Nowadays, pseudotuberculosis and intestinal yersiniosis, caused by Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, respectively, are usually combined under the same name «yersiniosis».
This approach is due to the similarity of the etiology, clinical picture, pathogenesis and approaches to the treatment of these diseases. Yersiniosis occurs in all age groups of the population.
Cases of disease are recorded at any time of the year. Clinical polymorphism of yersiniosis often leads to late verification of the correct diagnosis, lack of early etiotropic treatment and the development of severe complications.
For more information about modern approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of yersiniosis, read on estet-portal.com in this article.
What is the difficulty of timely diagnosis of yersiniosis
The need for timely diagnosis of yersiniosis is determined by the ability of these diseases to initiate the development of autoimmune post-infectious pathologies, in particular arthritis, glomerulonephritis, and systemic connective tissue diseases.
Clinical polymorphism of yersiniosis determines the complexity of timely diagnosis of the disease.
Due to the variety of clinical manifestations of yersiniosis, patients can contact doctors of various specialties: surgeons, general practitioners, gastroenterologists, infectious disease specialists, dermatologists, neurologists. Knowledge of pathognomonic symptoms and modern methods of diagnosing yersiniosis is necessary for every doctor for timely prescribing of therapy and preventing the development of post-infectious complications.
Follow us on Telegram
Epidemiological history and pathognomonic symptoms of yersiniosis
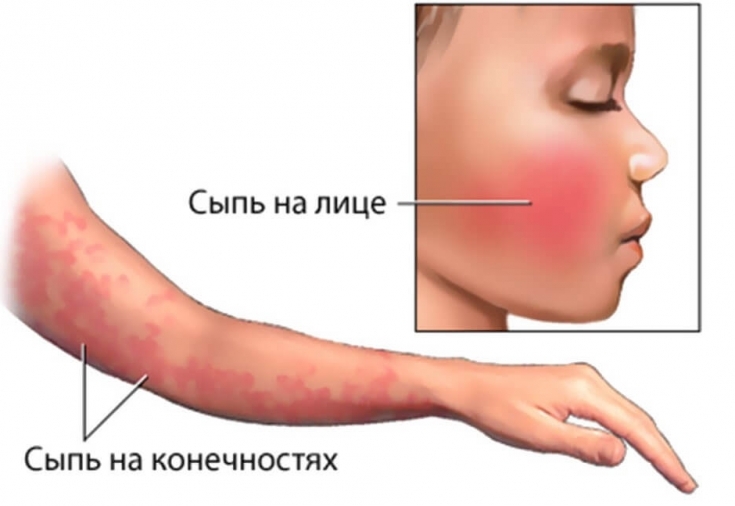
In the diagnosis of yersiniosis, a correctly collected epidemiological history is of great importance: the use of thermally unprocessed vegetables testifies in favor of the diagnosis of yersiniosis. "Hood, gloves and socks" symptoms are pathognomonic for pseudotuberculosis. Quite often, these signs can be diagnosed after the fact by the presence of lamellar peeling of the palms, feet and face.
The old name for yersiniosis (in particular, pseudotuberculosis) – "Far Eastern scarlet fever" - indicates the need for differential diagnosis of the disease with scarlet fever. Both nosological units are characterized by a small-spotted rash, but against the background of which a pale nasolabial triangle catches the eye.
The clinical sign by which it is possible to differentiate these diseases is the intensity of catarrhal phenomena in the oropharynx: with yersiniosis, inflammation is much less pronounced than with scarlet fever, or may be completely absent.
Treatment of herpes zoster: modern approaches and recommendations
Specific diagnosis of yersiniosis: laboratory research opportunities
Specific diagnosis of yersiniosis consists in bacteriological and serological research methods.
The substrate for bacteriological examination can be blood, feces, sputum, surgical material. This method is rarely used in clinical practice due to its low information content (less than 15%).
For the retrospective diagnosis of yersiniosis, serological research methods are used to identify specific antibodies: a four-fold increase in their titer over time confirms the diagnosis of the disease.
A highly specific method of serological diagnostics is ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), which, from the first days of the disease, makes it possible to identify specific antigens of Yersinia and can be used for early diagnosis of yersiniosis.
The most specific method for the specific diagnosis of yersiniosis is PCR (polymerase chain reaction). In the study of feces, this method allows you to confirm the diagnosis of yersiniosis with an accuracy of 99% already on the first day of the disease.
Erythema nodosum: why diagnosing the underlying disease is important
Treatment of yersiniosis: indications for antibiotic therapy and drugs of choice
With yersiniosis, in most cases, spontaneous recovery occurs. Indications for antibiotics are:
1. Sepsis;
2. Fulminant course of the disease;
3. Development of severe post-infection symptoms (particularly arthritis).
In the etiotropic therapy of yersiniosis, the drugs of choice in adults are antibiotics of the fluoroquinolone group: ciprofloxacin 500 mg 2 times a day for 7-10 days. Tetracyclines may be an alternative to fluoroquinolones. The combination drug Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim is the drug of choice for the treatment of yersiniosis in children.
In the treatment of yersiniosis in adults, the antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone group is the drug of choice, and in children – combined agent Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Dermatology" section. You might also be interested in Dangerous Tick Bites: Clinical Manifestations of Lyme Borreliosis.







Add a comment