Benign proliferation of breast tissues – mastopathy – often detected by a mammologist or gynecologist during a routine examination of patients aged 18 to 50 years (most often at 25 & ndash; 45 years). The main sign of breast mastopathy is the presence of seals, which, depending on the form of mastopathy, can be evenly distributed or localized. Every woman should be aware of the main symptoms of this pathology, since with mastopathy, the degeneration of benign formations into cancerous tumors is not excluded.
Factors influencing the development of mastopathy
There are a number of factors that can contribute to the development of mastopathy – from stress to hormonal imbalances. On the site http://mastomed.ru/ you can learn more about the causes, symptoms, types and methods of treatment of mastopathy of the mammary glands. As for the factors that increase the risk of developing this disease, they are:
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of the liver, gallbladder;
- endocrine diseases;
- obesity and diabetes;
- abortions;
- late pregnancies;
- inability to breastfeed;
- stress;
- injuries;
- bad habits;
- irregular sex life, etc.
Due to the risk of malignancy of benign tumors, it is highly not recommended to delay going to the doctor if there are signs of breast mastopathy.
Due to the danger of malignancy of benign tumors, it is highly not recommended to delay going to the doctor, therefore every woman:
- should have regular breast self-examinations;
- to know the main symptoms and signs of mastopathy.
How is regular breast self-examination carried out?
Of course, regular breast self-exams are not a substitute for a thorough examination by a qualified professional. However, during such checks, you will be able to determine in time the presence of lumps in the breast tissue, which will need to be urgently shown to the doctor in order to make a diagnosis and prescribe a treatment plan.
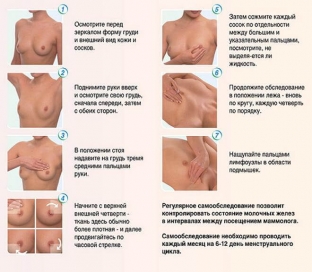
Self-examination is performed after the end of menstruation as follows:
- stand in front of a mirror and put your hands down;
- visually evaluate the size, contour, condition of the skin and nipples, as well as the symmetry of the mammary glands;
- check the symmetry of the chest by tilting and turning the torso with arms raised and spread apart;
- put your hands on your belt and move your shoulders and elbows forward, then check the above parameters again;
- alternately palpate both mammary glands with opposite hands, pressing with fingertips, describing a circle in a clockwise direction;
- palpate the axillary and supraclavicular regions;
- squeeze your nipples with your thumbs and forefingers to check for any discharge;
- feel the chest while lying down.
Regular breast self-exams are not a substitute for a thorough examination by a qualified specialist, but they can help you identify warning signs of the disease and seek professional help in a timely manner.
What signs of mastopathy of the mammary glands should alert you?
Signs of mastopathy of the mammary glands may vary depending on the type of disease, but there are three main symptoms of this pathology:
- swelling and pain in the chest area (especially before menstruation);
- the presence of seals in the mammary glands;
- discharge from nipples.
It is also necessary to contact a mammologist if you have:
- expressed breast asymmetry;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- presence of pain in the area of the shoulders, shoulder blades and armpits;
- changes in the shape, size of the breast;
- changes in the condition of the skin (stretched or wrinkled areas of the skin);
- changes in the shape and color of the nipples;
- discharge when squeezing the nipples;
- breast tenderness.
It is worth noting that in some cases, mastopathy of the mammary glands is characterized by an asymptomatic course, therefore, in many patients, this disease is detected during routine examinations. Remember that timely access to a doctor increases the chances of successful treatment and reduces the risk of dangerous complications of mastopathy.






Add a comment