Stones (stones) in the gallbladder have become faithful companions of the life of a modern person. Refined food, sedentary lifestyle, bad habits — The factors that provoke the disease can be listed endlessly. A to "feminine" the happiest event — pregnancy, which is often the first step on the road to gallstone disease and symptoms that make you endlessly swallow painkillers or even lie down on the operating table.
But such an outcome is most often the responsibility of the patient himself. Early contact with a doctor in most cases eliminates the need for surgical intervention. And & nbsp; for this you should "meet" with illness closer.
- Symptoms of gallstone disease: what what to look for
- Cholelithiasis treatment: what modern medicine offers
- Prevention of cholelithiasis: how to prevent disease
Symptoms of cholelithiasis: what what to look for
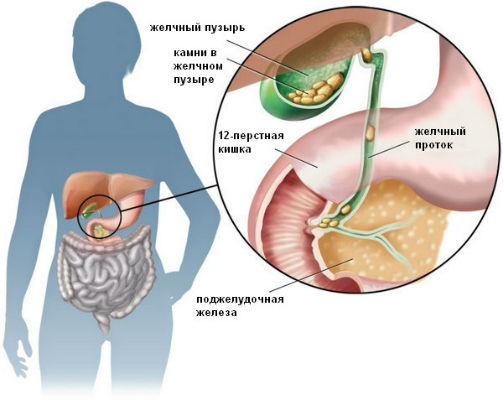
It is generally accepted that the indisputable evidence that stones have appeared in the gallbladder is pain. But in most pain — a sign that the stones have moved out of place and moved into the bile ducts. It is the stretching of their walls that causes spasms and hepatic colic — sharp, paroxysmal pain that causes twice and not breathe, so as not to provoke another attack.
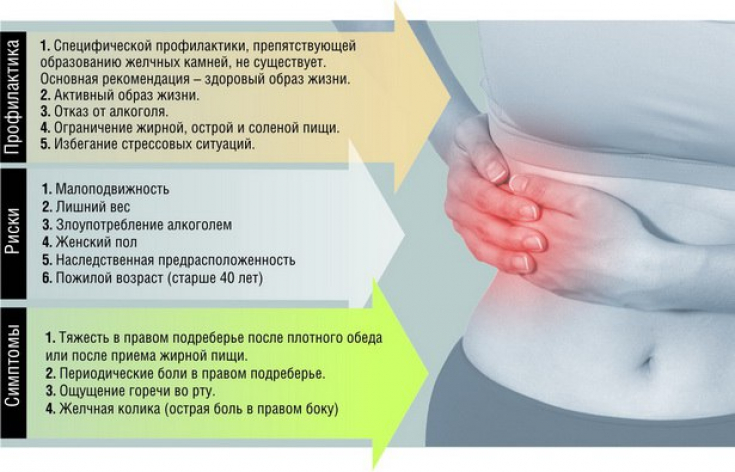
But at in the early stages of development of cholelithiasis (GSD) one can guess, and without pain, that something is wrong with the liver and gall bladder:
-
a feeling of heaviness in the upper abdomen and right hypochondrium;
-
heartburn;
-
early satiety;
-
belching with unpleasant bitter taste;
-
frequent episodes of bloating and flatulence;
-
unstable stools, in which constipation alternates with diarrhea;
Read also: Bloating: a temporary discomfort or symptom of illness
The listed symptoms are aggravated after eating, and after eating foods or dishes with a high fat content, there may be pulling pains in the right hypochondrium. a regularly — it's time to see a doctor.
First of all, an examination is carried out, which includes a biochemical blood test, ultrasound and / or x-ray of the gallbladder and GFDS (gastrofibroduodenoscopy). These diagnostic tools allow you to evaluate the functions of the liver, gallbladder and duodenum, determine the presence, localization and chemical composition of gallstones and, on the basis of this, form a treatment plan.
 Depending on the characteristics of the clinical case, the following directions may be used:
Depending on the characteristics of the clinical case, the following directions may be used:
- Conservative. The patient is prescribed preparations of chenodeoxycholic or other acids, which contribute to the dissolution of calculi, as well as antispasmodics that improve the patency of the bile ducts. Diet food is mandatory (table No. 5). If the size of the stones and the contractility of the gallbladder allows it — shock wave therapy is used: a hardware method of treatment in which stones are crushed by ultrasound to the state when they are painlessly removed in a natural way.
- Surgical. If conservative methods were ineffective or were initially inappropriate, surgical intervention is used. During the operation, the gallbladder is removed along with the stones contained in it.
Read also: Pain in side: causes and ways to eliminate an alarming symptom
Prevention of gallstone disease: how to prevent diseaseThere are there not many methods by which you can prevent the formation of stones in the gallbladder. But each them is effective on its own, and applied in combination with others, it allows you to reliably protect your health from JSD and from a number of other problems:
- Watch body weight. Exceeding BMI even by 2-3% increases the likelihood of stone formation by 10%.
- Check your cholesterol levels. Excess cholesterol — the cause of the development of cholelithiasis in more than 60% of all cases. Particular attention should be paid to this aspect by those who have a hereditary predisposition to disorders of lipid metabolism, and there are also family cases of cholelithiasis and atherosclerosis (this disease also provokes excess cholesterol).

- Create and maintain the correct regimen and food composition. Eliminate or minimize sausages, muffins, fast food, fatty meats in your diet.
- Maintain a sufficient level of physical activity, in good weather try to walk at least 3-5km per day, but if this is not possible — even a 5-minute daily gymnastics will reduce the likelihood of bile stasis and development of cholelithiasis.
Read also: Diet for liver disease: what you can and what you can’t eat
You might be interested: Perfect belly in 5 minutes!






Add a comment