Candida infection – a disease of fungal etiology caused by microorganisms of the genus Candida (mainly Candida albicans).
Microorganisms Candida albicans are yeast fungi that are representatives of the conditionally pathogenic flora of the human body. They are found in the gastrointestinal tract and oral cavity in 40-60% of clinically healthy people.
Fungi Candida albicans pose a high risk for patients with impaired immune status, especially for people with HIV infection, as well as those who take glucocorticoids and cytostatic drugs.
For more information about the main clinical forms of candidal infection, read on estet-portal.com in this article.
What is the relationship between the severity of Candida infection and immunodeficiency
The clinical picture of candidal infection depends on the patient's immune status.
In apparently healthy people with transient immunosuppression, Candida albicans can lead to characteristic lesions of the skin, oral mucosa, and genital organs. At the same time, in patients with chronic immunosuppression, Candida albicans is the cause of severe invasive and disseminated forms of candidiasis.
Without meeting a proper immune response, Candida albicans can spread throughout the body, affecting the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory organs, liver, and even the pancreas.
Fungemia caused by Candida albicans is 50% fatal.
Treatment of disseminated Candida infection consists of systemic antifungal therapy, as well as treatment of the underlying disease (in HIV-infected patients – use of antiretroviral therapy).
Vaginal microbiome: bacteria guarding women's health
Oral candidiasis: typical symptoms and treatment principles
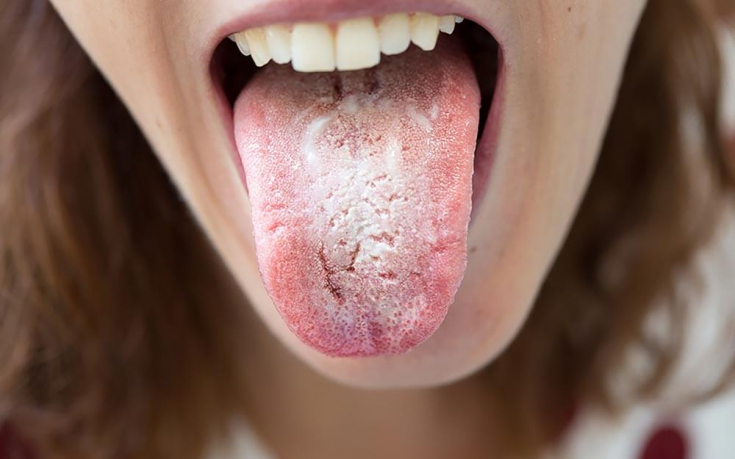
Oral candidiasis is characterized by the presence of typical white exudates on the oral mucosa (mainly on the tongue). More common in infants a few weeks old.
In adult patients with a normal immune status, oral candidiasis is observed quite rarely and proceeds in a mild transient form.
According to international protocols, oral candidiasis in patients with a normal immune status requires only observation. It is enough to confine ourselves to local antiseptics.
Candidiasis (thrush): causes, diagnosis, treatment
Features of local therapy of candidal angular cheilitis
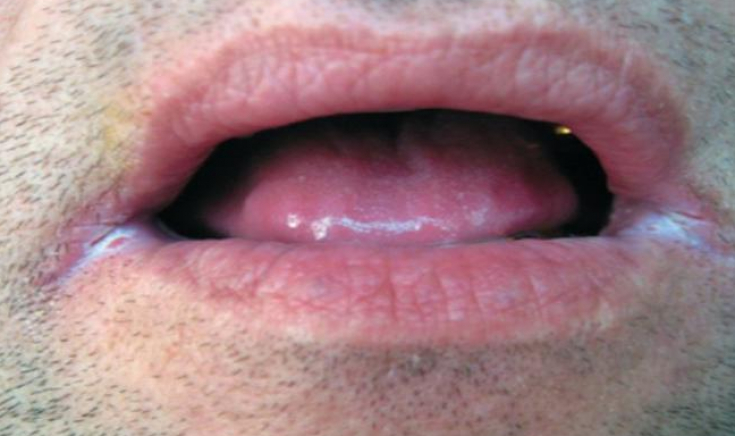
Candidal angular cheilitis can occur both against the background of previous oral candidiasis, and independently.
The use of dentures creates local conditions that favor the development of candidal angular cheilitis.
in patients with normal immune status is limited to the use of an ointment containing an antifungal agent of the azole group. In most cases, systemic antifungal therapy is not required.
Follow us onFacebook Candida albicans: clinical presentation and treatment of candidal intertrigo
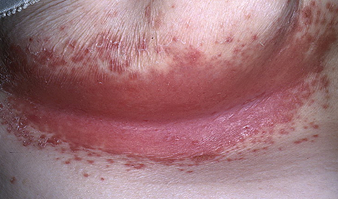
is characterized by a fungal infection of the skin, localized mainly in the natural skin folds of the human body. Today, the diagnosis of candidal intertrigo is often made unreasonably. At the same time, seborrheic eczema and psoriasis can hide under the guise of a candidal infection.
Typical localization of candidal intertrigo: skin folds under the breast, navel, axillary area, inguinal folds, as well as skin between the fingers and intergluteal region.
In this case, the skin becomes erythematous, sensitive, exudation is characteristic, papules and vesicles may form.
Treatment for candidal intertrigoconsists of topical application of an ointment containing a glucocorticoid and an antifungal agent for 1-2 weeks. In most cases, systemic antifungal therapy is not necessary.
If there is a tendency for a recurrent course of candidal intertrigo, the patient should be examined for the presence of diabetes mellitus and immunodeficiency.
Vaginal candidiasis – immunocompromised disease Clinical picture of the lesion of the periungual fold Candida albicans
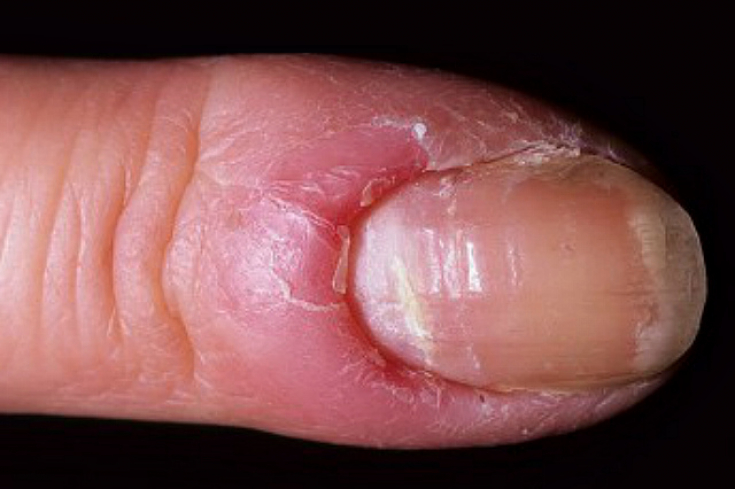
is characterized by an infectious lesion of the periungual fold. In this case, the etiological cause in most cases is a mixed infection of Candida albicans and S.aureus.
Candidal paronychiais often seen in patients who work in environments that require constant hand contact with water: cleaners, nurses, kitchen staff. Clinically, candidal paronychia is characterized by hyperemia and swelling of the periungual fold, marked pain and sensitivity.
Treatment consistsin the topical application of an ointment containing drugs from the azole group, natamycin or nystatin. Constant hand contact with water should be avoided, as excessive moisture creates optimal conditions for the development of a fungal infection.
Thus,Candida infection
– is a disease caused by fungi of the genus Candida. The clinical picture of candidal infection depends on the patient's previous immune status. Recurrent candidiasis may be an indicator that the patient is immunocompromised. Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Infectology" section. You may also be interested in
Effective antifungals for the treatment of vaginal candidiasis
You may be interested in: Artistic Dental Restorations.







Add a comment