Angioneurosis is not just a disease, but a whole group of diseases that are united by one common feature: for one reason or another, a person has a disorder of autonomic innervation, which develops increased excitability of the centers in the spinal cord responsible for vasomotor functions. As a result, capillary spasm occurs in some areas of the skin. If you do not start treatment on time, then in the future periods of asphyxia will be more frequent and longer, up to tissue necrosis. These symptoms can manifest themselves both as an independent disease and as a syndrome in some diseases.
Why does angioedema develop and how does it manifest itself
The causes of angioedema may be hidden in congenital insufficiency of some parts of the spinal cord, which affects the vasomotor centers at different levels of the autonomic nervous system. However, these lesions can also occur due to some infectious diseases, due to diseases of the adrenal glands, the thyroid gland. As a result, the tone of vasoconstrictors increases and a strong vasospasm occurs. Externally, angioedema is manifested by a sharp blanching of the skin on the hands and feet, sometimes on the nose and ears. The affected area quickly cools down so much that tissue necrosis can develop, as with frostbite. At the same time, toxins are released in the ischemic area, which irritate the nerve endings and cause severe pain.
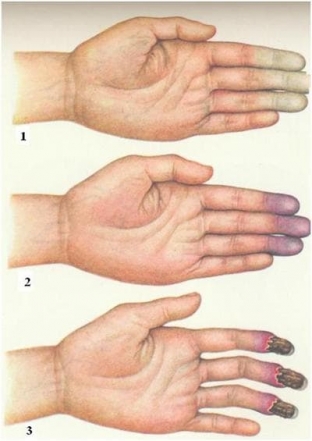 Angioneurosis usually has three stages of development, depending on the strength and depth of tissue damage, on the neglect of the process:
Angioneurosis usually has three stages of development, depending on the strength and depth of tissue damage, on the neglect of the process:
- first stage – spasms of capillaries are suddenly detected, and symmetrically, most often on the fingers and toes; the skin turns pale, grows cold, loses sensitivity; the attack lasts a few minutes or hours and passes; without treatment, seizures come more frequently, last longer and cause pain;
- second stage – with spasms, the skin acquires a bluish-violet hue; in places of asphyxia, the patient feels tingling and loss of sensitivity, sometimes severe pain; dilatation of the veins develops;
- third stage – spasms are long, against their background, the limbs swell, turn blue, become covered with bloody blisters; under the opened bladder, necrotic tissues are found, and necrosis can spread up to the bone; ulcers after blisters are tightened with the formation of scars.
The course of angioedema is chronic, attacks can occur several times a day, and at intervals of many months. & nbsp; In the most severe cases, although rare, tissue necrosis may progress to gangrene.
How can angioedema be treated and its prognosis
The peculiarity of angioedema is that it cannot be cured at all, although it happens that with the development of the disease in the pubertal period & nbsp; over time, complete recovery occurs. But the earlier treatment is started, the more favorable the prognosis for life. Patients are prescribed adrenoblockers of central and peripheral action, ganglionic blockers, tranquilizers. A good effect is given by the combination of their intake with antispasmodics – for example, preparations of nicotinic acid, calcium ion antagonists. Warm baths may be recommended for acute attacks. If conservative therapy fails, a preganglionic sympathectomy may be performed.
It is important to note that patients with angioedema are advised to carefully observe the temperature regime and avoid hypothermia – especially hands and feet, being in dampness, in contact with vibrating objects and toxic substances. You should also avoid work associated with prolonged tension of the fingers – playing musical instruments, computer typing.







Add a comment