Today, 3 main botulinum toxin preparations are most commonly used in the aesthetic medicine market:
- Botox;
- Xeomin;
- Dysport.
The efficacy and safety of all these drugs has been proven by numerous clinical trials. And, although almost all of them have the same properties – block neuromuscular transmission, yet different specialists prefer different drugs.
Manufacturers are trying to attract a doctor with the special advantages of their particular drug, but sometimes these data in different studies are extremely contradictory. At estet-portal.com we will talk about 5 popular myths about botulinum toxin drugs! It's going to be hot!
- Myth 1: Different botulinum toxin products give different results
- Myth 2: Different botulinum toxin preparations have different diffusion capacities
- Myth 3: The protein load of a botulinum toxin preparation is clinically important
- Myth 4: The production of neutralizing antibodies depends on the protein load of the drug
- Myth 5: Post-treatment management protocols are essentialus
Myth 1: Different botulinum toxin products give different results
Because botulinum toxin is one of the most used substances in aesthetic medicine, there have been numerous research studies on the effectiveness of different botulinum toxin preparations. Some studies have shown that Botox is the most effective, another that Dysport, the third that Xeomin.
However, the most reliable assumption is that there is no difference between these drugs.
Botulinum toxin: a terrible poison or an invaluable medicine
Lowe and colleagues found that Botox 30 units and Dysport 75 units (dose ratio 2:1) showed similar efficacy in correcting glabellar wrinkles.
In conclusion, there is no conclusive evidence of superior efficacy of one drug over others. However, when the doses are not equivalent, the results are not equivalent for obvious and obvious reasons.
Myth 2: Different botulinum toxin preparations have different diffusion properties
When talking about diffusion, many scientists were quick to speculate that since Dysport contains a lower molecular weight protein than Botox, the former will diffuse farther away from the injection site. However, no no evidence from any serious clinical studies to support this assumption.
Dynamic Facial Relaxation: Different Techniques for Injecting Botulinum Toxin
Diffusion can be uneven and is highly dependent on the density of receptors in any given target area. For example, a study was conducted in women with hyperhidrosis.
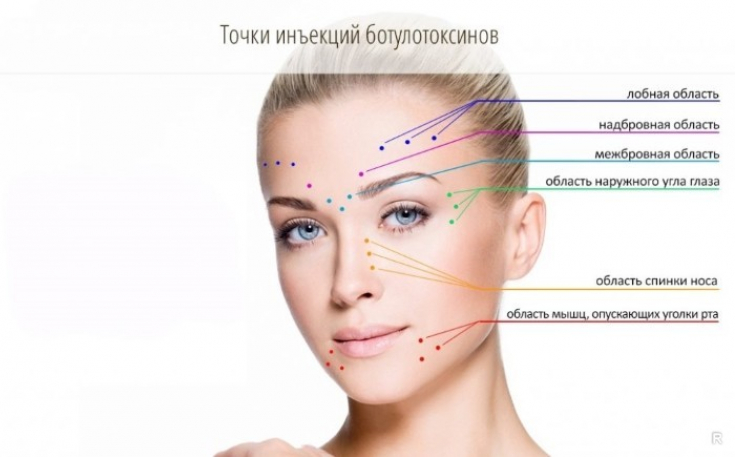
Botulinum toxin was injected at 3 points at different depths (2, 3 and 4 mm). The effect field was smallest at a depth of 3 mm, indicating a higher density of BoNT-A receptors in this area, and therefore, a large dose of neurotoxin is required to correct it.
These data suggest that skin type, anatomical location, and the number of BoNT receptors may be more important in determining the target area than injection depth and drug concentration.
Against this background, careful placement of the correct dosage of BoNT-A gives the best chance of good
Some authors suggest that
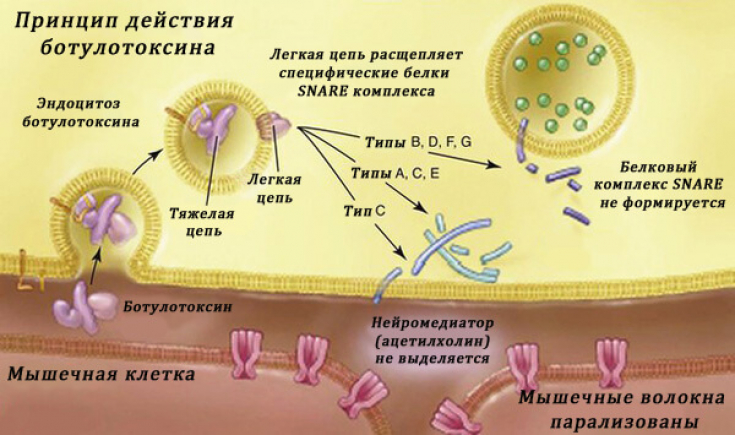
complexing proteinscould theoretically limit the spread and diffusion of BoNT-A from target tissues. Clinical studies related to the therapeutic or aesthetic use of the toxin have not confirmed differences in the diffusion of the free or complex form of BoNT-A products following muscle injection.
An early suggestion that associated proteins may play a role instabilizing the neurotoxin in the ampule
or in reducing diffusion after injection is incorrect. The emergence of a complex protein-free product, IncobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin), has demonstrated that binding proteins are not required for product stability. Protein loading may, at least in theory, influence
neutralizing antibody production(see Myth 4) and possibly a subsequent lack of clinical efficacy in some patients.
New generation botulinum toxin: an innovation in the neuromodulator market Restoration of Botox and Dysport results in complete
dissociation of the complexes, with at least 85% BoNT-A of Botox and 100% of BoNT-A of Dysport present as free neurotoxins. As a result, the proteins will not prevent or promote BoNT-A diffusion after reduction.
and long-term comparative studies are still needed. However, due to the lack of noticeable differences in immunogenicity and diffusion depending on the protein load,
the difference between modern preparationsof botulinum toxin seems to be clinically insignificant in the aesthetic medicine where very low doses of products are used. Myth 4: The production of neutralizing antibodies depends on the protein load of the drug
Initially, some researchers expressed concern that
protein loadwould increase the risk of neutralizing antibodies, which could undermine the effectiveness of treatment.
Read the most interesting articles inTelegram! Initially, there were reports that since the protein in Dysport is 40% lower than in Botox, and in Xeomin there is no protein load at all, these preparations
are less likely to contribute to the formation of neutralizing antibodiesthan Botox.
Therefore, the protein load of the drug can and does affect its effectiveness (which has not been proven), but cannot influence the formation of antibodies to the neurotoxin itself and reduce its effectiveness.
However, the risk ofallergic reactions
to a drug with a higher protein load relativebut higher. Myth 5: Post-treatment management protocols are essential
Many
instructions and restrictionsassociated with post-aesthetic treatment protocols for patients are widely used despite no evidence that they affect efficacy, adverse events, or severity.
Some clinicians suggest that patients should- keep their heads up for 6 hours
- after injection to reduce the chance of unwanted spread of the toxin. This advice may reflect fears of ptosis, however, botulinum toxin after 5-10 minutes after the procedure is no longer dangerous. Many clinicians suggest muscle massage
- to increase toxin absorption, flatten "bumps"; after injections. However, some authors advise carefulness when massaging, as diffusion is almost impossible to control. Increased muscle activity
- after the procedure will result in greater absorption of the toxin, however, this does not affect the duration of the effect, but its intensity. Ice or cooling
- are commonly used to increase comfort and prevent bruising after treatment. But according to some studies, cooling the area may reduce the effectiveness of BoNT and should probably be abandoned until more reliable data are available.
Methods to increase the duration and effectiveness of botulinum toxin action Available evidence suggests that
experienced physiciansget equally good results when working with all botulinum toxin preparations.
More useful and interesting information on our channel onYouTube:






