Arterial hypertension itself is a disease of the cardiovascular system, which is characterized by a significant increase in blood pressure, as a result of which the state of the body worsens and there is a risk of serious complications, such as acute cerebrovascular accident. At the same time, arterial hypertension can be a symptom of another pathology of the body – dangerous tumor of the adrenal glands. Pheochromocytoma develops from the adrenal medulla, namely from the chromaffin tissue, and arterial hypertension is one of its most pronounced symptoms.
The main symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment of pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a benign tumor of the adrenal medulla. In 10% of cases, pheochromocytoma can degenerate into a malignant tumor – pheochromoblastoma, which can also metastasize to other organs and lymph nodes in the body. Most often, pheochromocytoma is localized in one adrenal gland; rarely, both glands are affected by a malignant neoplasm. Sometimes the tumor may not be localized in the adrenal gland itself, but located along the sympathetic chain from the bladder to the brain. Such tumors are called paragangliomas. The mass of the tumor can reach more than 3 kilograms, which significantly affects the normal functioning of the body.
Pheochromocytoma:
- clinical picture of pheochromocytoma: main symptoms;
- laboratory and instrumental methods for diagnosing pheochromocytoma;
- treatment of pheochromocytoma: what methods will help get rid of the tumor.
Clinical picture of pheochromocytoma: main symptoms
Pheochromocytoma is a benign hormone-producing tumor: it produces the hormones adrenaline and norepinephrine into the bloodstream, which causes the appearance of a characteristic clinical picture of the disease. Depending on the amount and rhythm of hormone production, three main forms of pheochromocytoma are distinguished:
- asymptomatic-latent form of pheochromocytoma – occurs extremely rarely, the triggering factor of the pathology can be severe emotional stress;
- paroxysmal sympathoadrenal hypertension – characterized by the development of spontaneous attacks of arterial hypertension, which are accompanied by tachycardia and severe headache. An increase in pressure can be the result of hypothermia, overeating, burns, physical stress, and so on. At the same time, patients complain of pain in the heart, shortness of breath, vomiting, sweating, defecation disorders and other symptoms. Attacks of arterial hypertension in this type of pheochromocytoma can occur several times a year;
- Persistent hypertension occurs when bouts of high blood pressure become more frequent and permanent.
Laboratory and instrumental methods for diagnosing pheochromocytoma
One of the most characteristic diagnostic signs of pheochromocytoma is the occurrence of an attack of arterial hypertension during palpation of the adrenal tumor. Depressor tests are also used with the use of drugs that reduce blood pressure in such patients. During an attack of hypertension in the urine and blood of patients increases the level of glucose. According to the results of laboratory tests for pheochromocytoma, a high content of adrenaline and free catecholamines in the patient's daily urine and blood serum is determined. Instrumental research methods such as ultrasound, CT and MRI provide information about the location, size and structure of the tumor in the adrenal gland. Characteristic of pheochromocytoma is the localization of the neoplasm inside the adrenal gland.
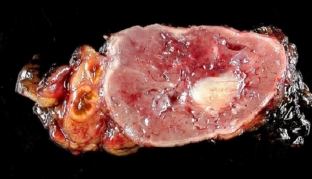
Pheochromocytoma treatment: what methods will help get rid of the tumor
Pheochromocytoma treatment should be started immediately, as there is a possibility of malignant transformation of tumor cells. In addition, jumps in arterial hypertension can provoke serious circulatory disorders and lead to death. Treatment of pheochromocytoma is performed only surgically: the patient undergoes an adrenalectomy – removal of the affected adrenal gland. Before surgery, it is necessary to eliminate all factors that can provoke attacks of arterial hypertension. For this purpose, the patient is administered adrenoblocking drugs. Hormone replacement therapy is recommended after the operation, since adrenalectomy can provoke the onset of acute adrenal insufficiency.







Add a comment