MODY-diabetes (maturity-onset type diabetes of the young − familial diabetes with a dominant type of inheritance, "Masonic" diabetes) − this is a heterogeneous group of diseases, which is characterized by genetic defects in pancreatic islet cells with a monogenic type of inheritance, in which there is impaired insulin secretion, less often − with impaired liver function, kidney function and insulin resistance.
For more information about the causes, varieties and modern approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus in young patients (MODY-diabetes), read the article on estet-portal.com.
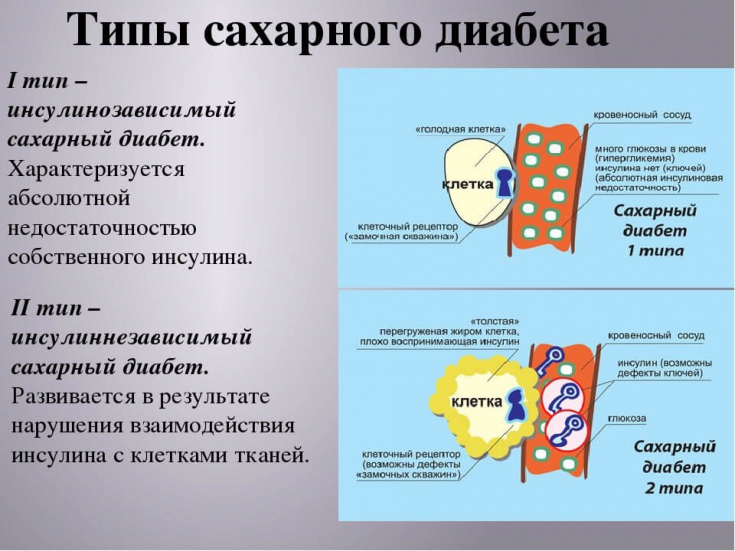
- Types of diabetes mellitus in young patients
- Approaches to the management of diabetes mellitus in young patients
- Results of a study of the method of diagnosing diabetes mellitus in young patientsov
Types of diabetes mellitus in young patients
The term MODY-diabetes was first introduced in 1974 by American scientists to define an atypical, slowly progressive form of diabetes mellitus (DM) in young patients who had a hereditary predisposition.
Follow us on Instagram!
MODY-diabetes is more often familial, when similar disorders of carbohydrate metabolism are also observed in one of the parents and relatives of the 2nd and 3rd degree of kinship.
So far, 14 types of MODY-diabetes have been known, of which the most common types are:
- MODY 1 (HNF4A / MODY);
- MODY 2 (GCK / MODY);
- MODY 3 (HNF1A / MODY).
This type of diabetes is diagnosed in 2-5% of the total number of people with various types of diabetes.
Read also: Glucagon-like peptide receptors: a new direction in the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Diagnosis of the various types of MODY based on clinical presentation alone is impossibleat.
Approaches to the treatment of diabetes mellitus in young patients
Genetic MODY diabetes accounts for about 1-4% of cases in children and adolescents.
Diagnosis of MODY is very important, because therapy depending on the genetic subtype differs significantly from the treatment of type 1 and type 2 diabetes: sulfonylurea derivatives, a special diet, and most importantly − insulin is not prescribed for this type of diabetes.
A team of scientists from Skane University Hospital, Malmo, Sweden, based on the results of a five-year study "Diagnosis of MODY diabetes in the absence of islet autoantibodies and moderately elevated glucose values" proposed a new screening method for MODY-diabno.
The method is based on the detection of at least three autoantibodies (AT) and changes in the level of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) in children and adolescents with diabetes.
Results of a study on the method of diagnosing diabetes mellitus in young patients
The study involved 3933 patients with diabetes mellitus aged 1-18 years who were tested for the presence of specific antibodies characteristic of type 1 diabetes: GADA , IA-2A, ZnT8 A and IAA.
Presence of MODY-subtypes of GCK, HNF1 A and HNF4A were tested in all participants by sequencing.
The most important diagnostic criterion MODY was found to be negative for all four types of antibodies: this is typical for 100% of patients with MODY and 11% of patients with other types of diabetes mellitus.
Other features include:
- low HbA1c;
- low plasma glucose;
- family history of diabetes mellitus;
- no diabetic ketoacidosis.
Read also: Development of new forms of insulin preparations for the treatment of diabetes
The scientists note that a genetic test based on a negative antibody result and a low HbA1c (<7.5%) would identify 78% of patients with MODY, and a negative antibody result and a family history of diabetes mellitus − 63%.

The investigators note that detection of IAA antibodies is difficult and may be the least useful for diagnosing MODY diabetes, while detection of GADA, IA-2A and ZnT8A is of high diagnostic value.
Read also: International Guidelines for the Treatment of Obesity in Children
The investigators recommend genetic screening for MODY-diabetes in young persons with normal body weight and negative for all three types of antibodies, moderate hyperglycemia with a level HbA1c <7.5% and/or family history of diabetes mellitus.
More useful information on our channel in Youtube:







Add a comment