Speech is given to a person for a clear formulation of his thoughts, requirements and desires. With the help of speech, a person communicates and understands others. Unfortunately, there are pathologies that relate to speech. This is a stutter that often starts at an early age. There are many children today who stutter when speaking. The solution to the problem is possible in most cases by eliminating the cause. What is the cause of stuttering in children?
What types of stuttering can be found in children?
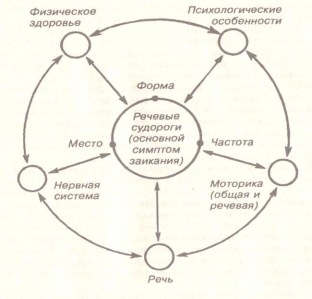
Stuttering in children develops according to two pathogenetic mechanisms - neurotic (logoneurosis), which is a functional disorder, and neurosis-like, which is associated with an organic lesion of the nervous system.
Depending on the nature of the clinical course of the process, the following variants of stuttering in children are distinguished:
- Waving – stuttering can both weaken and intensify in different situations, but does not go away and does not disappear.
- Recurrent – after a period of relative well-being, stuttering returns again.
- Permanent – stable course of stuttering.
There are 3 degrees of severity of speech convulsions: mild, moderate and severe. With a mild degree, a person stumbles only during spontaneous speech, it is almost not noticeable to others. The average degree is manifested in dialogic or monologue speech. In severe stuttering in children, speech spasms are long and frequent, accompanied by embolophrasia and accompanying movements. In some cases, communication becomes impossible through speech.
What are the main causes of stuttering in children?
Among the causes of stuttering in children, it is worth highlighting a group of predisposing factors that, in combination, provoke the development of stuttering in one child. These factors include hereditary predisposition, damage to the central nervous system in utero and the neuropathic constitution of the child. Hereditary predisposition refers to the congenital weakness of the speech apparatus.
Such children often have enuresis, increased vulnerability, anxiety, night terrors along with stuttering. Stuttering in children can appear against the background of perinatal brain damage during toxicosis during pregnancy, intrauterine hypoxia, birth asphyxia or birth trauma.
In recent years, stuttering in children has become a very urgent problem, as the number of stuttering children is increasing every year. Medicine explains this fact by the introduction of computer technologies and video games into everyday life, which bring a large stream of audiovisual information. affecting the weak nervous system in children.
It is important to understand that the completion of the process of formation of the cerebral cortex falls on the age of 5 years. Any excessive nervous tension before this age is fraught with the development of stuttering in a child. It can be a strong fright, prolonged nervous tension or conflicts with others, fear, a strong negative impression and everything related to negative emotions.
Infections of the nervous system can contribute to the development of stuttering in children. Also, stuttering can occur when a child is overloaded with complex material, learning several foreign languages from an early age, or when retraining a left-hander to a right-hander.
Peculiarities of neurotic and neurosis-like stuttering in children
Neurotic stuttering appears after an acute psychological situation and develops abruptly. Parents can accurately indicate the time of occurrence of stuttering in children. This often occurs between the ages of 2 and 6. When talking, these children experience respiratory and vocal convulsions. Children accompany their speech with flaring of the wings of the nose and accompanying movements.
Neurosis-like stuttering after an organic lesion and speech disorder develops slowly. Speech stutters are provoked by articulation spasms. At the same time, speech is monotonous, inexpressive, its pace is accelerated. The deterioration of speech in a stable course of neurosis-like stuttering in children is caused by overwork or increased speech load. The EEG shows increased convulsive readiness.
Methods of treating stuttering in children. Is recovery possible?
Stuttering in children is treated with an integrated approach. Medical and recreational procedures (massage, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, hydrotherapy), psychotherapy are carried out. Trainings are conducted to master different forms of speech for children. Much attention is paid to the development of phonetics, grammar and vocabulary, logorhythmic classes, speech therapy massages, respiratory and articulatory gymnastics. Stuttering correction is carried out according to the author's methods.
If you properly organize medical and recreational work for stuttering children, then stuttering disappears completely, although relapses are possible. In order to prevent the development of stuttering in children, it is important to strive for a favorable course of pregnancy, take care of the emotional and speech development of the child, and with the initial manifestations of stuttering, contact a speech therapist.






Add a comment