Urolithiasis is familiar to a huge percentage of the world's population. With age and the negative impact of environmental factors, including junk food and an inactive lifestyle, normal kidney function is disrupted and favorable conditions are created for the formation of stones in the organs of the urinary system. In most cases, the diagnosis of urolithiasis is not difficult, since the disease has a characteristic clinical picture. But the clarification of the size, localization and other features of the formed stones is of fundamental importance for the selection of the correct method of treatment.
Laboratory methods for diagnosing urolithiasis
Laboratory research methods are the primary stage in the diagnosis of urolithiasis. Mandatory are general clinical blood and urine tests, which provide valuable information about the functional abilities of the kidney and indicate the presence of a pathological process in the body. Based on the results of a general blood test, it can be concluded that there is decompensation of kidney function, which is always accompanied by anemia. An increase in the level of ESR and leukocytosis with a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left may indicate the addition of an infectious process. Depending on the intensity of the pathological process, the following changes in the general analysis of urine are determined:
- small amount of protein;
- erythrocytes in urine;
- a large number of leukocytes;
- leukocyte casts;
- bacteria in pyelonephritis.
X-ray findings in urolithiasis
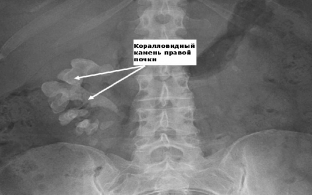
Important information in urolithiasis is provided by an X-ray examination, which should begin with a survey urography. On the X-ray image, the shadows of the formed stones are visualized, which makes it possible to clarify the place of their localization. After the introduction of a contrast agent, excretory urography is performed, which allows obtaining information about the anatomical and functional changes in the kidneys. The degree of expansion of the renal structures, their characteristic changes are determined. Often the radiopaque substance fills the pyelocaliceal system of the kidneys to the level of their obstruction. In patients with complete patency, retrograde ureteropyelography is performed.
Highly informative ultrasound examination for urolithiasis
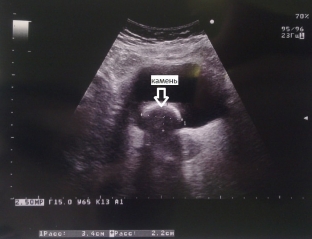
One of the most informative methods for diagnosing urolithiasis is ultrasound. Ultrasound examination allows to determine the characteristic acoustic signs of stones of the renal calyces and pelvis: stones give a strong echo signal, an acoustic cylindrical or conical shadow is formed behind the stone, the intensity of which depends on the composition and size of the stone. Coral-like stones on ultrasound have the appearance of an echogenic structure that repeats the shape of the pelvicalyceal system, completely or partially filling it. It is important to take into account the fact that ultrasound allows you to see stones larger than 3 mm.
Differential diagnosis of urolithiasis: main diseases
In more than 20% of cases, urolithiasis gives an atypical clinical picture and can mimic various diseases, for this purpose it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of urolithiasis. Most often, urolithiasis is differentiated with the following pathologies:
- acute appendicitis – often the localization of pain is different, appendicitis begins gradually, and not acutely, like renal colic, there is no irradiation of pain in the pelvic organs. Additional diagnostic methods help clarify the diagnosis;
- acute intestinal obstruction – the main distinguishing features are determined by the results of x-ray examination;
- acute cholecystitis – different localization of painful sensations and anamnestic data;
- acute pancreatitis – this disease is characterized by girdle pain and an increase in the level of diastase according to the results of laboratory tests, which does not occur with urolithiasis.







Add a comment