Disturbances in the metabolism of minerals in the human body primarily affect the condition of his bones. With vitamin D deficiency in childhood, a dangerous disease rickets occurs. In adults, mineral deficiency manifests itself in the form of a pathology such as osteomalacia.
This disease is characterized by softening of bone tissue and deformation of human bones, resulting in muscle weakness, bone pain, functional failure, and often bone fractures even with very little trauma.
Therefore, effective diagnosis and treatment of osteomalacia syndrome should begin as early as possible.
Diagnosis and treatment of osteomalacia syndrome: basic methods
Patients with osteomalacia syndrome seek medical help with characteristic complaints that make it possible to suspect this particular endocrine pathology. Attention is drawn to the presence of fractures in such patients, which were not associated with significant trauma. Excessive flexibility of the bones provokes the development of severe pain and weakness in the muscles, which are also specific symptoms.
However, it is possible to establish an accurate diagnosis by conducting the necessary amount of laboratory and instrumental research methods, after which a treatment regimen for osteomalacia can be recommended to the patient.
Osteomalacia:
- laboratory methods for diagnosing osteomalacia syndrome;
- instrumental methods for diagnosing osteomalacia syndrome;
- effective treatments for osteomalacia syndrome.
Laboratory methods for diagnosing osteomalacia syndrome
When conducting laboratory tests for the diagnosis of osteomalacia syndrome, it is important to identify specific indicators that indicate the presence of this particular pathology. With a deficiency of vitamin D in laboratory parameters observed:
- decrease in blood phosphate levels,
- calcium concentration in the blood at the lower limit of normal or below normal,
- low calcidiol level;
- increased parathyroid hormone;
- alkaline phosphatase increase.
All of these indicators are highly likely to indicate the presence of osteomalacia syndrome in adult patients. Differential diagnosis by laboratory parameters is carried out with primary loss of phosphates, metabolic acidosis, osteoporosis and some other pathological conditions.
Instrumental methods for diagnosing osteomalacia syndrome
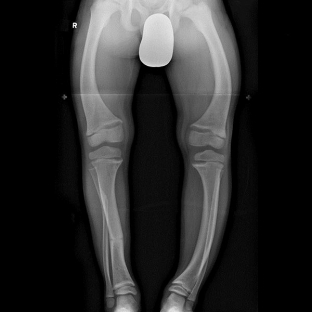 Instrumental research methods are also widely used to diagnose osteomalacia syndrome. With the help of a histomorphological study, it is possible to assess the rate of calcification and bone formation. For this, the double tetracycline label method is used, according to the results of which, in osteomalacia, the distance decreases between two tetracycline labels, and a non-mineralized matrix appears. X-ray studies are the most informative in osteomalacia syndrome. Important signs of osteomalacia are changes in the vertebral bodies: blurring of their patterns, concavity of the edges, sometimes compression fractures.
Instrumental research methods are also widely used to diagnose osteomalacia syndrome. With the help of a histomorphological study, it is possible to assess the rate of calcification and bone formation. For this, the double tetracycline label method is used, according to the results of which, in osteomalacia, the distance decreases between two tetracycline labels, and a non-mineralized matrix appears. X-ray studies are the most informative in osteomalacia syndrome. Important signs of osteomalacia are changes in the vertebral bodies: blurring of their patterns, concavity of the edges, sometimes compression fractures.
A characteristic radiological symptom of osteomalacia is the detection of Looser's zones – fissures or narrow lines that transmit x-rays, have sclerotic margins, and are perpendicular to the cortical margin of the bone.
Effective treatments for osteomalacia syndrome
The treatment of osteomalacia syndrome primarily pursues the following goals: elimination of vitamin D deficiency, hypophosphatemia and hypocalcemia. Patients are prescribed preparations of natural vitamin D, its active metabolites or their analogues. Calcium preparations must be added in case of deficiency of its intake or absorption, in case of hypocalcemia.
Phosphorus preparations are indicated for hypophosphatemia, but in clinical practice they are rarely given to adult patients. In some cases, such as hypovitaminosis D associated with malabsorption syndrome, patients are prescribed calcitriol and alfacalcidol in doses that do not cause hypercalciuria and hypercalcemia.







Add a comment