Synovial sarcoma is one of the most common soft tissue malignancies. Among this group of neoplasms, synovioma occupies 33% of cases. Synovioma is based on atypical transformation and proliferation of cells of the synovial membrane, tendon sheaths and tendon bags. Synovioma is defined in patients aged 15 to 20 years. Joint damage is observed in 40% of cases of malignant synoviomas with a predominant lesion of the ankle and knee joints. Synovioma of the tendon sheaths and mucous membranes of the articular capsules also occurs. What are the causes and clinical manifestations of synovioma?
Causes and classification of malignant neoplasm - synovioma
The reasons for the atypical transformation of synovial cells with the subsequent development of synovioma could not be clarified. Predisposing factors include immunosuppressive treatment in patients with cancer or after organ transplantation. What a synovioma looks like, read further on estet-portal.com. Based on the cellular structure, there are 6 forms of synovioma – giant cell, alveolar, fibrous, histoid, adenomatous and mixed.
Classification of synovioma by tissue structure:
- Cellular – consists of glandular tissue, which has cysts and papillomatous outgrowths.
- Fibrous – the composition contains fibers, which in structure resemble the elements of fibrosarcoma.
What are the main clinical manifestations of synovioma?
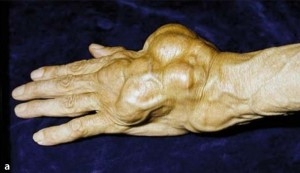 Synovioma is manifested by the development of pain in the affected joint or soft tissues. The pain limits the movement of the joint.
Synovioma is manifested by the development of pain in the affected joint or soft tissues. The pain limits the movement of the joint.
On palpation of painful places, tumor-like formations without clear boundaries are found. The formation can have a different consistency and reach a size of up to 20 cm.
The most common localization of synovioma – soft tissues or joints of the lower extremities. Synovioma is also accompanied by fever, loss of appetite and increased fatigue. A malignant neoplasm metastasizes with the detection of metastases in the abdominal organs and in the skin.
Methods of treatment and prognosis in the development of synovioma
The diagnosis of synovioma can be confirmed with a biopsy. The main method of treating synovioma is an operative method with its radical removal. The operation is performed with the capture of healthy tissues, as well as in compliance with the rules of ablastics. The presence of a large tumor may require resection of large areas of soft tissue and bone.
In some cases, it is necessary to amputate a limb. After removal of the joint, prosthetics can be performed to restore the function of the limb.
Before and after the removal of the synovioma, radiation therapy is performed. Before treatment, it allows you to stop the growth of synovial sarcoma, and after surgery, radiation exposure is aimed at preventing tumor recurrence. Chemotherapy is prescribed as a palliative treatment in the later stages, as well as in the presence of metastases. In the presence of synovioma, five-year survival is achieved in 40% of patients.







Add a comment