Chromomycosis is caused by special dark-colored fungi, in the family of which there are many different types of pathogens, and they are quite widespread in nature. The most common complaints of chromomycosis are patients who often have to deal with work related to the earth, contact with wet wood, and straw harvesting. This disease is sometimes called verrucous dermatitis because the skin rashes look like warts, and they can grow, bleed, fester, and if left untreated, chromomycosis can affect the lymph nodes and cause serious complications.
What do skin lesions look like with chromomycosis
After the pathogen has entered the body, a purple bump appears on the skin. The incubation period for chromomycosis is usually several weeks, but the disease can manifest and after many months. A patient at a doctor's appointment complains of some general weakness and fatigue, subfebrile temperature, headaches and lack of appetite, and when examining the body – most often on the feet and legs, on the hands – peeling tubercles are revealed, which grow and become like a blackberry. The number of nodules and plaques increases, they can tightly adjoin each other, and then the lesion begins to resemble a cauliflower. Sometimes a papillomatous-ulcerative form of chromomycosis develops,
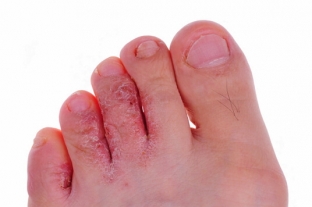
Symptoms of chromomycosis and features of the forms of the disease
At the initial stage, the manifestations of the disease resemble psoriasis plaques, but later they transform into elements characteristic of chromomycosis. These can be:
bumps – a reddish conical formation, similar to a wart, is covered with a crust, new similar elements gradually appear around it, they merge into a conglomerate, darken, and then soften and ulcerate, papillomatous growths with bloody-purulent discharge may appear on their surface;
knots – dense formations in the hypodermis with bluish skin above them, gradually soften and become covered with ulcers, the tubercles that appear nearby gradually merge into dense scalloped plaques and become covered with crusts.
Chromomycosis can take the following forms:
- nodular – initial stage with erythematoid papules;
- tumor – merged large nodular conglomerates;
- verrucose – superficially resembles rashes of vulgar warts;
- scaly – looks like flat hyperkeratotic foci of different sizes;
- scar – in the center of the annular focus there are sclerotic areas, and on the periphery there are new rashes.







Add a comment