Soft sliding in the joint of bones, ligaments and tendons is provided by the synovial fluid, which is located in the articular bag. Stress on the joints over time leads to inflammation of the joint capsule (bursa), and excessive accumulation of fluid or pus. This leads to swelling of the periarticular bag and, accordingly, the entire knee. The answer to the question: why do my knees hurt and swell? – could be bursitis. In this article, we will study how to treat bursitis, the main causes and symptoms of this disease.
Causes and symptoms of bursitis
In rare cases, bursitis occurs without a known reason. More often, the cause of development is a knee blow, injury, stretching of the ligaments – any injury can lead to inflammation of the periarticular bag. The usual fall, hitting the corner of a cabinet or sofa, damage to the soft tissues of the knee or skin provokes swelling of the knee, pain begins, fluid accumulates in the bag, which, through infectious influence, turns into pus. It can also be caused by being overweight, which puts undue stress on the joints.
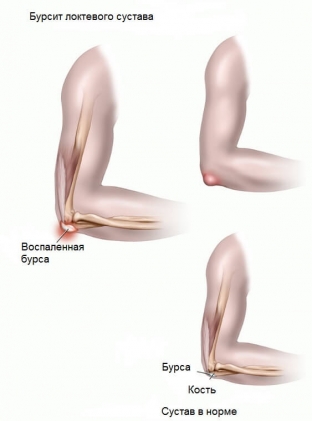 Another important reason for the development of bursitis is the constant stress on the joint if it is in one position for a long time. For example, a student may develop elbow bursitis due to constant elbow pressure on a table. In this case, the disease was dubbed "student's elbow". Another type of this disease – "maid's knee" is the name given to knee bursitis. This species develops due to excessive strain on the knees during cleaning.
Another important reason for the development of bursitis is the constant stress on the joint if it is in one position for a long time. For example, a student may develop elbow bursitis due to constant elbow pressure on a table. In this case, the disease was dubbed "student's elbow". Another type of this disease – "maid's knee" is the name given to knee bursitis. This species develops due to excessive strain on the knees during cleaning.
During the development of arthritis or gout, when joints throughout the body are affected, this can lead to the accumulation of exudate in the knee or any other joint that takes up most of the load.
In addition, in addition to the listed reasons, there may be internal factors that provoke the development of bursitis. Infection in the bursa leads to the accumulation of pus, which is very difficult to remove without surgical intervention.
The calcareous form of bursitis is an inflammation of the periarticular sac due to a metabolic disorder. In this case, in addition to the inflammatory process, the accumulation of calcium salts begins in the joint – this leads to limited mobility of the limbs.
Read also: The enemy is inside you – signs of a chronic inflammatory process in the body
Symptoms of bursitis:
- swelling of the joint in the area of the periarticular bag;
- pain on palpation;
- restricted mobility;
- skin redness;
- temperature increase in the area of the bag or in the entire knee;
- for the acute form – fever (infectious form).
How to treat bursitis: a release methodology
What the patient can do:
- limit joint movement;
- try to keep the joint elevated;
- make warm and cool compresses to reduce pain and (The easiest compress is a potato compress. To do this, you will need to take a few raw potatoes, peel them, cut them into thin slices and apply to the sore elbow. Secure the compress with gauze and a bandage and leave overnight.);
- Take a pain reliever;
- only after the pain is relieved, the joint can be kneaded by light movements;
- See a doctor if possible for a diagnosis.
What the doctor should do:
- examination and history taking (health, general well-being, recent injuries to the knee or other joint);
- x-ray of the joint;
- tire to restrict movement;
- prescribing additional medications (strong analgesics, antibiotics);
- appointment of physiotherapeutic procedures or exercise therapy;
- puncture.
The choice of methods for treating bursitis depends on the correctness of the diagnosis. According to the causes and symptoms of the development of the disease, you can choose the appropriate treatment. If bursitis occurs at the initial stage: there is a slight swelling and some discomfort when moving – treatment may be limited to physiotherapy, as well as anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs. These remedies are aimed at relieving pain and swelling. If the cause of development is an infection, then no lotions and painkillers can help in this case. Only surgical intervention can contribute to a complete recovery. Carrying out a puncture and taking antibiotics can neutralize this disease. Puncture is the removal of excess synovial fluid or pus from the joint capsule. After extracting the exudate, a composition of antibiotics or an anti-inflammatory drug is injected into the bursa. Such an injection will help locally prevent further infection of the tissues and help the joint return to working capacity more quickly.






Add a comment