There are usually two types of milia: primary and secondary.
Primary milia – they are benign, keratin-filled cysts arising from a hair follicle observed just below the surface of the skin. And secondary milia are the result of an inflammatory process. In children and adults (both women and men), they usually occur around the eyes and on the cheeks.
Primary milia are common in infants, commonly referred to as milk spots, which often resolve. Milia seen in adults tend to be chronic.
Miliums can be a serious aesthetic problem, as it is difficult to hide them with makeup. In this regard, on estet-portal.com we will consider the main causes of these formations, and also effective methods to eliminate milia.
- Clinical presentation and causes of milia
- Techniques for removing milia
- Risks and complications of miliumo treatmentin
Clinical picture and causes of milia
The cause of milia in children and adults is unknown, however there are some studies that suggest that milia in adults is primarily caused by skin damage and/or use of products containing mineral oils and lanolin .
Milia may occur because the skin is not able to absorb this product, and over time it accumulates in the follicle.
On physical assessment, primary milia present as a firm, subcutaneous, uniform, pearly white to yellowish bulging lesion, usually 1-3 mm in diameter.
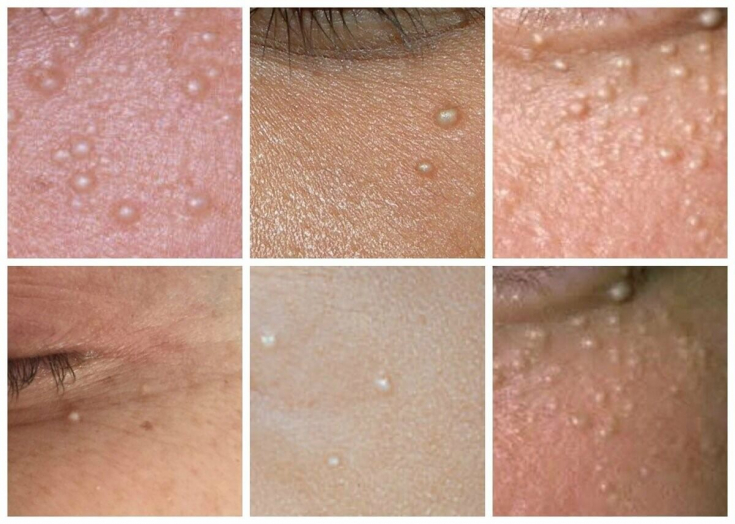
Millia are asymptomatic, non-itchy, and usually located on the face, especially around the eyes. Usually one milium can be seen, as well as groups of 3-10 miliums.
Secondary milia appear as separate plaques. These plaques can develop after skin trauma, such as burns, blisters, skin resurfacing, and even tattoos.
Secondary milia may also occur after topical use of corticosteroids. It is assumed that the appearance of milia is associated with a malfunction of the pilosebatory unit.
Unlike primary milia, which do not need further investigation, it is important to find out the cause of secondary milia in order to avoid recurrence of the evidence of education
.Find out the causes of milia on the face
Techniques for removing milia
Millia are harmless on their own, however, when they don't go away on their own (as they often do in children), there are several treatment options available.
No topical or systemic drugs are effective in treating primary and secondary milia, however, in some cases, a positive effect is observed with therapy with tretinoin
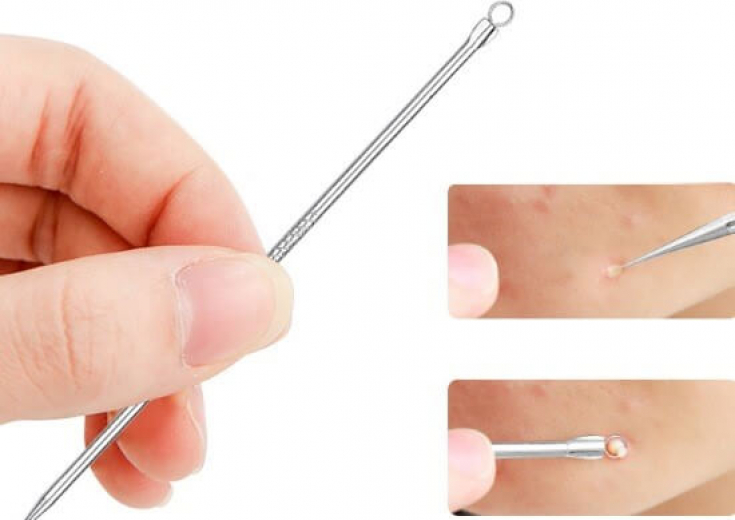
.Deroofing
(removing the milium cover) is the most commonly used technique, where a sterile needle is pierced into the skin, then the contents of the milium are removed. For a successful outcome, it is important to ensure that all milia are removed. This procedure is fast and has minimal risks.
Hyfrecation
(a procedure using an electrosurgery machine) can be used to destroy the milia. This treatment option uses a fine-tipped needle that delivers an electric current or radio frequency.Also, cryotherapy is sometimes used to freeze milia
a.Read the most interesting articles in Telegram!
Risks and complications of milia treatment
When choosing the appropriate milium treatment, it is important to be sure that the procedure is both effective and safe. Milia are often located near the eyes
, making the region dangerous to work in.For some patients, local anesthesia
.may be recommended to relieve discomfort after milia treatment.None of the procedures can guarantee that the milia will be completely removed, although most often these lesions respond well to treatment.
Because milia recurrence is possible, topical retinoids may be recommended for prevention, and skin care products that contain mineral oils and >lanolin
.Millia on the skin – a signal about a malfunction of the body







Add a comment