Folliculitis of the head can be caused by various causes that cause inflammatory processes, but the addition of a staphylococcal infection is especially dangerous in this situation. Staphylococcus causes a chronic relapsing course of several forms of head folliculitis, which may differ in the intensity of inflammation and symptoms, but as a result end in cicatricial atrophy and baldness of the affected areas. Read about the features of the course of staphylococcal forms of head folliculitis at estet-portal.com.
Manifestations of head folliculitis and features of the development of the disease
Folliculitis of the head is an acute inflammatory process with a purulent lesion of the hair follicle. The development of head folliculitis depends on the cause of its appearance, those types that are caused by staphylococcus are especially difficult.
The main characterizing symptom of the disease is the development of a limited inflammatory infiltrate in the form of a bright red, very painful nodule.
After two or three days after the formation, the nodule turns into a pustule, in the middle of which a hair is visible or the mouth of the hair follicle is visible in the form of a gray dot. The pustule can open with the release of purulent contents and the formation of erosion, but inflammation also spreads into the follicle. In this case, the hair follicle is destroyed with the impossibility of recovery and with & nbsp; scar formation.
Forms of staphylococcal head folliculitis
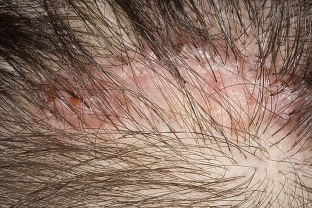
Epilatory folliculitis of the head. The process begins with the appearance of painful bluish-red papules on the scalp. They are clearly delimited from the surrounding tissues and gradually spread, capturing all new follicles. Inflammation develops around the hair follicle, but without signs of suppuration, necrosis develops in the depths of the papule. Infiltration around hairs brown, soft, scaly, without tendency to coalesce.
Epilatory folliculitis of the head has a persistent, slow chronic course, papules may eventually turn into pustules. Hair follicles are gradually destroyed, being replaced by cicatricial atrophy. Many small foci of persistent alopecia appear on the head, which spread eccentrically, sometimes merge with each other. The skin in these foci is smooth, white, completely hairless. The progression of the disease is indicated by the appearance of new inflamed follicles along the periphery of the scalp.
Undermining head folliculitis. The process begins with the onset of ostiofolliculitis, then the inflammation spreads to the surrounding tissues. On the parietal and occipital part of the head, pink painful nodules the size of a pea or even larger are formed. Small inflammatory elements gradually merge, fistulous passages form between abscesses. The skin in the lesions becomes purple-bluish in color, bumpy and painful when touched. The nodules suppurate, and when they are opened, multiple fistulas are found, interconnected. If you press on such a nodule, pus is released from the fistulous passage.
In the future, melting of the surrounding tissues may occur with the formation of ulcers separated from each other by patches of skin with hair. Gradually, the nodules turn pale, the process ends with the formation of rough, slightly convex, irregularly shaped scars of different sizes. The skin in these lesions is smooth and shiny, completely devoid of hair.
Principles of therapy for staphylococcal head folliculitis
It is very important to explain to the patient that the disease is severe, with a chronic course, prone to relapses. Careful adherence to the doctor's recommendations will certainly alleviate the condition and slow down the progression of the process, but the hair on the affected areas will no longer grow.
Therapy for head folliculitis caused by staphylococcus aureus is based on the prescription of systemic antibiotics.
The antibacterial drug is selected for each patient individually, based on the sensitivity of his body to certain antibiotics. A drug (eg, cephalexin, dicloxacillin) is given by mouth and topically as an ointment. A good therapeutic effect is the use of ultraviolet irradiation of the affected areas with a course of up to 10 sessions. If folliculitis develops in patients with diabetes mellitus, then a corrective diet is prescribed in addition to therapy.







Add a comment