TB infection is one of the major medical problems of the 21st century. Modern medicine is actively developing, and with each & nbsp; year, more and more advanced methods of diagnosing and treating various diseases are invented. To date, research continues in the field of phthisiology. However, the TB epidemic has yet to be completely eradicated. The use of the BCG vaccine has significantly reduced the number of TB patients, but new cases continue to be diagnosed. Timely diagnosis of tuberculosis allows not only to identify and eliminate the pathological process in a particular patient, but also to prevent the spread of infection.
What methods of TB diagnostics are used today
Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis is a rather long and complicated process, since this disease in some cases can be asymptomatic. At the same time, the clinical picture of pulmonary tuberculosis resembles some other pathologies of the broncho-pulmonary system, so it is especially important to conduct a differential diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. To date, to confirm the diagnosis of tuberculosis infection, a comprehensive diagnostic approach is used: laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are used, complaints and anamnestic data are carefully analyzed. each patient.
Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis:
- what groups are the methods of diagnosing tuberculosis;
- microbiological diagnosis of tuberculosis: Ziehl-Nelsen microscopy;
- radiological picture in pulmonary tuberculosis: what can be seen in the picture.
What groups are the methods of diagnosing tuberculosis
Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis necessarily includes several successive stages. In this case, all diagnostic methods used are divided into three large groups:
- a mandatory diagnostic minimum, which includes an analysis of complaints and anamnestic data of the patient, clinical blood and urine tests, sputum microscopy according to Ziehl-Nelsen at least three times, as well as chest x-ray and Mantoux test;
- additional non-invasive and invasive research methods include microbiological diagnostics by PCR and sputum culture with the determination of the resistance of Koch's sticks to drugs, computed tomography of the lungs and ultrasound, enzyme immunoassay, bronchoscopy with biopsy, puncture of the pleural cavity, thoracoscopy and open biopsy lung;
- optional methods are aimed at studying the functional state of internal organs and metabolic processes, and include determining the level of blood glucose, examining the function of the liver and external respiration, determining the gas composition of blood and pulmonary blood flow, and so on.
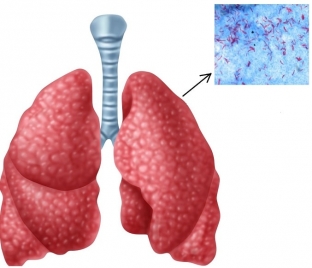
Microbiological diagnosis of tuberculosis: Ziehl-Nelsen microscopy
To detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the sputum of patients, the following microbiological diagnostic methods are performed:
- sputum microscopy according to the Ziehl-Nelsen method;
- fluorescence microscopy of pathological material;
- polymerase chain reaction;
- cultural method.
Microscopy of sputum preparations using the Ziehl-Nelsen method is currently the main method for diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis. Based on the results of this study, it can be concluded whether acid-fast mycobacteria are present in the study preparation. Smears of pathological material are treated with carbolic fuchsin, after which they are discolored with a solution of sulfuric acid or hydrochloric alcohol, and re-stained with a solution of methylene blue. Further, the preparations are analyzed using a light microscope with an immersion system: mycobacteria are stained red, and the surrounding background – to blue.
X-ray picture in pulmonary tuberculosis: what can be seen in the picture
X-ray examination of the chest is also a fairly simple and affordable method for diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis. Radiography is carried out in direct and lateral projections, which is necessary for reliable clarification of the localization of the pathological process. The X-ray picture of pulmonary tuberculosis is distinguished by polymorphism both in the nature of infiltrative changes and in the localization of pathological foci. Manifestations of specific tuberculous inflammation can be varied: from single and multiple confluent foci to lobar tuberculous pneumonia. Most often, the favorite place for the localization of the tuberculous process is the apical, posterior and upper segments of the lungs. At the same time, for all variants of pulmonary tuberculosis, not only focal and infiltrative shadows are characteristic, but often the presence of cavities, which,






Add a comment