– injectable dermal fillers that are used in cosmetology to reduce wrinkle depth, replenish lost volume and restore normal face architectonics. They are based on hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxyapatite, poly – L- lactic acid and other components.
Hyaluronic acid-based
fillers are currently considered the safest, as complications associated with them can be eliminated with hyaluronidase enzyme. On
estet-portal.com read what happens during the injection of fillers, what are complications of contouring and what to do if they occur.
- What happens after a filler injection
- Types of complications after fillers
- How to avoid complications after filler injections
- Ischaemia: management of the most serious complicationi What happens after a filler injection
After the filler is injected into the tissue, a whole cascade of processes occurs:
1. Coagulation:A fibrin clot forms after injury. Captured platelets degranulate and secrete inflammatory chemokines.
2. Inflammation:leukocytes enter the wound area. First, neutrophils appear, then macrophages and lymphocytes come. Leukocytes cleanse the wound of bacteria and any foreign bodies, respectively, by activating fibroblasts.
3. Proliferation:activated fibroblasts, myofibroblasts produce and deposit ECM (extracellular matrix) components that serve as a skeleton in the tissue regeneration process.
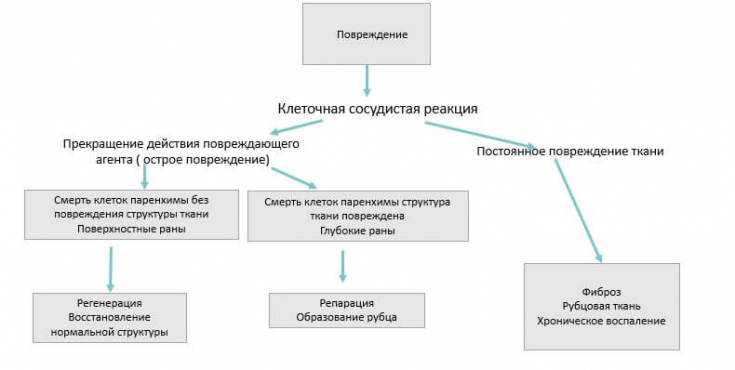 4. Remodeling:
4. Remodeling:
Dr. Patrick Tracy: Even a simple injection procedure, a doctor must learn from a knowledgeable specialist Types of complications after injection of fillers
After the introduction of dermal fillers, the following may develop:
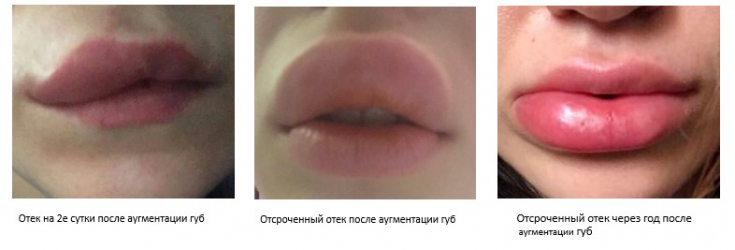
- Short-term complications
- (resolve quickly without treatment):
- appearance of itching and swelling;
- bruises;
- delayed edema.
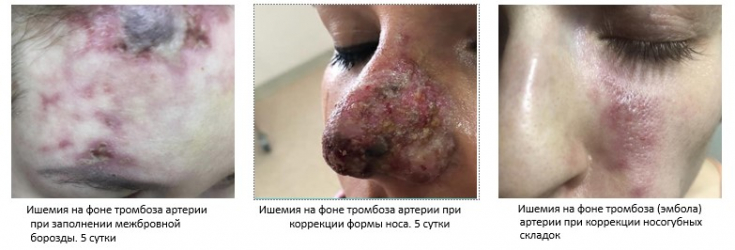
- Long-term complications
- (require serious treatment approach):
- the appearance of dense nodes under the skin;
- allergic reactions;
- puffiness of the face;
- vascular embolism;
- disturbance of tissue blood supply;
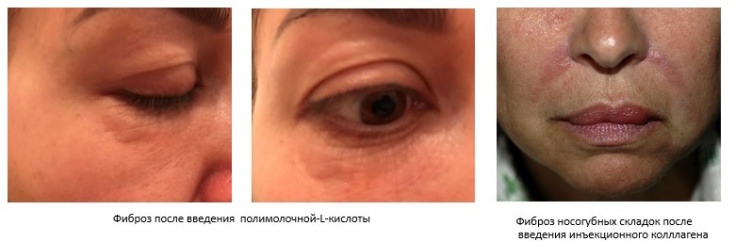
- fibrosis.
 These complications may be caused directly by the drug itself, or may depend on the design of the syringe or the qualifications of the doctor.
These complications may be caused directly by the drug itself, or may depend on the design of the syringe or the qualifications of the doctor.
Restoring the skin and activating its reparative properties How to avoid complications after filler injections
Based on the causes of complications, how can adverse reactions be prevented?
First, and probably most important, is
knowledge of anatomy. Knowledge of topographic anatomy – safety of doctor and patient.
In second place – correct tactics for the prevention of vascular complications. It is important to perform an
prior to filler injection.
NewErgonomic Syringe 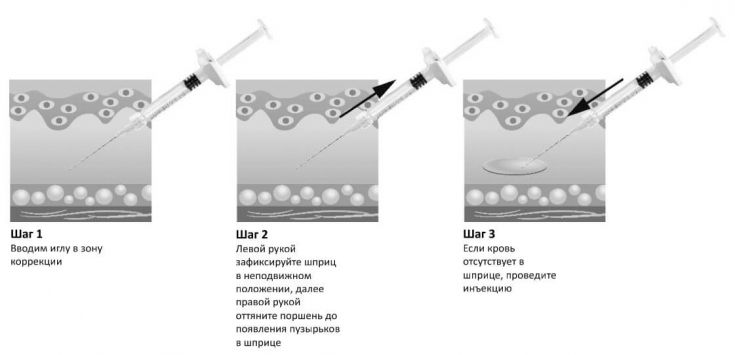 Filler ALEXA, introduced by Hyalual, easy to perform aspiration test.
Filler ALEXA, introduced by Hyalual, easy to perform aspiration test.

. It must meet the highest quality standards and be as safe as possible.
fillers is of the highest purity biosynthetic origin for maximum safety and predictable volumetric results.
Alexa's BDDE residual is 2x safer than FDA guidelines and is proof of safety.
 99.999% of the BDDE reacted in ALEXA fillers is non-toxic to the skin.
99.999% of the BDDE reacted in ALEXA fillers is non-toxic to the skin.
 During the production of
During the production of
fillers, titanium-niobium knives are used to grind the filler mass. The use of this type of knife eliminates the ingress of heavy metal particles into the gel after grinding to ensure maximum purity of the filler.
Stabilization of the
Alexa
Wet sieving of hydrogel particles ensures batch-to-batch particle size accuracy. Uniquely selected particle sizes for each product of the line allow you to be sure of the success of fillers in different areas and depths of the skin.
! Ischaemia: management of the most serious complication If, in compliance with all safety rules, with the right choice of dermal filler,
embolization of the vesselstill occurs, for example, as a result of a variant anatomy of a particular patient, the doctor needs to clearly know the algorithm of emergency care.
Treatment of acute ischemia:
Hyaluronidase
3000-6000 IU, over the entire affected area every hour until visual restoration microcirculation;- Dexamethasone – 8 mg IV; Suprastin 2mg IM; Local
- – warm compress, nitroglycerin ointment;
- LMW heparin: Clexane 40 mg s.c.; Pentoxifylline, nicotinic acid.
- Treatment of acute ischemia on days 2-6:
Hyaluronidase
3000-6000 IU, over the entire area of lesions every hour 3-5 times, 2-3 days in a row;- Dexamethasone – 8 mg IM; Sildenafil – 100 mg once a day, 5 days;
- Suprastin 2mg IM;
- Clarithromycin 500mg 5 days;
- Heparin: Clexane 40 mg s.c.;
- Pentoxifylline, nicotinic acid.
- Thus, if you clearly know the
- algorithm of care , you can quickly help the patient and prevent the development of serious adverse reactions.







Add a comment