Gonorrhea remains one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Gonorrhea in men occurs mainly in the form of a lesion of the urethra – urethritis.
Depending on the clinical manifestations, fresh and chronic gonococcal urethritis are distinguished. In half of the cases, the disease is asymptomatic or mild, which complicates the timely diagnosis of gonorrhea and leads to undesirable consequences.
Gonococci can also infect any mucous membrane of the body and cause serious complications from the internal organs.
On estet-portal.com read about the symptoms and specifics of the course of gonorrhea in men, as well as complications caused by venereal disease.
Acute gonococcal urethritis: varieties, stages and features of the course
Fresh acute gonococcal urethritis begins with hyperemia and swelling of the urethral sponges, sharp pain during urination and profuse yellow-green purulent discharge from the canal throughout the day. The incubation period is 3-10 days, but can be up to 2 weeks.
Follow us also on Telegram
In acute anterior gonorrheal urethritis, an inflammatory reaction of the mucous membrane of the distal part of the urethra and pain at the beginning of urination are characteristic, and in acute total urethritis, when inflammation covers the urethra throughout, the pain intensifies at the end of urination – sign of urethrocystitis.
Also, with a total lesion of the canal, there are frequent urges to urinate – up to 15-20 times a day and painful erections.
Over time, acute inflammation, if left untreated, can progress to a subacute stage, in which the symptoms of the disease become mild.
Manifestations of torpid urethritis follow after subacute, and may also occur at the onset of the disease.
Chronic gonococcal urethritis: sluggish course of a dangerous disease
Chronic gonorrheal urethritis is characterized by mild itching when urinating, as well as scanty discharge that occurs in the morning or when pressure is applied to the urethra.
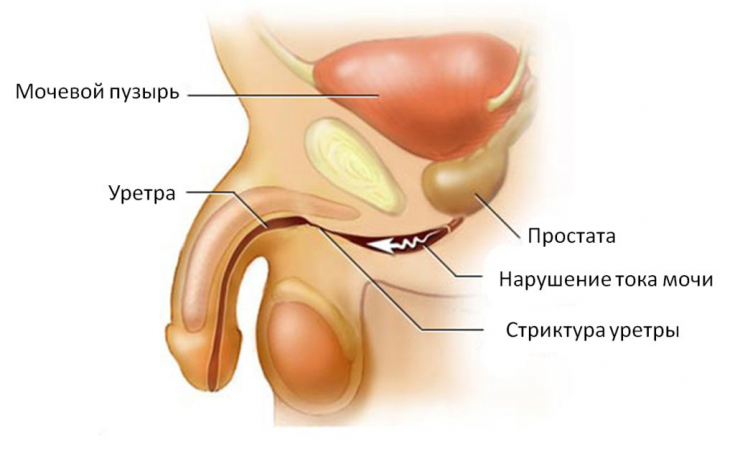
Urethritis can be posterior or anterior, but is usually total. The discharge in the chronic form is so viscous that it remains in the canal and can be isolated only by visual examination of the urine – in the form of threads or flakes.
The inflammatory process can also spread to the prostate gland and seminal vesicles.
Chronic gonorrhea in men has a torpid character with periods of exacerbation that spontaneously disappear.
Gonorrhea – one of the most dangerous sexual infections
What threatens men's health with gonorrhea: complications of the disease
Quite often, gonorrhea in men is not limited to urethritis alone.
Depending on the localization of the infectious process, the following complications of the disease are distinguished:
• littrait – inflammation of the alveolar tubular glands in the urethra;
• tysonite – inflammation of the glands of the foreskin;
• vesiculitis –damage to seminal vesicles;
• colliculitis –inflammation of the seminal tubercle;
• prostatitis – infection of the prostate with damage to the posterior urethra;
• epididymitis – inflammation of the epididymis;
• orchitis – gonococcal testicular lesion;
• balanoposthitis and phimosis – inflammation of the skin of the head and the impossibility of its exposure. infertility.
Extragenital manifestations of gonococcal infection include: proctitis, gonarthritis, blennorrhea, gonococcal stomatitis and pharyngitis, skin and nervous system lesions also occur.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Venerology" section. You may also be interested in:
Gonorrhea in women: features of the course and specifics of therapy







Add a comment