Scientific and clinical studies on the effectiveness of various drugs based on botulinum toxin have shown that their effectiveness is quite comparable. But the complexing proteins contained in most of them can cause ineffective procedures or the need to inject the botulinum toxin preparation more often than it was intended when it was prescribed.
Differences in treatment outcomes are due to varying levels of purification, and clinicians need to be aware of the difference between botulinum toxin preparations to ensure their safe and effective use. Read more about the high purity of Merz's Xeomin® and minimize the risk of addiction at estet-portal.com.
Features of botulinum toxin preparations and their purpose
Botulinum neurotoxin injections are a valuable treatment for many indications. At one time they revolutionized the field of aesthetic medicine, and today botulinum toxin injections are the leading cosmetic procedure performed worldwide.
Botulinum toxin is produced by the fermentation of the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. Its therapeutic use was first approved by the US FDA for the treatment of blepharospasm, hemifacial spasm and strabismus in 1989. Since then, the number of commercial botulinum toxins and their use has expanded for both clinical and aesthetic indications, and botulinum toxin products are now (with validated indications by country and product) used to address the following problems:
- aesthetic facial correction,
- symptomatic relief of blepharospasm,
- treatment of severe hyperhidrosis,
- headache prevention in adults with chronic migraine,
- treatment of urinary incontinence,
- multiple sclerosis therapy.
Neurotoxin Type A formulations are the most widely used worldwide and are approved by the US FDA for aesthetic use. There are currently three leading botulinum neurotoxin type A (BoNT/A) products on the market in the western hemisphere:
- onabotulinumtoxin A (ONA, Botox/Vistabel®, Allergan Inc., Irvine, USA), abobotulinumtoxin A (ABO; Dysport®/Azzalure®, Ipsen, Paris, France),
- incobotulinumtoxin A (INCO, Xeomin/Bocouture®, Merz Pharmaceuticals GmbH, Frankfurt, Germany).
Recently published statistics from the International Society of Aesthetic and Plastic Surgery show that BoNT/A injections are currently the most popular of all cosmetic procedures worldwide, and doctors of various specialties are integrating botulinum toxin injections into their practice.
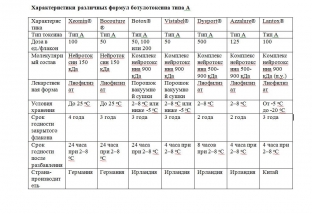
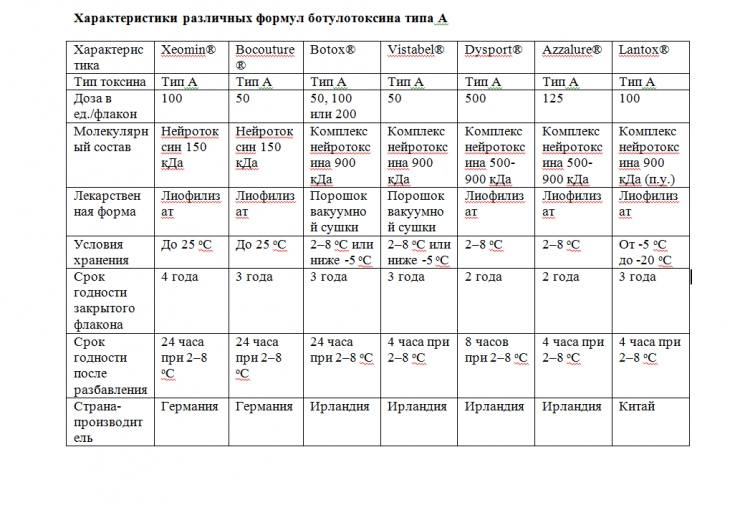
Composition specificity of different botulinum toxin formulations
The active protein in all commercially available botulinum toxin preparations is a neurotoxin, the amino acid sequence of which is identical for all preparations known on the market. Depending on the target tissue, BoNT/A can block cholinergic neuromuscular innervation of striatal and smooth muscles or cholinergic autonomic innervation of exocrine glands – and this mechanism of action is identical for all botulinum toxin preparations.
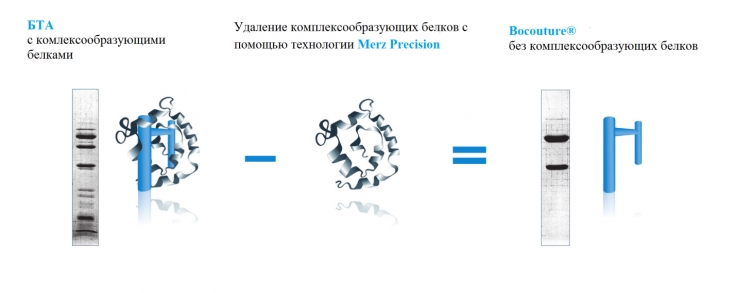
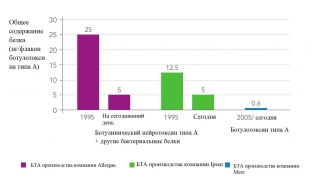
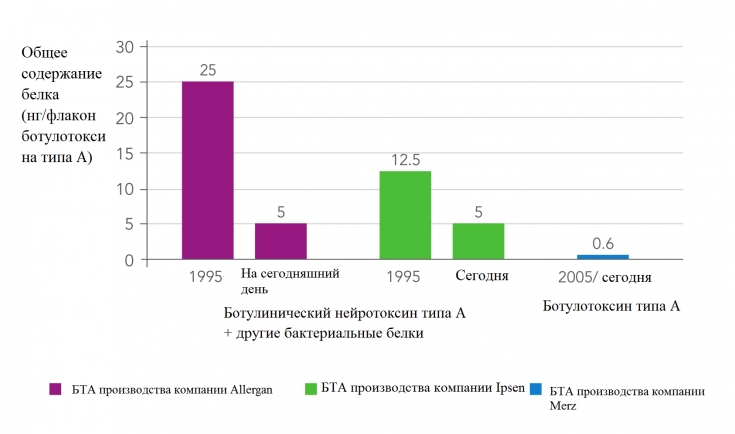
The INCO botulinum toxin preparation (Xeomin) differs from other similar preparations (ONA and ABO) in that it does not contain complexing proteins and consists only of the 150 kDa neurotoxin responsible for the therapeutic effect.
Studies on the specific activity of the neurotoxin have shown that INCO (Xeomin), manufactured by Merz, has the highest specific biological activity compared to ONA and ABO. Xeomin does not contain other clostridial proteins, and this minimizes the risks of the body producing antibodies, and therefore addiction to the drug.

Why formulation stability is important for botulinum toxin preparations
According to relevant product labels, ABO has a 2-year shelf life at 2-8°C, ONA can be stored for 2 or 3 years at 2-8°C (depending on the number of units) or in the freezer. The shelf life of Xeomin (INCO) is 3 or 4 years at room temperature. After reduction, ONA and INCO are stable for 24 hours at 2-8°C and ABO is stable for 4 hours at 2-8°C. The long shelf life and less severe temperature limits allowed for Xeomin indicate that it does not require complexing proteins for stability.
Among the top three botulinum toxin products, Xeomin is the only one that is stable in lyophilized form for 4 years at room temperature, while ONA and ABO products must be refrigerated
In a stress tolerance study, Xeomin survived up to 60°C. C within 1 month without loss of effectiveness.
Immunogenicity – an important factor in successful therapy with botulinum toxin preparations
Immunogenicity – is the ability of a protein product to induce the formation of antibodies. As with any therapeutic protein, botulinum toxin is considered a foreign substance and is therefore capable of inducing an immune response in the body, especially when administered repeatedly. This can lead to the development of neutralizing antibodies, which can cause the procedure to fail.
Preclinical data have shown that, unlike ONA and ABO, INCO (Xeomin) does not result in the production of neutralizing antibodies after repeated injections. Scientists have investigated the immunological reactivity of botulinum toxin in purified and complex forms and have demonstrated that any preparation of botulinum toxin with complexing proteins induces a stronger immune response than purified 150 kDa neurotoxin.
Complexing proteins can induce an inflammatory response, while pure BoNT/A additionally binds to lymphoblasts and fibroblasts. In addition, pure BoNT/A did not affect the release of inflammatory cytokines during ongoing studies, while the combination of BoNT/A and complexing proteins increased the release of several inflammatory cytokines.
Thus, the main difference between the three BoNT/A products is related to the presence or absence of complexing proteins. Xeomin consists only of pure neurotoxin and does not contain other clostridial proteins. Its foreign protein load per toxin unit is lower than that of OHA and ABO. Complexing proteins are not required for the efficacy of injectable BoNT/A preparations and are not required for stability.
The presence of inactive molecules in a clinical formulation of botulinum toxin will contribute to the overall protein load of the formulation without increasing its clinical efficacy. New scientific evidence suggests that complexing proteins can induce an immune response. The use of highly purified Xeomin minimizes the risks of an immune response and significantly increases the effectiveness of botulinum toxin therapy.







Add a comment