (for example, ceftriaxone and doxycycline) is possible. Additionally, immunomodulators, local antiseptics (chlorhexidine) can be recommended. If necessary, antiallergic drugs are used, drugs are prescribed to strengthen blood vessels.







Add a comment