One of the most dangerous diseases for humans is meningitis, as it is accompanied by complications and death. The problem with the initial detection of infection with the bacteria that causes meningitis is the masking of the main symptoms of inflammation of the brain under other diseases. If there is a cough, headaches, a sharp increase in temperature, then it can be not only the flu or bronchitis, but also meningitis. In order to recognize the disease in time, it is necessary to clearly know what signs of meningitis in adults and children are observed in the first minutes.
Meningitis is a disease of the brain, it is an inflammatory process in the cortex of the brain and spinal cord. This disease can be primary, that is, the first symptoms of meningitis immediately develop in the body after infection, or secondary – as a consequence of an infectious disease.
How meningitis develops in an adult body
The disease develops rapidly, viruses and fungi infect the soft tissues of the brain, as well as cerebrospinal fluid, and even the first symptoms can lead to coma and irreversible consequences in the human body. An adult usually suffers from bacterial meningitis. The causative agents of this form of the disease are pneumococcus or spirochetes, as well as tubercle bacillus or Haemophilus influenzae. It is possible to become infected with these bacteria by airborne droplets, through dirty vegetables and fruits, unwashed hands, personal hygiene products (in kindergartens, schools, workplaces).
From the first days of infection, inflammation begins in the mucous membrane of the nose and throat – these are the first signs of meningitis in adults. Basically, meningitis is acute, with a rise in temperature to 40-41 degrees, severe headaches, dizziness, vomiting. If the first signs of this disease are observed, the patient should be immediately hospitalized and treated.
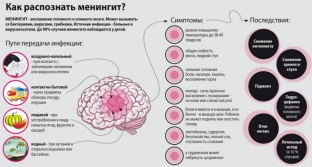
Consequences and possible complications of meningitis in adults
Meningitis in any manifestation is dangerous for its complications even with timely hospitalization. The degree of consequences is indicated by the level of damage to other organs. There may be visual impairment and loss or loss of hearing, decreased brain activity, partial paralysis, epilepsy, hydrocephalus, and hormonal dysfunction is also possible.
Main signs of meningitis in adults
- General signs of infection
- increase in body temperature;
- joint and muscle pain;
- skin pallor;
- rapid pulse, shortness of breath;
- low blood pressure;
- decreased appetite;
- refusal to eat, but due to thirst, the patient drinks a lot.
- Specific signs of meningitis
- dizziness, fear of sound and light, vomiting – appear 2.3 days after the onset of the disease. The gag reflex is triggered during an excessive headache, the patient does not experience the desired relief. Since meningitis is associated with inflammation of the brain, there is an increased sensitivity – visual, auditory, tactile. It will seem to the patient that the slightest sound, like an electric shock, will deliver unbearable pain.
- headaches begin almost immediately and appear against the background of increased intracranial pressure due to the effect on the roots of the brain. The patient cannot clearly say in which part it hurts more, most likely there is no localization of pain, heaviness and breaking are felt in the whole head.
- Rigidity of the muscles at the back of the head appears from the first moment of the development of the disease and is permanent, meaning difficult or often impossible bending of the head.
The following symptoms and signs of meningitis in adults may also appear:
- Bekhterev's symptom is a contraction of muscles (facial) when tapping on the cheekbones.
- Pulatov's symptom is pain when tapped on the skull.
- Mendel's symptom – this is pain when pressing on the external auditory canal.
- Kernig's symptom characterizes the state when the legs, bent at the knees and hip joints, cannot straighten.
- Brudzinsky's symptom – a condition is characterized when a person involuntarily bends his legs when his head is tilted to his chest.






Add a comment