Today, dermatomyositis remains an actual and little-studied disease. The connective tissue lesion has a complex, recurrent course and a characteristic clinic.
Dermatomyositis – chronic idiopathic inflammatory myopathy, which is characterized by symmetrical lesions of the proximal muscles and typical foci on the skin. In 30% of patients, there is no skin lesion, in which case the disease is called polymyositis.
Pathology is quite rare, mainly in women 20-50 years old, children aged 1.5 to 16 years can also get sick. Read on estet-portal.com about the characteristic signs of dermatomyositis, etiological factors and classification of the disease.
Dermatomyositis etiology: trigger and genetic factors
The etiology of dermatomyositis is not fully understood. It is known that the disease often occurs after infectious lesions of the upper respiratory tract, exacerbations of tonsillitis, pharyngitis, as well as due to measles, influenza, rheumatism and streptococcal infections.
Antigenic mimicry is important, which provokes the appearance of autoantibodies to muscles, followed by the formation of immune complexes.
Genetic predisposition also plays an important role in the development of the disease: 40-50% of patients are carriers of certain HLA antigens (B8 and DR3).
Follow us on Facebook
Trigger factors for the development of dermatomyositis include: physical and mental trauma, hyperinsolation, hypothermia or overheating, vaccination and exacerbation of chronic infections.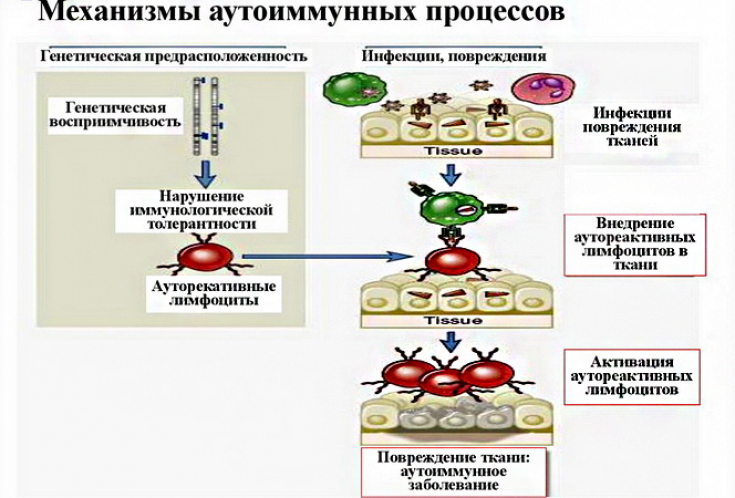
Dermatomyositis: typical clinical presentation and classification
Idiopathic (primary), symptomatic (secondary) and juvenile (children's) dermatomyositis are distinguished.
In addition to the general symptoms, specific signs of the disease are distinguished:
• bright (heliotrope) erythema around the eyes in the form of glasses;
• progressive muscle weakness;
• impaired motor function of muscles;
• speech disorder, dysphagia;
• Erythematous-spotted rash on the face, joints, back and sternum;
• muscle soreness on palpation;
• Gottron's papules (on the extensor surface of the interphalangeal joints);
• lesion of mucous membranes (conjunctivitis, stomatitis, cheilitis);
• formation of subcutaneous calcifications;
• damage to the heart, lungs, kidneys, nervous system and endocrine glands.
Skin manifestations precede muscle damage on average for several months or even years.
With a long course of the disease, hypo- and depigmented areas, atrophy, telangiectasias can be observed.
What are the forms of systemic scleroderma
The course of the disease: how it proceeds and what complicates dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis can occur in several forms. The disease is characterized by acute, subacute and chronic course.
1. acute course is characterized by generalized muscle lesions up to complete atrophy. There is dysphagia and damage to internal organs with a risk of death. With timely treatment, a transition to a chronic or subacute course is possible;
2. subacute course lasts for 1-2 years with a gradual increase in symptoms;
3. chronic course is characterized by a more favorable prognosis. There is moderate muscle weakness, myalgia, erythematous rash. In some cases, there may be no skin involvement.
Complications of dermatomyositis are paresis of the swallowing muscles and smooth muscles of the esophagus, aspiration pneumonia, respiratory failure, vascular damage (Raynaud's syndrome), cardiovascular lesions (myocarditis, congestive heart failure), kidney failure, as well as an increased risk of developing oncopathology.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Dermatology" section. You may also be interested in: Lupus erythematosus:








