The reason for the appearance of carbuncles and furuncles of the skin is the activation of staphylococcus, which penetrates through minor injuries and causes inflammation, sometimes threatening with serious complications. The weakening of the body's defenses and even an incorrect, sedentary lifestyle leading to obesity can push the development of furunculosis. In complicated forms of the disease, systemic antibiotic therapy is prescribed. What is a skin furuncle? Read more about possible complications of a skin boil on estet-portal.com.
What is the cause of skin furuncle formation?
Folliculitis is a deep, necrotizing form of folliculitis that affects the subcutaneous tissue. Several boils may coalesce to form carbuncles.
Skin boils are usually caused by colonization of the skin surface with staphylococcus bacteria.
This pathogen can spread into the dermis through the walls of the follicles, as well as penetrate through scratches and cuts in the skin, which ultimately leads to the formation of a skin boil. The production of certain enzymes and substances by this microorganism, such as proteases, enterotoxins, leukocidins, leads to inflammation.
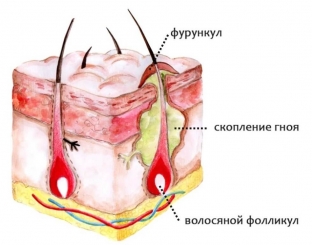
The nature of the manifestation of boils and symptoms of the disease
A boil appears under the skin as a round, painful nodule, at the top of which is usually a small pustule. Further, the follicular abscess increases and fluctuates. Then the boil softens and spontaneously opens. This opening process pushes out pus and a core of necrotic tissue. The process of opening a skin boil may result in scarring.
Most often, skin boils are localized on parts of the body with hairline, where skin friction and maceration occur.
The face, scalp, buttocks and armpits are particularly affected. The carbuncle, which has many drainage holes, is typically located on the neck, back, and thighs.
The following changes become predisposing factors for the appearance of boils and carbuncles:
Possible complications in the development of skin furuncle
Severe systemic symptoms such as fever and malaise are more commonly present with carbuncle. If the infection is localized in the nasolabial zone, it is fraught with the entry of staphylococcus into the cavernous sinus through the venous blood and can lead to thrombosis. Other complications of skin furuncle can be osteomyelitis and peripheral abscess.
In some patients, recurrent furunculosis can develop even when there are no staphylococci on the skin and there are no lesions that would violate its defense mechanisms, notes estet-portal.com. In these patients suffering from repeated infections, staphylococcus aureus may persist on the nasal mucosa. In this case, the anterior part of the nasal cavity becomes the reservoir of its distribution, from where it enters the skin, and then reinfection of furunculosis occurs. Less commonly, a reservoir of pathogenic staphylococci can be found in the perineum or axilla.
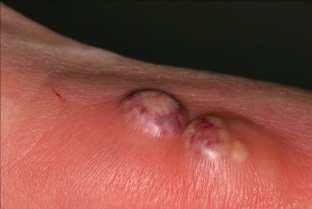
General therapeutic approaches to the treatment of skin furuncle
Furuncles and carbuncles, when accompanied by fever or localized on the face, are best treated with systemic antibiotics. If there are isolated foci in other parts of the body, treatment is usually carried out with local remedies – for example, saline compresses, but sometimes surgical drainage of pus is required.
For recurrent skin boils, apply an antibiotic ointment topically to potential sites of infection (eg, nostrils, axillae, perineum). Eradication of recurrent lesions is often difficult.
Thus, in the treatment of carbuncles and furuncles of the skin, in most cases, a long course of antibiotic therapy with adjuvant measures is required.







Add a comment