Angioneurotic edema is a pathological reaction of the body to various biological and chemical factors. For the first time this condition was described back in 1882 by Heinrich Quincke, thanks to which it received another name - – Quincke's edema.
With the development of angioedema in their practice, every doctor can meet, regardless of specialty. In some cases, the pathology leads to a rapid increase in respiratory failure, and if emergency assistance is not provided, the consequences will be fatal.
This article on estet-portal.com describes the most common causes that can lead to the development of angioneurotic edema, and also outlines an algorithm for therapeutic measures to eliminate it.
Clinical picture of angioedema: we recognize the pathology quickly
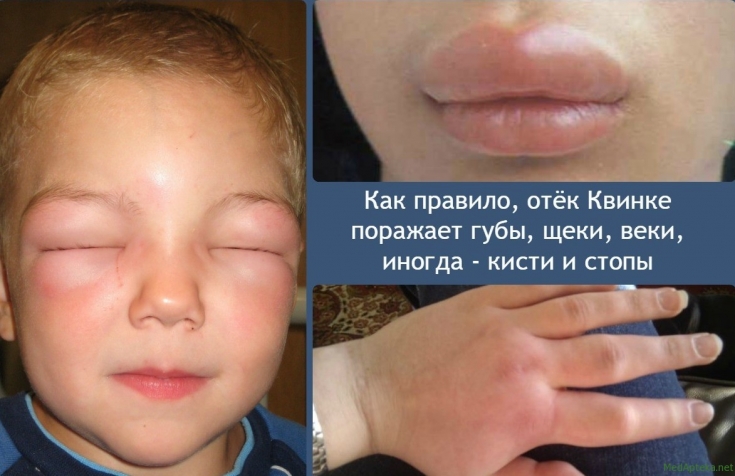
The clinical picture of angioedema is characterized by the sudden development of edema in places where there is a large layer of subcutaneous fatty tissue or mucous membranes are localized.
Typical locations for swelling are lips, tongue, eyelids, cheeks, it can also occur on the limbs, trunk or genital area.
The appearance of the skin often does not change, or erythema may occur. The patient feels tingling or pain in the areas of swelling, rarely complains of itching. The sudden onset of swelling of the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, in particular the larynx, can lead to death.
Follow us on Telegram
Symptoms of the development of laryngeal edema are a change in the nature of the voice and a rapid increase in respiratory failure. In such cases, the doctor must act immediately.
What can cause angioedema
The occurrence of angioedema can be provoked by various factors.
The most common causes of pathology are:
1. Medications (ACE inhibitors (angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors), ARBs (angiotensin II receptor blockers), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other medicines);
2. Infectious agents;3. Food (oral allergy syndrome);
4. Hymenoptera;
5. Latex;
6. Physical factors: vibration, pressure, heat or cold;
There is also a hereditary form of angioedema. This is a very rare condition, with a prevalence of less than 1:50,000 of the population.
Read also:
Histamine burst: how an immediate allergic reaction develops
Treatment of angioedema: drugs to eliminate pathologyFirst of all, it is necessary to eliminate triggers that could contribute to the occurrence of angioedema. In the treatment, antihistamines are used, the dose of which should be several times (up to 4x) higher than the average therapeutic dose: 1-2 tablets in the morning and evening for 1-2 weeks. Antihistamines are effective against urticaria (histaminergic angioedema).
Analgesics, in particular non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, may be used if necessary, unless they themselves are the cause of angioedema. Topical application of gels with a cooling effect also helps to eliminate the symptoms of pathology.
Glucocorticoids: modern classification and important practical aspects
Angioedema of the upper respiratory tract: urgent measuresIf there are signs of life-threatening edema of the upper respiratory tract, therapy should be carried out immediately. Such patients should be hospitalized.
Emergency measures include:
1. Intubation of the trachea;2. Adrenaline 0.01 mg/kg IV to be repeated every 10-20 minutes;
3. In case of development of hypoxia – oxygen therapy;
4. Injection of glucocorticoids: methylprednisolone 40-80 mg IV bolus;
5. Infusion-detoxification therapy: saline solution or Ringer's solution IV 60-80 drops/min.
Patients who have experienced angioedema for the first time should be advised to identify and eliminate the cause of its development.
It is important to inform the patient about the mechanism of occurrence of his pathological condition, and the need to comply with all medical measures assigned by the doctor. The specialist must have the skills to help in the event of angioedema, as in some situations this can save the patient's life.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the Dermatology section. You might also be interested in:
What your doctor needs to know about modern antihistamines.
Material based on Guideline «Angioedema» (2018).







Add a comment