A herniated disc is also called an intervertebral or intervertebral hernia, it occurs for various reasons and manifests itself in the protrusion of certain parts of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal. Intervertebral discs – connective structures located between the vertebrae. In the center of the intervertebral disc is an elastic nucleus, which is surrounded by strong rings. This structure provides both strength and flexibility of the intervertebral disc. In case of injuries or certain diseases, a herniated disc may occur.
Intervertebral hernia – why and where they occur most often
The most common is a herniated disc in the lumbosacral spine, detailed information about which you can find here. The second most common is a herniated disc in the cervical region, and the least common cases of protrusion of the disc in the thoracic spine.
Intervertebral hernia is most often obtained by people in their prime – aged 35 to 50 years. In children and the elderly, cases of such a violation are quite rare, although they are not completely excluded.
What causes the intervertebral disc to protrude into the spinal canal?
A herniated disc is the result of abnormally increased pressure within the very disc that connects the vertebrae. And there can be several reasons for the increase in pressure:
- Injuries – falls, strong blows to the vulnerable area.
- Incorrect lifting of weights.
- Overweight.
- Sudden movements to the side.
- Posture disorders (lordosis, kyphosis, scoliosis).
- Osteochondrosis.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Some infections.
Symptoms of intervertebral hernia depending on the degree of the disease
A herniated disc causes symptoms that can be divided into three groups:
- painful;
- vertebrates;
- root.
- At any stage of the intervertebral hernia, the patient is accompanied by pain. The intensity of pain depends on the stage of the disease. With a small hernia, the pain in the affected spine is dull and intermittent. With a long stay in a sitting or standing position, as well as physical exertion, during coughing and sneezing, there is an increase in pain. The further the disease progresses, the more frequent and acute the pains become, they can even radiate to the legs and head, depending on the location of the hernia. Leg numbness – also a common occurrence with a herniated disc in the lower back.
- Spinal symptoms include limitation of movement, inability to straighten up due to pain. It is difficult for a person to maintain stability, there is a violation of posture, an unnatural inclination of the torso.
- If the roots of the spinal cord are compressed as a result of a hernia, a number of symptoms are possible, for example: weakening of the muscles of the foot and femoral part of the leg – it is almost impossible to stand on tiptoes and jump; numbness of the skin of the fingers; possible paralysis, etc.
Because a herniated disc, left unattended by a specialist, can lead to disability, it is very important to consult a specialist if chronic pain occurs in any part of the spine. Remember, the smaller the hernia, the easier it is to get rid of.
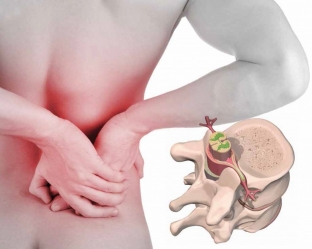
Herniated disc: treatment with available methods
First of all, patients with osteochondrosis should be regularly checked by a doctor for the presence of an intervertebral hernia. Also, in ninety cases of chronic or prolonged pain in the back, the cause of the problem is precisely a herniated disc. Patients often make the mistake of self-medicating and aggravating their condition to such an extent that surgery is indispensable.
If the location and stage of the intervertebral hernia is favorable for treatment (i.e., with timely treatment), it is possible to get rid of the problem without surgery, namely with:
- Special massages.
- Therapeutic exercise.
- Wearing a corset.
- Be careful when driving.
- Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Novocaine blockades.
If during the diagnosis the doctor states the risk of serious complications, he informs the patient about the need for an operation (urgent or delayed). Surgery is also necessary if other treatments have failed.
Remember that surgery to remove a hernia and then stabilize the spine is very dangerous – the possibility of dangerous damage to the spinal cord or nerves cannot be ruled out. Therefore, doctors urge to treat possible symptoms of intervertebral hernia as soon as possible after their occurrence – this will help to avoid unnecessary financial costs and risk to life.






Add a comment