The formation of the spine is a very important process on which the health of the entire musculoskeletal system depends – motor apparatus. The presence of pathological changes in the spine and paravertebral tissues leads to the development of scoliosis. Scoliosis is one of the most common pathologies of the musculoskeletal system in children. In the presence of scoliosis, the spinal column is bent, it rotates around the longitudinal axis, which is manifested by changes in the internal organs and static-dynamic disturbances. Why does scoliosis develop? How to detect scoliosis in children?
Classification of scoliosis in children. Stages of development of scoliosis
Approximately 10% of adolescents today have scoliosis, with girls being much more likely to have it.
The danger of scoliosis in children is not only in a cosmetic defect, but also in the displacement of internal organs and disruption of their functions.
There are 3 types of curvature of the spine: S – figurative, having 2 arcs of curvature, Z – figurative, which has 3 arcs of curvature, as well as C – figurative, having only one curvature along the spine. Scoliosis is classified by the degree of curvature of the spine, which is measured in degrees.
Classification of scoliosis in children:
- Scoliosis 1st degree – lateral curvature is less than 100. There are minor signs of torsion on the radiograph.
- Scoliosis 2 degrees - the angle of curvature is from 100 to 250. There is a deformation of the vertebral bodies at the top of the curvature and pronounced torsion.
- Scoliosis grade 3 – observed at an angle of curvature from 250 to 500, torsion is pronounced, changes in the spine are fixed.
- Scoliosis of the 4th degree is characterized by a curvature angle of more than 500. At the same time, the deformation of the spinal column is pronounced, the chest is displaced, the internal organs are compressed, which significantly impairs their functions.
Causes and symptoms of scoliosis in children. Detection of scoliosis in a child
Congenital scoliosis in children can be triggered by anomalies in the development of the spine. These are synostosis of the spinous processes, hemivertebrae, wedge-shaped vertebrae, impaired rib formation and vertebral dysplasia – sacral region.
Acquired scoliosis in children occurs on the basis of diseases, injuries, nervous – muscle and metabolic disorders. With congenital dislocation of the hip or after a birth injury, static scoliosis is observed.
Idiopathic scoliosis is detected at the age of 6-7 years. At this age, there is the first jump in the growth of the child. How and when scoliosis is detected in children, estet-portal.com knows.
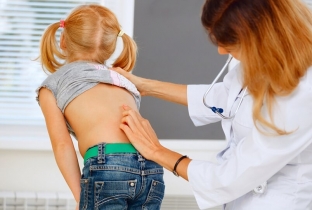
Scoliosis in children is detected during a preventive examination by an orthopedist or pediatrician:
- Scoliosis of the 1st degree is manifested by lowering of the head, flattened shoulders, oblique pelvis, asymmetry of the waist and forearms, stoop.
- Scoliosis of the 2nd degree is manifested by pathological rotation of the vertebrae along with the above symptoms. In the lumbar region, a muscle roller is palpable. The curvature of the spine remains even when the position of the body changes.
- Scoliosis grade 3 is diagnosed on the basis of a pronounced rotation of the vertebrae, manifested by muscle contractures, a delineated costal hump, bulging of the costal arches and weakening of the abdominal muscles.
- Scoliosis of the 4th degree is manifested by a significant deformation of the skeleton, the costal hump is very pronounced, the paravertebral muscles are stretched, in the concavity zone, the muscles and ribs sink.
Scoliosis of the 1st and 2nd degree usually occurs in the absence of subjective complaints. Scoliosis of the 3rd and 4th degree is manifested by pain in the back and heart, shortness of breath, fatigue and stiffness of movements.
The presence of scoliosis in children requires treatment, since progressive scoliosis leads to compression and dysfunction of internal organs, which in some cases can be life threatening. You can learn about the treatment of scoliosis in children in our next article.






Add a comment